Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Perspect Integr Med > Volume 2(2); 2023 > Article
-
Review Article
A Review of Major Secondary Data Resources Used for Research in Traditional Korean Medicine -
Chunhoo Cheon
 , Bo-Hyoung Jang*
, Bo-Hyoung Jang* , Seong-Gyu Ko*
, Seong-Gyu Ko*
-
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine 2023;2(2):77-85.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.06.002
Published online: June 23, 2023
Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- *Corresponding authors: Bo-Hyoung Jang, Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyungheedae-ro 26, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea, Email: bhjang@khu.ac.kr. Seong-Gyu Ko, Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyungheedae-ro 26, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea, Email: epiko@khu.ac.kr
- *Corresponding authors: Bo-Hyoung Jang, Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyungheedae-ro 26, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea, Email: bhjang@khu.ac.kr. Seong-Gyu Ko, Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Korean Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Kyungheedae-ro 26, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea, Email: epiko@khu.ac.kr
©2023 Jaseng Medical Foundation
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/).
- 1,026 Views
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
- Research in health care using secondary data is steadily increasing worldwide. In this study, secondary healthcare data was reviewed, so that the information can potentially be used for Korean medicine research. The characteristics of the data, including the variables related to Korean medicine and the method of obtaining data, were summarized. The Korean medicine variables were extracted from the Korean Medicine Utilization Survey, Korea Health Panel, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Medical Service Experience Survey, and the health insurance claims data. Except for health insurance claims data, the data was obtained through relatively simple procedures. There were differences in the characteristics of each secondary data and the extent to which it was used in Korean medicine research. Many Korean medicine studies using secondary data will be conducted in the future and researchers must understand the characteristics of the data and analyze it appropriately.
- Secondary data resources refer to data that has been collected for no specific research purposes but are often used by researchers in the healthcare sector [1]. With the development of computer technology and sophisticated analysis techniques, there has been increasing emphasis on the importance of data analysis in different medical fields. The newly emerged term “digital health” refers to the use of this information to manage illness and health risks [2]. In this context, data analysis and the interpretation of data play important roles. It has been reported that South Korea has been actively building secondary data resources and disclosing a wide range of raw data [3]. Compared with other countries, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, South Korea, Denmark, and Finland showed a high level of availability of healthcare data, maturity, research utilization, and government policy support [4]. In most countries, using secondary data resources stirs up controversy between the industry sectors that intend to utilize the data and those who emphasize the importance of privacy and protection of personal information. In South Korea, three representative laws relating to healthcare data were revised in 2020 and these revisions are expected to facilitate and further promote healthcare data utilization [5].
- In South Korea, doctors who majored in traditional Korean medicine (TKM) have the same legal and social status as doctors who studied conventional Western medicine [6]. There is much research into TKM, however, there is only a limited number of Korean medicine studies using secondary data resources, and most of the research topics for these studies are about the use of Korean medicine [7]. Although there has been a gradual increase in the number of published Korean medicine research articles evaluating treatment effects, more types of conditions and diseases need to be investigated. For example, musculoskeletal conditions/diseases are common reasons for patients’ visits to TKM clinics, and account for a significant proportion of consultations [8,9]. Therefore, for TKM to play a key role in this era of digital health, more studies applying various research methods for different conditions/diseases and utilizing secondary data resources are needed, and analysis of medical data should be performed with reference to electronic medical record data. Lifelog data of patients who have received or are receiving TKM should eventually lead to promoting health care management where TKM is used. As a first step to promoting Korean medicine research by utilizing secondary data resources, the following should be investigated: the type of data resources available, the variables in each case, and how the resources have been utilized to date.
- Previous studies have reviewed Korean medicine research using secondary data resources, but these studies mainly discussed research themes of published papers or specific research methods [7,10]. Therefore, after examining major secondary data resources that can be used for Korean medicine research, each data resource’s characteristics were reviewed and variables related to Korean medicine were summarized, and strategies and methods for utilizing these data resources were presented.
Introduction
- This study reviewed the National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency report where domestic secondary data resources are introduced, published research on secondary data resources, studies that used secondary data resources, and the website, and guidelines on the use of data for various agencies that provide secondary data resources. Among different secondary data sources, those that included variables related to TKM were included in the analysis. Data provided by Korean agencies were included, and those that did not have Korean medicine-related variables were excluded from the analysis even if those resources included variables related to Korean medicine in the past.
