Funded articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Funded articles
Editorial
- A Pilot Trial of Integrative Medicine for Stroke Rehabilitation: Expert Recommendations for the Development and Sustainability of Integrative Medicine
- Chihyoung Son, Go-Eun Lee, Joo-Hee Seo, Inae Youn, Jin-Won Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):1-6. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.001
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 694 View
- 17 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 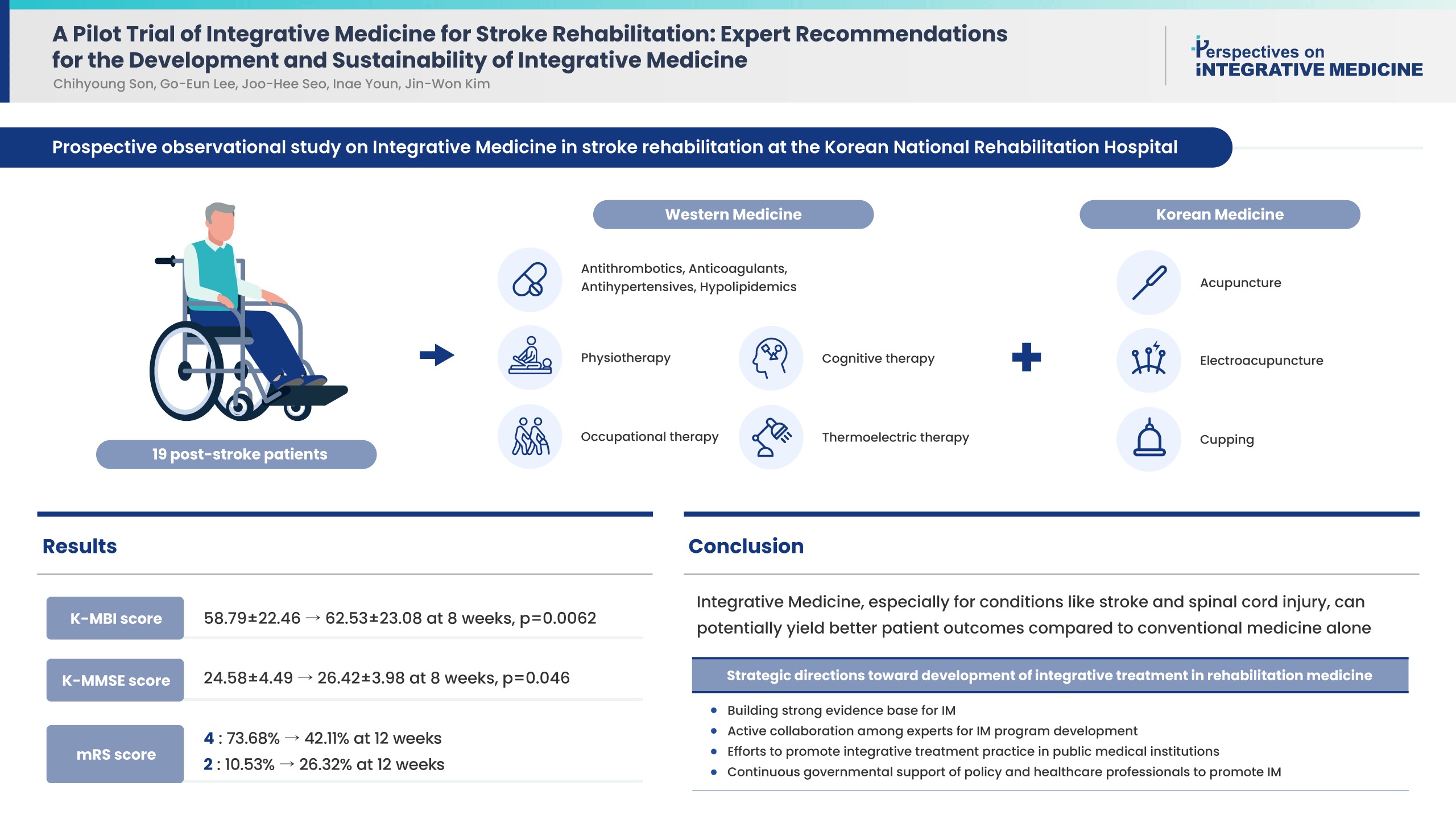
- Background
Strategies towards development and sustainability of integrative treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine are needed. National expert recommendations based on the implementation of Integrative Medicine (IM) in stroke rehabilitation and IM outcomes would be invaluable.
Methods
A pilot study was performed and the effectiveness of combining Korean traditional medicine and Western conventional medicine in post-stroke patients (ischemic stroke n = 15 and hemorrhagic stroke n = 4) was evaluated, and recommendations were developed through consensus with physicians in national centers of rehabilitative medicine. Outcome measures [Korean Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI), Korean Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), Modified Rankin Scale (mRS), and EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L) assessment were used at baseline, 4, 8 (K-MBI, K-MMSE, mRS, and EQ-5D-5L) and 12 weeks post treatment (EQ-5D-5L and mRS).
Results
Improvements were observed in functional and cognitive abilities at 8 weeks (K-MBI score p = 0.0062; K-MMSE score p = 0.046). Quality of life improvements (EQ-5D-5L) were observed but were not statistically significant. The disability assessment (mRS) indicated a gradual improvement from baseline to 12 weeks. No adverse events were reported. For effective, patient-centered IM treatment: (1) build a strong evidence base for IM as compared with Western medicine alone or traditional medicine alone; (2) active expert collaboration; (3) IM promotion in public medical institutions; and (4) continued government support.
Conclusion
Functional and cognitive abilities of stroke patients statistically significantly improved following 8 weeks of IM treatment. Strategies have been suggested towards the development and sustainability of IM treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine.