- The agencies that provided secondary data resources included in the analysis, variables related to Korean medicine and sociodemographic information, data acquisition methods, and the brief characteristics were summarized and presented. In addition to variables directly related to Korean medicine, some indirectly related variables that were frequently used as covariates were presented in the analysis.
Materials and Methods
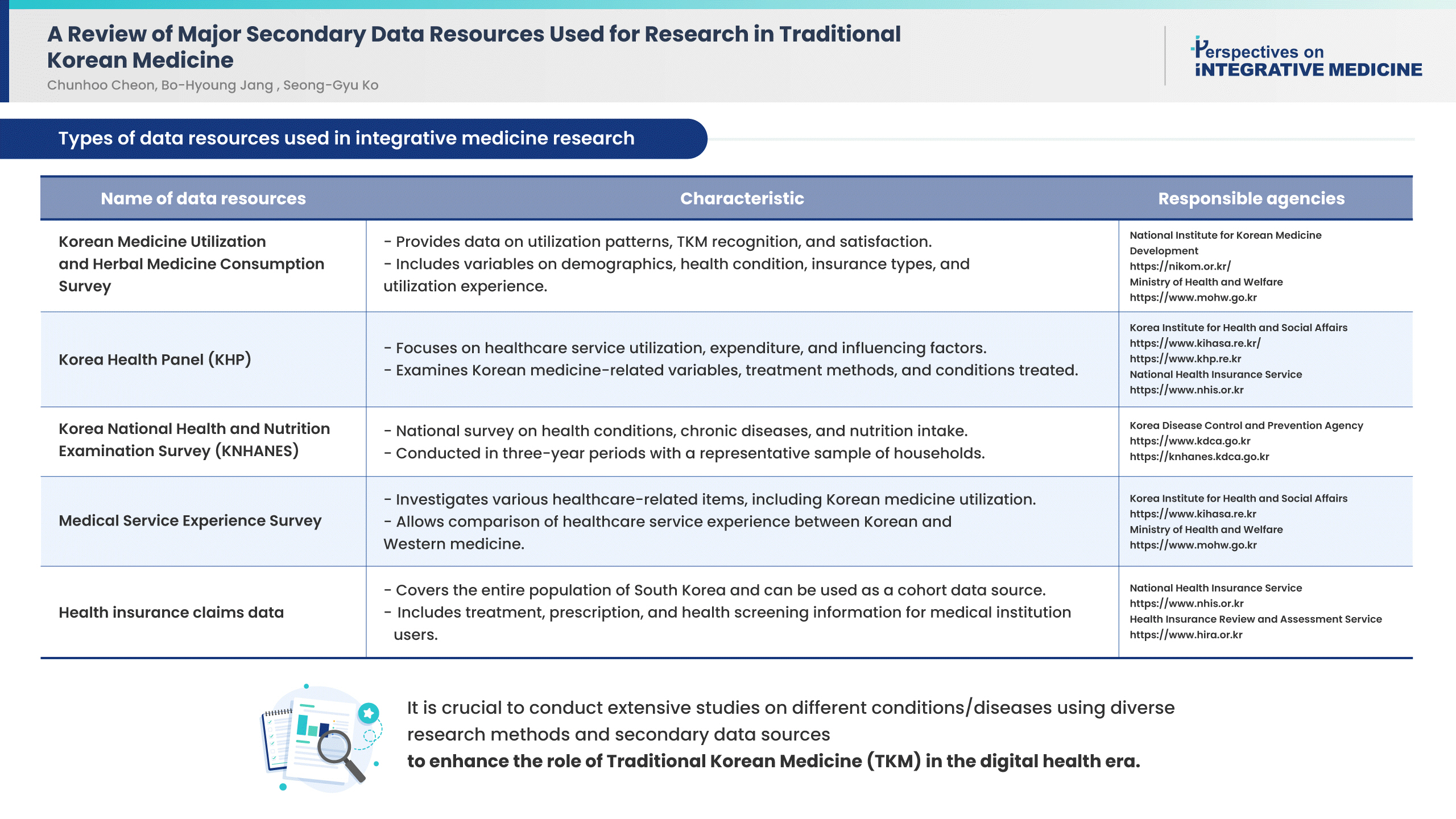
- The names and agencies that provided the data and a brief description of secondary data resources for South Korea, including variables related to Korean medicine are presented in Table 1.
- 1. Korean medicine utilization and herbal medicine consumption survey
- The Korean medicine utilization and herbal medicine consumption survey is a national statistical data survey performed by the National Institute of Korean Medicine Development, which provides data on the status of utilization of Korean medical services, TKM recognition and demand for, and patterns in the utilization of Korean medicine. The survey is divided into the general population and users of Korean medicine services, both populations are representative of the national population aged 19 and older. The Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey did not present a list of variables because most of the survey items were related to Korean medicine. The survey further categorizes the 2 populations of respondents into outpatients and inpatients to examine the experience of Korean medicine utilization, individual perception of Korean medicine, the status of Korean medicine utilization, intention to use the service and recommendation to others, their health condition, and types of national health insurance and other private insurance. The sociodemographic variables surveyed included sex, age group, marital status, education level, occupational status, and household income. The microdata of the Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey can be acquired after agreeing to the terms of use on its website (https://www.koms.or.kr/), submitting a plan of data utilization, and obtaining approval in the review process. The survey has been conducted every three years since 2008, and the microdata generated became available to the public in 2017; the microdata of the 2017 and 2020 surveys are currently accessible to the public.
- 2. Korea health panel
- The Korea health panel (KHP) specifically aims to build a database to analyze patterns in the utilization of healthcare services, the amount of healthcare expenditure, and influencing factors. Currently, the 2nd KHP survey is in progress, and 8,500 households nationwide are included in the survey sample based on the census registered in 2016. Since the KHP survey is a panel survey, it is conducted on the same participants yearly. In the KHP, Korean medicine-related variables are examined by asking for the types of medical institutions visited for healthcare services, expenditures related to healthcare services, and collaborative treatment. The survey also investigates the purpose of inpatient and outpatient services in Korean medicine, the conditions/diseases treated, and treatment methods (Table 2). The KHP data can be downloaded via e-mail by completing the consent form for the use of data on its website (https://www.khp.re.kr/) and sending the form to the person in charge.
- 3. Korea national health and nutrition examination survey
- The Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES) provides national statistics on health conditions, the prevalence of chronic conditions/diseases, and food and nutrition intake for the general population in South Korea. The survey is based on a complex sample design to ensure the representativeness of the Korean population. The survey has been conducted over eight periods (three years per period); in the 8th survey, 4,800 households were included. The Korean medicine-related variables included in the survey were: an item on checking the intake of Korean herbal medicine as a method of weight control, and the inclusion of Korean medicine hospitals/clinics when surveying the experience of inpatient or outpatient care (Table 3). The 3rd KNHANES in 2005 included the use of Korean medicine services for one year, intention for use in the future, types of Korean medicine services used, and co-payments for Korean herbal medicine; however, these items were only included in the KNHANES 2005. The raw data from the KNHANES can be obtained from the KNHANES website (http://knhanes.kdca.go.kr/) after user information registration and consent on the use of data. Currently, data from 1998 to 2020 are publicly available.
- 4. Medical service experience survey
- In the Medical service experience survey, various items related to healthcare services were investigated according to the health condition, experience with healthcare service, perception of the healthcare system, awareness of burden in medical expenditure, experience of health screening/examination, personal characteristics, and household characteristics. Using the survey, it was possible to identify whether the medical institution that the respondent recently visited was a Korean medicine hospital/clinic and whether the respondent used the service frequently (Table 3). Thus, the survey serves as a data resource that allows comparative analysis of the participants’ healthcare service experience between Korean and conventional Western medicine. The raw data from the Survey on the Medical Service Experience Survey can be obtained by completing an application form, pledge, and research proposal from the Health and Welfare Data Portal (https://data.kihasa.re.kr/) of the Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs and upon approval of the submitted forms. Data from 2017 to 2020 are currently available to the public.