Review Articles
- Characteristics and Quality of Traditional Chinese Therapies and Integrative Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines for Musculoskeletal Disorders Published in Mainland China
- Xue-Feng Wang, Jing-Ling Zuo, Lin-Jian Li, Lan-Dan Xu, Xiao-Zhong Liu, Si-Si Ma, Jian-Ping Liu
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):7-17. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.002
- Funded: National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 630 View
- 15 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 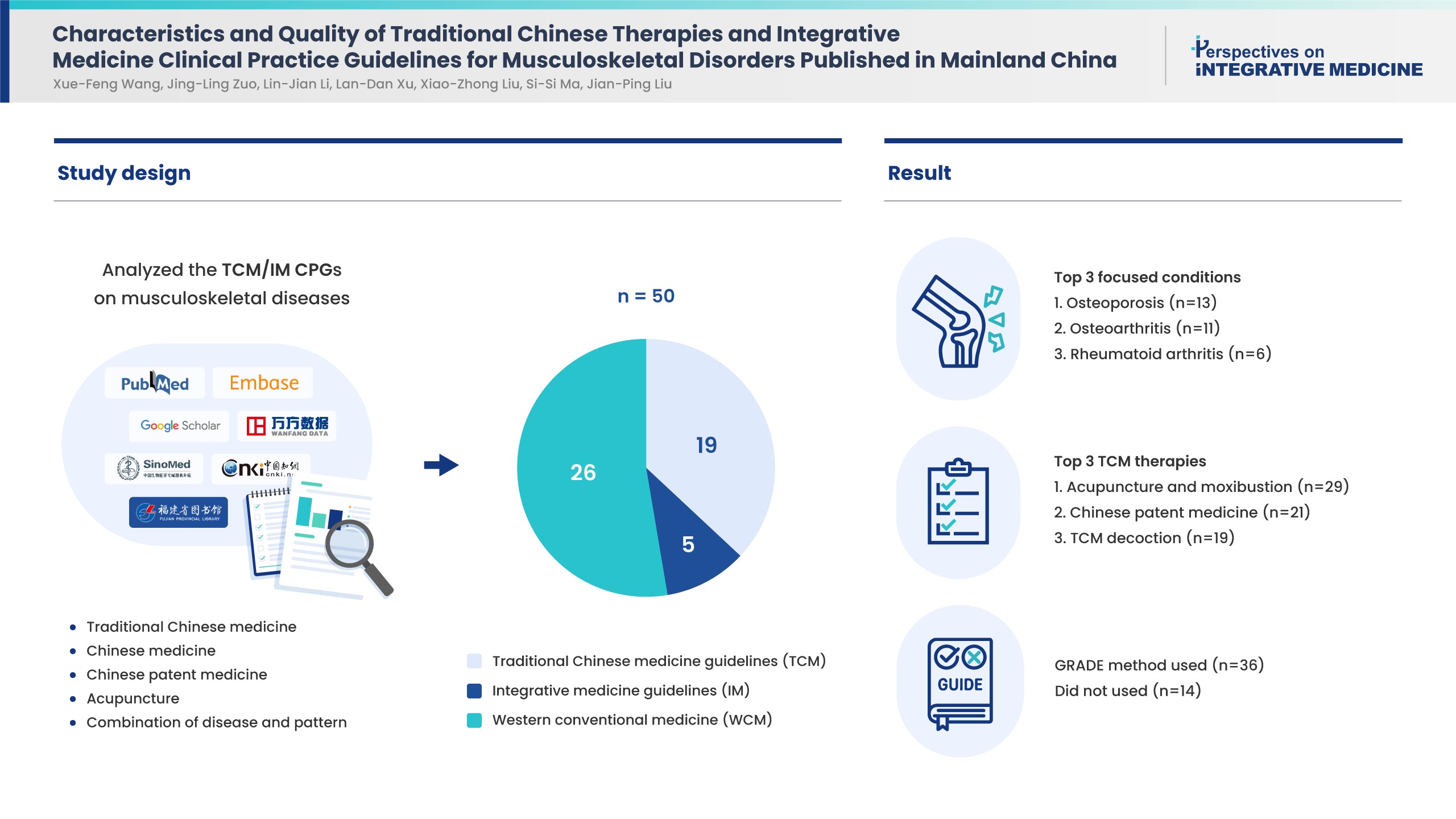
- Background
Musculoskeletal disorders are prevalent in adults. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and integrative medicine (IM) are commonly used treatments which have clinical practice guidelines (CPGs). This study aimed to determine the characteristics and quality of these CPGs.
Methods
CPGs which recommended TCM/IM therapies in musculoskeletal conditions/diseases published in Chinese or English between January 2018 to December 2022 in mainland China were retrieved and analyzed for guideline classification, funding source, conflict of interest, and methodology. Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ including 6 domains, was applied to assess CPG quality.
Results
Of the 50 CPGs included, there were 19 TCM, 5 IM, and 26 western conventional medicine (WCM) guidelines of which osteoporosis (13, 26%), osteoarthritis (11, 22%) and rheumatoid arthritis (6, 12%) were the most frequent diseases. The TCM therapies recommended by the CPGs successively were acupuncture and moxibustion, Chinese patent medicine, and TCM decoction based on syndrome differentiation. Nearly half of the CPGs reported funding source (52%) and conflict of interest (48%). Thirty-six CPGs used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations method to present summaries of evidence, the remaining did not report the method. Based on Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ scores, “clarity of presentation” scored the highest (55%), while “applicability” was the lowest (6%). No CPG was recommended without change, and 23 CPGs were not recommended.
Conclusion
The quality of CPGs for musculoskeletal conditions/diseases in China is generally low. Future CPGs should pay more attention to standardized developing procedures.
- A Modern Interpretation of Cold-Heat Pattern in Traditional Medicine with a Focus on Thermo-Regulation
- Younggwang Kim, Jee Young Lee, Joongho Lee, Sanghun Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):18-28. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.003
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 495 View
- 15 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 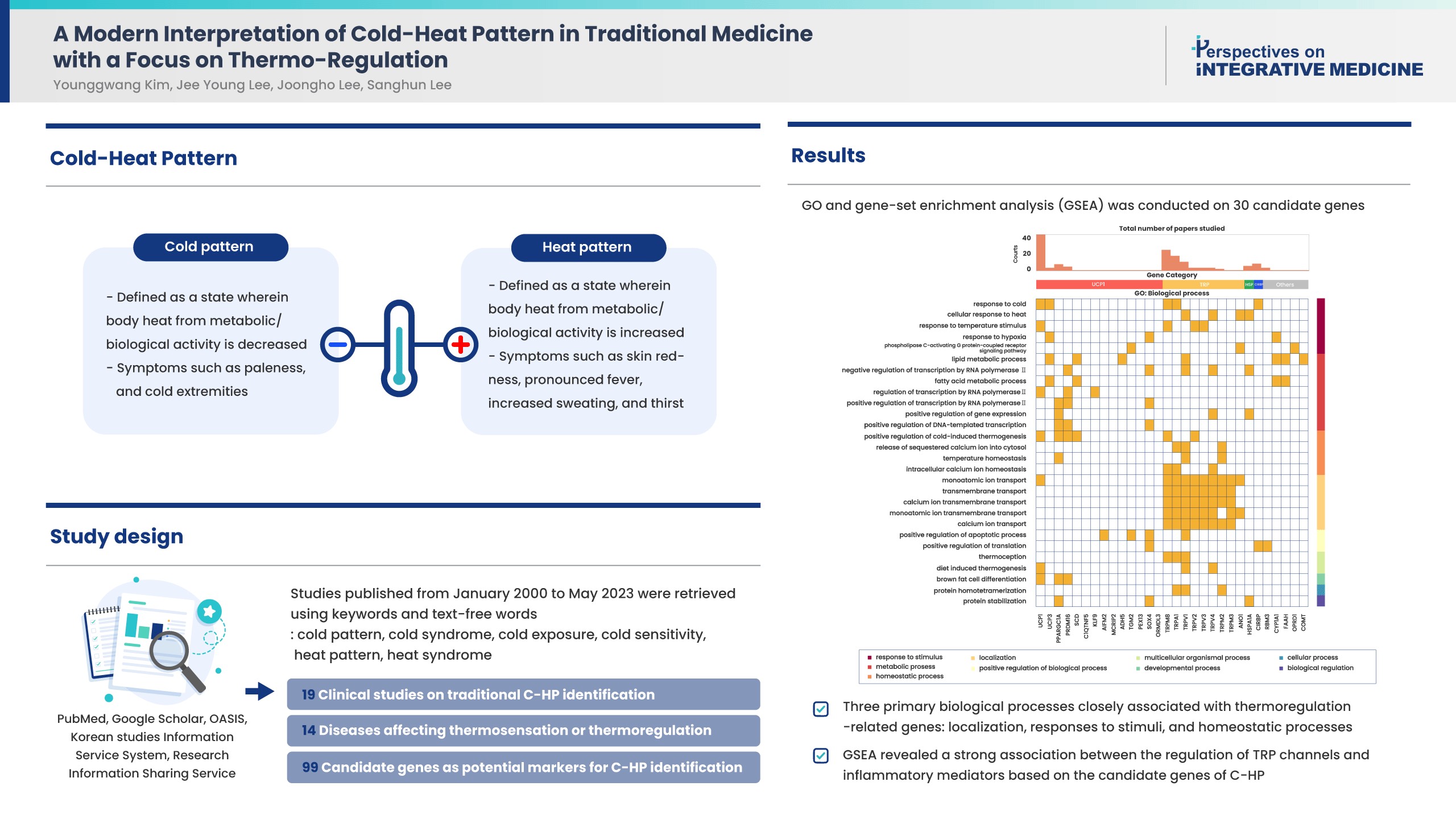
- Cold-heat patterns (C-HPs) in Traditional East Asian Medicine are essential for individually diagnosing and treating patients. However, the concept of C-HPs and their biological mechanisms (thermoregulation) remains unclear. C-HPs studies published between January 2000 and May 2023 were retrieved from 5 databases (PubMed, Google Scholar, OASIS, Korean studies Information Service System, and Research Information Sharing Service). Among the 8,373 articles screened, 132 were included in the review and categorized. Nineteen articles were clinical studies related to traditional concept of C-HP identification, 14 studies investigated diseases affecting thermosensation or thermoregulation, and 99 studies identified candidate genes as potential markers for C-HP identification. Further analysis, including gene ontology, and gene set enrichment analysis of the candidate genes, revealed 3 primary biological processes closely associated with thermoregulation-related genes, including localization, responses to stimuli, and homeostatic processes. Notably there was a significant association between the candidate genes and inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential channels (p < 0.001). A significant association between C-HPs and inflammation-related pathways across thermosensation-related and thermoregulation-related clinical and preclinical studies was observed, suggesting that the traditional concept of C-HPs should be studied further from an immunological perspective.