- 5. Health insurance claims data
- The health insurance claims data of South Korea includes treatment history information, prescription history information, and health screening information for users of medical institutions in Korea. Since the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) is a single insurer for national health insurance, it holds the data for almost the entire national population, making it the largest data set among domestic data related to healthcare. Variables related to Korean medicine include whether the medical institution used for healthcare services were Korean medicine hospitals or clinics and whether the type of services used were inpatient or outpatient care from institutions of Korean medicine. Since the survey includes most of the treatments related to the claim of health insurance coverage, details of the treatments can be checked, such as acupuncture, moxibustion, cupping, Chuna manual therapy, Korean medicine physical therapy, and prescription of herbal medicines (Table 3). Various analyzes on Korean medicine are possible by determining Korean medicine-related variables, other medical use-related variables, and user characteristics variables in the insurance data (Table 3). Health insurance claims data is largely divided into data provided by the NHIS and those provided by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA). There are customized data that provides data on the total population according to the requests, and sample cohort data, and health screening cohort that provide data of the sample representative of the entire population of South Korea. In addition, there are the elderly cohort, inpatient cohort, and pediatrics and adolescent cohorts that provide data by extracting a sample that can represent the target cohort. The working women cohort and health screening of infants and children cohort provided by the NHIS are no longer available. Detailed descriptions of the currently available sample cohort data are shown in Table 4. The sample cohort of the HIRA consists of general information on specification, medical treatment history, diagnosis statements, outpatient prescription history, and information on medical care institutions. There are two routes to acquiring the data. Data provided by the HIRA can be obtained through the Healthcare Bigdata Hub (https://opendata.hira.or.kr/); data provided by the NHIS are obtained through the National Health Insurance Sharing Service (https://nhiss.nhis.or.kr/). Before the application for data, the Institutional Review Board approval of the researcher’s affiliated institution must be obtained, and the study protocol and Institutional Review Board review result notification must be submitted for deliberation. For customized data, a data request statement with a selection of the variables should also be completed and submitted. The method of access to health insurance claims data frequently changes. Currently, customized data can be accessed for analysis by directly visiting the analysis center which is operated by the NHIS and the HIRA. Other cohort data can be accessed remotely on a virtual PC built by the data provider and used for analysis.
- The characteristics of each database are summarized as follows. Similar to cohort data, the KHP acquires data from the same participants every year. Using this, it is possible to observe changes in the status of the participants’ medical use. Since health insurance claims data is data for the entire population of South Korea, it can be used as a cohort data source. Among the health insurance claims data, the national sample cohort provided by the NHIS can be used as a cohort data source because the included participants were followed up for a certain period of time. However, the national patients sample provided by the HIRA is not cohort data because the participants are newly selected every year. In other data, such as data generated by the KNHANES and the Korean Medicine Utilization Survey, participants are newly selected to represent the entire population each time. The most detailed data available for Korean medicine research is the Korean Medicine Utilization Survey. This is because the treatment and level of satisfaction received from a Korean medicine institution for the treatment of a specific condition/disease are also investigated. However, it has the disadvantage that the sample size is not large enough to study specific conditions/diseases. Since health insurance claims data has a large number of participants and treatment method data, it can be used when conducting research on specific conditions/diseases. The source of data for the HIRA and the NHIS is the national health insurance data of South Korea, which is the same. It is provided in different forms by the two institutions. The most significant difference is that the NHIS can provide cohort data and the HIRA cannot.
Results
- Among secondary healthcare data resources available in South Korea, this study selected those with variables related to Korean medicine that can be utilized for Korean medicine research and investigated the Korean medicine-related variables including the resources, data characteristics, and data acquisition methods. In addition to the differences in the surveyed variables, each data resource had different characteristics, and these differences should be well understood and utilized for research.
- The healthcare data that was associated with the most diverse range of variables relating to the utilization of Korean medical services was obtained from the Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey. However, the disadvantage of this survey is that it is a survey of service users which although it was conducted on 1,010 outpatients and 904 inpatients, the sample size was too small when specific conditions/diseases were analyzed [11]. Therefore, most studies using this data have mainly investigated characteristics, or satisfaction of the general public, or service users [12,13]. A previous study did analyze the current status of treatment methods for low back pain, a condition with a relatively high proportion of patients utilizing Korean medicine services [14]. The Medical Service Experience Survey includes an item on whether the participant has experience in using other medical institutions for treating the same condition/disease, but it does not investigate the condition/disease that has been treated. Therefore, the Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey provides the most suitable data to analyze whether or not the users of Korean medicine service also use other medical institutions, and related analyses have been published [15,16]. The survey is conducted once every three years and the released data are only those results from 2017 and 2020 which is limiting. If the data was continuously collected, accumulated, and published, the survey could provide detailed data to analyze the utilization of Korean medicine.