Original Articles
- Acupuncture Needles and the Risk of Lymphedema After Breast Cancer Surgery: A Retrospective National Cohort Study
- Ye-Seul Lee, Yucheol Lim, Jiyoon Yeo
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):29-36. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.004
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 644 View
- 23 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 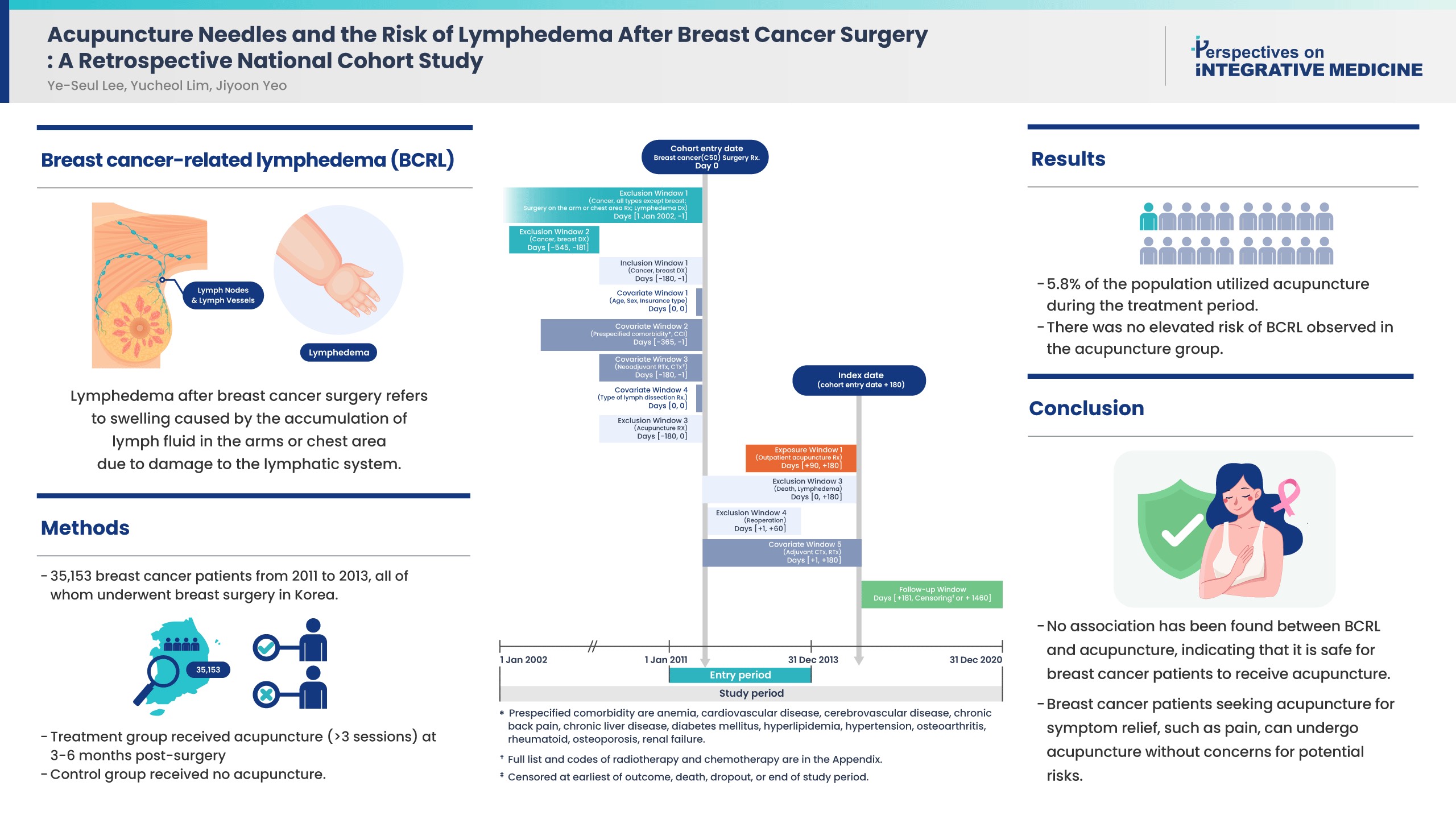
- Background
Controversies remain over the impact of using needles on breast cancer patients after surgery due to risk of breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL). While recent literature suggests that vascular access during the postsurgical stage does not affect the risk of BCRL, the impact of acupuncture on the risk of BCRL during the postsurgical stage has not been studied.
Methods
This study included 35,153 patients from 2011 to 2013 who were newly diagnosed with breast cancer in a population-based cohort from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. All patients received breast surgery, and the treatment group received acupuncture for more than 3 sessions in the 3-6 months post-surgery. The control group did not receive acupuncture. The incidence rate ratio, Kaplan-Meier curve, and Cox proportional hazards models were used to compare the risk of BCRL, and death between groups.
Results
About 5.8% of the study population received acupuncture during the 3-6 months post-surgery treatment window. After propensity score matching, the acupuncture treatment group did not show an increased risk of BCRL (IRR 1.017, 95% CI 0.868-1.193; unadjusted HR 1.018, 95% CI 0.868-1.193). This risk was robust in all multivariate Cox proportional hazards models.
Conclusion
An association of BCRL with acupuncture was not observed. Patients who received acupuncture to manage symptoms such as pain during the 3-6 months postsurgical stage did not have a higher risk of developing BCRL. Breast cancer patients who seek acupuncture to alleviate post-surgery symptoms such as pain, can receive acupuncture without concerns for potential risk of BCRL.
- Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy and Photontherapy in Cervicobrachialgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Bianca dos Santos Bobadilha, Talita Bonato de Almeida, Maria Imaculada de Lima Montebello, Maria da Luz Rosário de Sousa
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):37-44. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.005
- Funded: Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 543 View
- 10 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 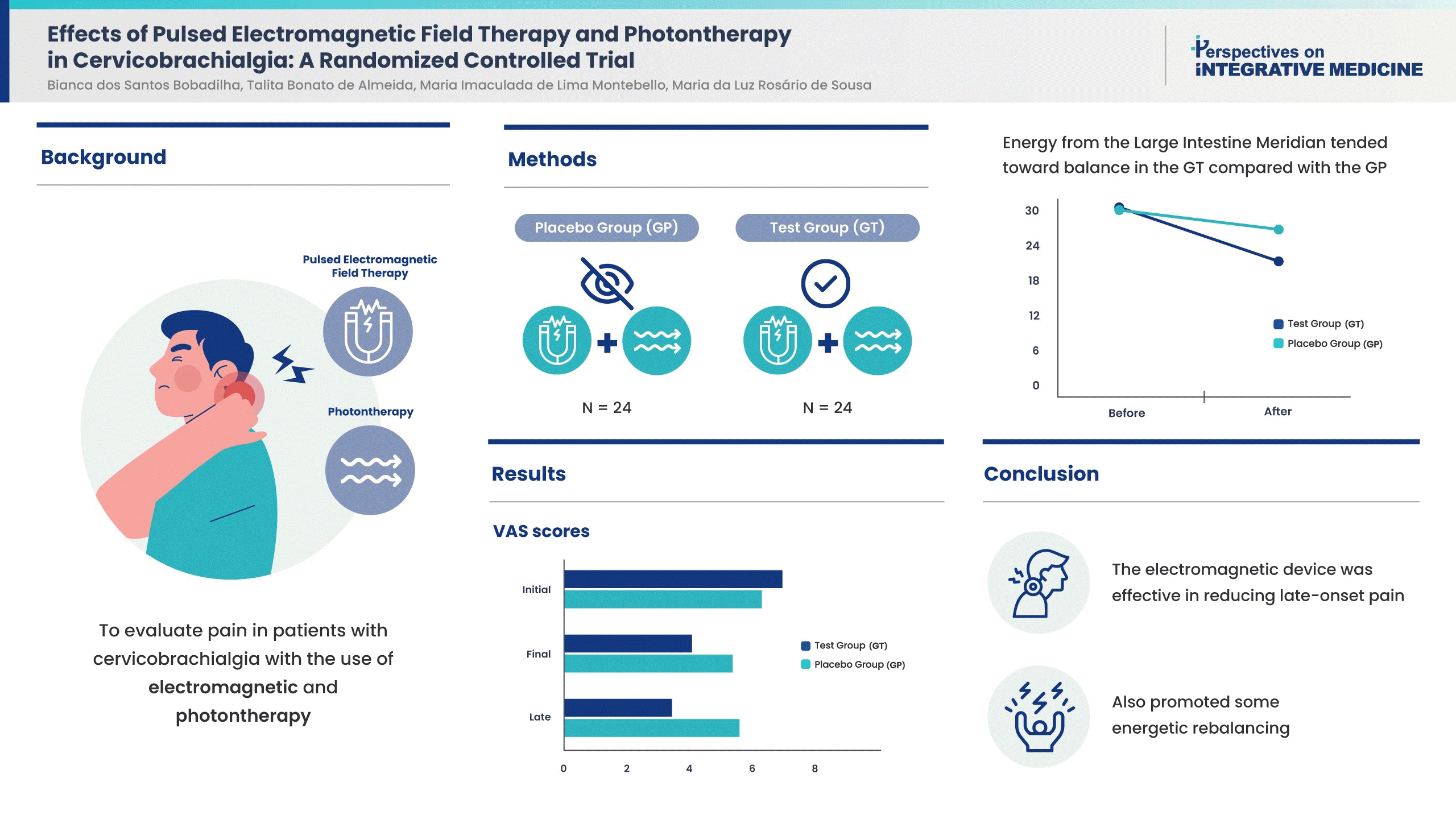
- Background
Cervicobrachialgia is a painful condition commonly treated with medication and physiotherapy. The aim was to evaluate pain following electromagnetic and photontherapy, and examine patient energy profiles.
Methods
There were 48 patients experiencing pain [Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score ≥ 4] who were not receiving medication and physiotherapy and were randomized into Test Group (GT); electromagnetism using a Kenkobio device (intensity = 0.055 mT/frequency = 60 Hz) and photon therapy; a photon therapy blanket, and Placebo Group (GP); the Kenkobio device was turned off and the blanket was not used. Pain was assessed using the VAS, before, immediately after treatment, and the following day. Algometry was also carried out before and after the treatment to understand the pain threshold at bilateral acupoints GB20 and GB21. The energy profile was assessed using Ryodoraku measurements before and after the session.
Results
The GT achieved a greater reduction in pain the following day than GP. Both groups were equal for left GB20 and right GB21 points considering algometry and, after the intervention, a reduction in pain in the GT was noticed only in the left GB20 (CI [95%]: 0.09-0.99, p = 0.019). The average energy level was low and dropped further following treatment. Furthermore, energy from the Large Intestine Meridian tended towards balance in the GT compared with the GP [CI (95%): 0.58-15.75, p = 0.035]. No adverse effects were reported.
Conclusion
The combined use of electromagnetic and photontherapy were effective in reducing pain in patients and promoted energy rebalancing.
Protocol
- Validation of a New Sham Acupuncture Needle for Double-Blind Trials: A Study Protocol
- Sung Min Lim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):57-60. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.008
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 572 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
To establish efficacy in acupuncture treatment, rigorous randomized controlled trials (RCT) are needed. Non-invasive sham acupuncture needles are an effective tool for practitioner/participant blinding. This study presents a protocol for the validation of a newly developed sham acupuncture needle.
Methods
A double-blind RCT will be conducted on 66 healthy adults who will be randomly assigned (using computer-generated random numbers) to either the verum (n = 33) or sham (n = 33) acupuncture needle group. The needles will be inserted at 2 acupuncture points: LI4 (upper limb) and ST36 (lower limb). The primary outcome measure is the practitioner/participants belief that they received verum or sham acupuncture. The secondary outcome measures are participant-rated sensations (penetration, pain, and de qi). Adverse events will be recorded with detailed explanations, categorizing occurrences according to related or unrelated to acupuncture. As the newly developed sham acupuncture has not been studied before, an exploratory approach has been adopted. Descriptive statistics, t test, and χ² test will be applied appropriately.
Results
This study is intended to provide a protocol for the validation of a sham acupuncture needle by using a double-blind RCT setting, and the results will hopefully contribute to the standardization of the needles used for sham acupuncture. The outcomes aim to determine the reliability of practitioner/participant blinding, participant experience of sensations, and lay groundwork for a standardized control group for clinical trials in the future. The newly developed non-invasive sham acupuncture needle may reduce bias and improve reliability in the size effect of acupuncture treatment.
Review Article
- Effectiveness and Safety of Low-Level Laser Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sang Jun Lee, Seung Jin Noh, Jeong Rock Kim, Kyung Bok Park, Sae-rom Jeon, Yejin Hong, Dongwoo Nam
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):155-163. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.003
- Funded: Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 1,462 View
- 44 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Low-level laser treatment (LLLT) is used to treat low back pain (LBP) however, its effects on lumbar disc herniation (LDH) remain unclear. The safety and effectiveness of LLLT for LDH was determined using a systematic review of randomized clinical trials.
Methods
Studies on LLLT in adults with LDH were identified from 12 worldwide databases. A risk of bias assessment and a meta-analysis with categorization according to the type of control used (inactive, active, or add-on) was performed. The quality of evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation.
Results
The quantitative analyses included five studies. LLLT was significantly more effective at treating LDH [leg pain visual analog scale (VAS) mean difference (MD): -1.90, 95% confidence interval (CI): -2.01, -1.80, I2 80%; LBP VAS MD: -0.79, 95% CI: -0.87, -0.71, I2 80%] than inactive controls (placebo or sham). The quality of the evidence ranged from “low” to “very low.” As an add-on to usual care, LLLT significantly improved pain intensity and disability compared with usual care (leg pain VAS MD: -2.52, 95% CI: -2.65, -2.40, I2 97%; LBP VAS MD: -1.47, 95% CI: -1.58, -1.36; Oswestry Disability Index MD: -4.10, 95% CI: -4.55, -3.65, I2 6%). However, the quality of the evidence ranged from “moderate” to “low.”
Conclusion
LLLT significantly improved outcomes compared with the inactive controls, but was not more effective than usual care for LDH. In combination with usual care, LLLT was significantly more effective than usual care alone highlighting the potential of LLLT.
Original Articles
- Improvement in Growth in Adolescents with Average Height Using A Massage Chair: A Prospective Single Arm Pre-Post and National Standard Data Comparison Study
- Sul Gi Park, Gyu Tae Chang, Jin Yong Lee, Sun Haeng Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):164-172. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.004
- Funded: Bodyfriend, Inc.
- 475 View
- 12 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
This study aimed to examine the changes in height, weight, and bone age between pre- and post-intervention when using a BEG-100 massage chair daily.
Methods
Thirty-five children aged 11 years who were close to the average height (145-155 cm) were included in the study. There were 34 participants who used the BEG-100 massage chair for 24 weeks. Daily intervention consisted of 20 minutes of lower body massage and 10 minutes of whole-body massage. Height, weight, and adverse events were checked every five visits, while a hand X-ray was used before and after massages. The height percentile and height standard deviation score (SDS) were calculated using the 2017 Korean growth chart. The bone age and predicted adult height using radiographs were computed using the Tanner-Whitehouse method. The paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used according to normality of data to determine statistical significance.
Results
A total of 31 children were included in the final analysis. The height percentile and height SDS significantly increased after BEG-100 massage chair use (2.39; p = 0.032, and 0.07; p = 0.036, respectively). However, these changes were not significant in children whose baseline height was shorter than the average. There were no significant differences in bone age, height for bone age, predicted adult height, or sitting height/height ratio. None of the participants complained of adverse events.
Conclusion
The height percentile and SDS of teenagers increased after use of massage chair therefore, it is necessary to perform larger randomized controlled clinical studies. Trial registration: KCT0004673.
- Structural and Criterion Validity of a New 6-item Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ-6) on Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain Receiving Integrative Medicine
- Yoon Jae Lee, Gyu Chan Shim, Changsop Yang, Chang-Hyun Han