- The KHP has drawn continuous interest in their database from researchers of Korean medicine because the survey includes items on the use of Korean medicine, including herbal medicines, which are not covered by health insurance, and are not investigated in other healthcare data resources. Studies on the analysis of determinants related to the selection of Korean medicine services or those with comparative analysis between Korean medicine and conventional Western medicine have been published [17,18]. It should be noted that the total cost of purchasing herbal medicines as reported by the KHP is the question of the cost spent at “pharmacy or Korean medicine pharmacy.” Until 2019, the cost of herbal medicines prepared at Korean medicine clinics or hospitals was separately investigated under the amount of expenditure for herbal medicines. However, since the KHP survey in 2020, this information was included in the item of medical expenditure of each household, and analysis should take this change into account Recently, a study focused on a specific disease, cancer, and the results of analyzing the incidence of cancer on the effects from the use of healthcare services, including Korean medicine, were published [19]. The KHP data allows for the most extensive analysis of the use of healthcare services and medical expenses and has the advantage of enabling the analysis of the dynamics through repeated questions for the same household over time. Therefore, continuous interest from Korean medicine researchers is essential for the KHP survey.
- The KNHANES contains a wide range of variables related to health and nutrition, thus drawing much interest from researchers in various fields such as medicine, dentistry, public health, and nutrition [20–23]. However, because there are few variables related to Korean medicine, this limits the interest of Korean medicine researchers in the KNHANES. Until the 2015 survey, the medical institutions used were classified by type; thus, analyzing the use of services by Korean medicine clinics/hospitals was possible. A previous study analyzed the determinants of the combined treatment of Korean and Western medicine for patients with hypertension using the 2010–2014 data [24]. Since the KNHANES in 2016, inpatient and outpatient care included the treatment received from Korean medicine institutions, and no distinction was made between institutional types; therefore, analyzing the utilization of Korean medicine was impossible.
- The Community Health Survey data for evaluating health-related factors by region are similar to those of the KNHANES, but no variables are related to Korean medicine. Since all of these healthcare data serve as basic data for national health-related policy-making, Korean medicine-related variables should be included in the KNHANES and Community Health Survey to incorporate Korean medicine into the national healthcare policy actively. Although these two surveys have few variables related to Korean medicine, they include various lifestyle factors in their surveys. Therefore, Korean medicine researchers with an interest in lifestyle factors could analyze these surveys. One study analyzed various lifestyle habits based on the KNHANES data in association with Yangsaeng therapy, a type of Korean medicine, and another study analyzed the parameters of herbal medicine intake during an investigation into weight control strategies [25,26].
- Since The Medical Service Experience Survey classifies medical institutions that have been visited into conventional Western medicine hospitals and clinics, Korean medicine hospitals/clinics, and dental hospitals/clinics, the survey allows an understanding of each institution’s level of service, and the public’s perception of that healthcare system. Since most variables focus on healthcare services, researchers have little interest in the Medical Service Experience Survey compared with other data resources. However, some studies have analyzed the determinants of satisfaction with healthcare services [27,28]. As for Korean medicine-related papers, a study analyzed factors influencing the use of Korean and Western medicine [29]. Although this is a data resource with few health-related variables, since the level of satisfaction with the service provided by medical institutions also affects treatment outcomes, more research should be conducted with an interest in different healthcare services.
- Data from health insurance claims draws much interest and attention from many researchers in the field of medicine because it contains an extensive range of items and has data for the entire Korean population. Since healthcare data of this scale is rare, even on a global level, the research utilizing the data and the health insurance claims data has attracted much attention [30–32]. However, there are some drawbacks. Firstly, since the data is administrative information for insurance coverage claims, it may differ from the actual health information of the users. Secondly, the data does not include the treatment information not covered by health insurance. For example, the decoction, which accounts for a significant portion of Korean medicine services, cannot be analyzed using the health insurance claims data because the national health insurance does not cover it. As for Korean medicine research based on the health insurance claims data, a previous study reported that receiving acupuncture was associated with a low lumbar surgery rate, and another study reported that receiving acupuncture was associated with a low rate of knee surgery for osteoarthritis [33,34]. Some studies have compared the status of using traditional medicine between South Korea and Taiwan, a country that has traditional medicine doctors, operates a health insurance system, and discloses claims data, similar to South Korea [35,36]. Since many comparative studies on treatment effects are conducted using health insurance data, researchers of Korean medicine must continue to pay attention to this type of data. Compared with other secondary data resources, requesting data from health insurance claims to analysis takes a substantial amount of time; therefore, a research plan considering this aspect is required. It has become possible to statistically analyze the health insurance claims data in combination with other healthcare data, drawing the interests of many researchers.