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):182-189. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.006
- Funded: Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine
- 599 View
- 17 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 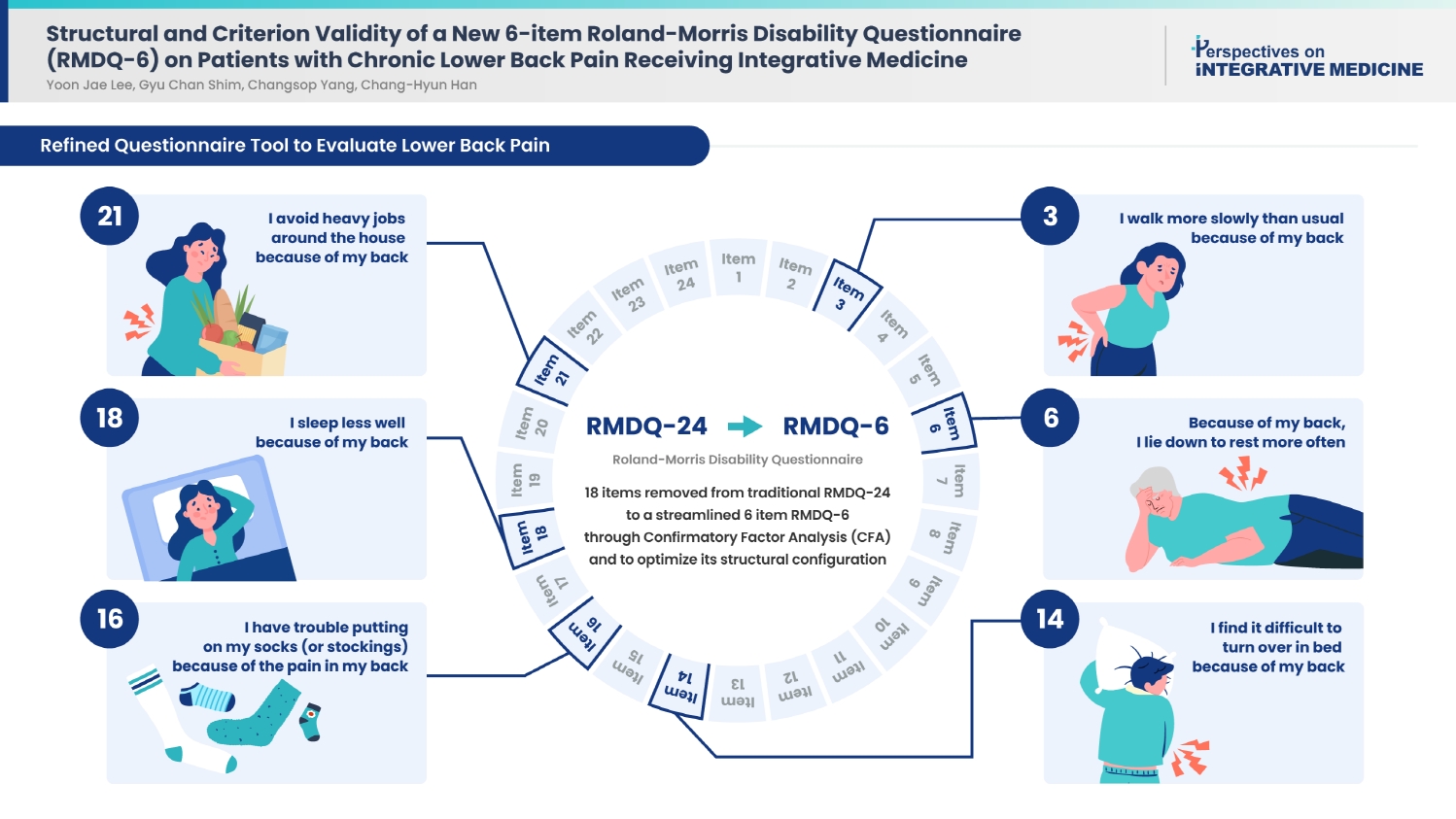
- Background
Lower back pain (LBP) is a leading cause of disability worldwide. The Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) has been widely used to assess functional impairment in patients with LBP. However, its length and redundancy calls for a more concise and optimized version.
Methods
We conducted a secondary analysis of data from two randomized controlled trials comparing pharmacopuncture and physical therapy for chronic LBP. We focused on 132 patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms and analyzed their baseline data to evaluate the structural validity of the RMDQ. We used R packages lavaan and semPlot for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Model fit were assessed through various indices, including comparative fit index, Tucker–Lewis index, root mean square error of approximation, and standardized root mean squared residual.
Results
A total of 18 items were ultimately removed to produce a streamlined 6-item structure. Our model met the fit index criteria, yielding a one-domain, 6-item RMDQ structure. While the relative indices fell slightly short of the ideal values, the RMDQ-6 derived through CFA correlated well with the original version.
Conclusion
This study developed a more concise version of RMDQ through CFA to optimize its structural configuration. This concise instrument can be proposed as an efficient tool to assess the functionality of patients with LBP.
Protocol
- Acupuncture for Rectal Cancer Patients with Low Anterior Resection Syndrome: A Mixed Method Pilot Study Protocol
- Ming Yang, Honglin Jiang, Lin Xu, Qiaoli Zhang, Xun Li, Liu Han, Yudong Bao, Lu Yang, Mi Zhang, Lihua Zheng, Ningyuan Liu, Jianping Liu, Jinchang Huang
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):195-201. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.008
- Funded: Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research
- 565 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This protocol aims to facilitate the evaluation of acupuncture in the treatment of low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) on the bowel in rectal cancer patients.
Methods
This pragmatic pilot study was designed using a convergent parallel mixed methods design combining a single-arm trial and semi-structured qualitative interview.
Results
Sixty patients with LARS will be recruited from out/inpatient departments. For evaluation of efficacy, the single-arm objective performance criteria will be used in the pilot study in which all eligible participants will receive electroacupuncture mainly on Baliao acupoints three times a week for four weeks. The LARS scale, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre Bowel Function Index, and anorectal manometry will be used to assess symptoms and pressure changes. The European Quality of Life Five Dimensions Questionnaire and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Quality of Life Questionnaire-Core 30 will be used to evaluate quality of life. Semi-structured interviews will be conducted among twenty participants to understand their experience and feelings. The qualitative and quantitative data will be analyzed and summarized before comparative analysis. Qualitative themes derived from qualitative analysis will be ranked with the variables of quantitative statistics. Finally, we will answer the research question from multiple perspectives by comparing different types of evidence for the same dimension.
Conclusion
This mixed method study design will potentially evaluate the feasibility and effects of electroacupuncture for LARS and gain an in-depth understanding of the attitudes, experiences, feelings, and acceptance among patients with LARS.
Guideline
- ACURATE: A Guide for Reporting Sham Controls in Trials Using Acupuncture
- Ye-Seul Lee, Song-Yi Kim, Hyangsook Lee, Younbyoung Chae, Myeong Soo Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):100-106. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.004
- Funded: Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 1,089 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This paper presents the Acupuncture Controls gUideline for Reporting humAn Trials and Experiments (ACURATE) checklist, an extension of The Consolidated Standards for Reporting of Trials (CONSORT) and to be used along with STandards for Reporting Interventions in Clinical Trials of Acupuncture (STRICTA) when both real and sham acupuncture needles are used in the study. This checklist focuses on a clear depiction of sham needling procedures to enhance replicability and enable a precise appraisal. We encourage researchers to use ACURATE in trials and reviews involving sham acupuncture to assist reporting of sham acupuncture procedures and the related components.
Original Articles
- Bojungikgi-tang Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages and C57BL/6 Mice
- Hyo In Kim, Yohan Han, Jinbong Park
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):107-116. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.005
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea
- 797 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study evaluated the anti-inflammatory effect of Bojungikgi-tang (BJT) in a model of acute lung injury (ALI) in mice.
Methods
Murine cell line macrophages (RAW264.7) were treated with BJT for 30 minutes before lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. The levels of cytokines, mRNAs, proteins, and related markers were investigated. In addition, BJT (200 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to C57BL/6 mice for 2 weeks prior to an intraperitoneal injection with LPS to induce sepsis and ALI; 24 hours post LPS injection, mice were sacrificed and blood was collected from the infraorbital vein. Lung tissue was harvested, hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed, the wet/dry ratio of the lung tissue was measured, and the serum cytokine levels were analyzed.
Results
Compared with LPS treatment, BJT suppressed LPS-induced mRNA expression and secretion of inflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 macrophages. Furthermore, inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, toll-like receptor 4, phosphorylation of mitogenactivated protein kinases, and phosphorylation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells were inhibited by BJT. In mice, LPS-induced pathological changes in lung tissues, such as abnormal histological structures, immune cell infiltration, and lung edema were less severe following BJT treatment. BJT inhibited the LPS-induced increase of cytokines such as interleukin 4, 6, 10, and tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Conclusion
BJT had an inhibitory effect in the pathological progress of LPS-induced sepsis and ALI and may be a promising therapeutic agent in the future.
- Effectiveness of the Korean Medicine-Based Postnatal Healthcare Program: A Retrospective Observational Study
- Joohee Seo, Doeun Lee, Hansong Park, Inae Youn, Jungtae Leem, Minjung Park
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):117-125. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.006
- Funded: National Medical Center
- 1,334 View
- 31 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Insufficient postpartum care can negatively affect mothers’ health. The aim of the Korean Medicine-based Postnatal Healthcare Program (KMPHP) is to prevent and treat Sanhupung by rapid intervention in postpartum care.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted using data from 37 postpartum women who participated in the KMPHP between April 2019 and April 2020. The women had received at least one type of Korean medicine treatment (herbal medicine, acupuncture, electroacupuncture, pharmacoacupuncture, or Chuna manual therapy) for at least one session. General characteristics were collected from the medical records, and postpartum symptoms (taken from a questionnaire) were investigated. Outcome measures included pain intensity, quality of life (QoL), and postpartum depression.
Results
The effectiveness of the KMPHP was determined using the paired-sample Wilcoxon test and significant improvements in the scores were observed using the Korean version of the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (from 8 to 5, p < 0.01), EuroQol-5 Dimension-5L (from 0.82 to 0.83, p = 0.02), and EuroQol Visual Analog Scale (from 70 to 80, p < 0.01). The womens’ pain scores (Numeric Rating Scale) reduced from 4 to 3 after treatment, but the difference was not significant. As a result of analyzing the effects of each intervention, herbal medicine show a significant effect on womens’ depression, QoL and pain, and non-pharmacological intervention showed synergistic effects with herbal medicine.
Conclusion
Korean medicine-based interventions may be effective in the management of postpartum health by improving mothers’ emotional status, QoL, as well as reducing pain.
Protocols
- Systematic Review Protocol for Sham Acupuncture Validation Research
- Sung Min Lim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):131-133. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.008
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 652 View
- 7 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
Streitberger and Park sham needles have been developed and used as non-penetrating sham acupuncture needles that can be blinded in randomized controlled clinical trials assessing the efficacy of acupuncture. Ideal sham acupuncture should not be distinguishable from an actual acupuncture treatment provided to the experimental group to ensure patient blinding; additionally, it should not have any physiological or biological effect. Providing evidence for such sophisticated sham acupuncture devices is critical, as control settings in clinical studies are based on research verifying their validity.
Methods
Three core electronic databases - PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials - will be used to search for validity verification studies of sham acupuncture devices. Clinical studies that verify the validity of non-penetrating sham acupuncture devices will be included in the review.
Results
The study design, participant information, experimental and control groups, study population’s experience with acupuncture, outcome variables, and results of studies that verify the validity of sham acupuncture devices will be systematically reviewed.
Conclusion
This systematic review of validity verification studies of sham acupuncture devices is expected to help the development of more sophisticated sham acupuncture, as well as the design of studies verifying its validity in the future.
- Effectiveness and Safety of Duantengyimu-tang for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Protocol for a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Gyoungeun Park, Jeong-Hyun Moon, Eun-Jung Kim, Won-Suk Sung
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(2):134-137. Published online June 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.009
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 715 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Per-oral pharmacological medication is a representative treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and has improved over several guidelines. However, limitations of long-term use of these medications including adverse events, led to the introduction and utilization of complementary and alternative treatments for RA. Several herbal medicine decoctions have been reported to be effective and safe; a recent study introduced Duantengyimu-tang (DTYMT). Regardless of the pharmacological effects of the DTYMT components, there are concerns about its safety. Therefore, this systematic review (SR) will focus on the effectiveness and safety of DTYMT treatment for RA.
Methods
Searches for randomized controlled trials using DTYMT treatment for RA will be performed using multiple electronic databases, manual searches, and emails (if necessary). A summary will be written using data on outcome measurements of the study participants, interventions, adverse events, and risk of bias in the studies. The primary outcomes will be disease activity scores including effective rate, tender joints, swollen joints, and morning stiffness. The secondary outcomes will include adverse events and blood tests for RA (erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and rheumatoid factors). This SR will use Review Manager software to perform a meta-analysis, the Cochrane Collaboration “risk of bias” tool, and determine the quality of evidence using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation method.
Results
This SR will investigate the clinical effectiveness and safety of DTYMT treatment in patients with RA.
Conclusion
This SR aims to be informative for patients and clinicians in clinical practice, researchers, and policymakers in managing RA.


 First
First Prev
Prev