- This study had several limitations. Among the secondary data resources in South Korea, resources that include Korean medicine-related variables may not have been included in this analysis. The data resources for this review were selected considering the ease of obtaining data for analysis and the applicability to Korean medicine research. Variables of data resources may vary depending on the timepoint of access, and for health insurance data, variables that can be analyzed may vary depending on policies. However, these factors were not considered in this study. Researchers must consider the accessibility of healthcare data and the variables of the data resources during research planning. It is hoped that this review will serve as a useful guide for researchers to conduct on Korean medicine research based on secondary data resources.
- This study reviewed secondary data resources that can be used for Korean medicine research, and the methods for utilizing each type of data resource have been discussed. Since each data resource has its advantages and disadvantages, it is necessary to identify the characteristics of each data resource and select the most appropriate data resource for the research topic to conduct analysis.
Discussion
-
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: CC, BHJ, and SGK. Methodology: CC, BHJ, and SGK. Writing – Original Draft: CC. Writing – Review & Editing: CC, BHJ, and SGK.
-
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there was no conflict of interest.
-
Ethical Statement
Ethical approval was not applicable because this was a review article.
-
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
-
Data Availability
Data sharing was not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Article information
| Name of data resources | Responsible agencies |
|---|---|
| Korean Medicine Utilization Survey |
National Institute for Korean Medicine Development https://nikom.or.kr/ Ministry of Health and Welfare https://www.mohw.go.kr |
| Korea Health Panel |
Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs https://www.kihasa.re.kr/ https://www.khp.re.kr National Health Insurance Service https://www.nhis.or.kr |
| Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency https://www.kdca.go.kr https://knhanes.kdca.go.kr |
| Survey on the Experience with Healthcare Service |
Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs, https://www.kihasa.re.kr Ministry of Health and Welfare https://www.mohw.go.kr |
| Health insurance claims data |
National Health Insurance Service https://www.nhis.or.kr Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service https://www.hira.or.kr |
- [1] Hwang J, Shin S, Kim J, Oh S, Kang H, Park S, et al. Domestic secondary data resources utilization in healthcare research. Seoul (Korea), National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, 2013.
- [2] Meskó B, Drobni Z, Bényei É, Gergely B, Györffy Z. Digital health is a cultural transformation of traditional healthcare. Mhealth 2017;3:38. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [3] Yoon S-J, Kim YA, Kim HJ, Yoon J, Kim A, Hong S-w, et al. Policy planning strategies for data production and management in health care for evidence-based health care policy making: The case of secondary databases. Seoul (Korea), National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, 2013.
- [4] Oderkirk J. Survey results: National health data infrastructure and governance. OECD Health Working Papers. No 127 2021.
- [5] Son YH. Revision of Data 3 Law and Utilization of Personal Healthcare Data in Platform Economy Era. J Ind Prop 2021;67:437−78.Article
- [6] Fei W. A Study on Collaborative Medical Care System of Korean Medicine and Western Medicine. Chung Ang J Legal Stud 2021;45(2):207−42.
- [7] Kim KH, Jang S, Sung JW, Lee HW, Choi YH, Shin Y-C, et al. A Review on studies of Korean Medicine using secondary data. J Soc Prevent Korean Med 2016;20(1):29−42. https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201614652520612.page.
- [8] Lee WJ, Han CH, Yang C, Lee SH, Kim D, Ha I. Analysis of outpatient expenditure trends using Korean Health Panel Survey data of patients diagnosed with lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. J Int Med Res 2021;49(10):3000605211051583. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [9] Cho Y, Yeo J, Lee YS, Kim EJ, Nam D, Park YC, et al. Healthcare Utilization for Lateral Epicondylitis: A 9-Year Analysis of the 2010–2018. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service National Patient Sample Data. Healthcare (Basel) 2022;10(4):636. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [10] Hyun MK. How can the concurrent use of conventional medicine and Korean medicine be defined in the National Health Insurance Service database? Integr Med Res 2021;10(2):100485. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [11] Ministry of Health and Welfare. Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey 2017 Microdata User Guide. Osong (Korea), Ministry of Health and Welfare, 2018.
- [12] Lim J, Lee K-J. Influencing factors of using Korean Medicine services - focusing on the 2017 Korean Medicine Utilization Survey. J Korean Med 2021;42:12−25.Article
- [13] Yoon L-S, Lim B-M. The Determinants and Behavioral Intentions of Korean Medicine Utilization in Youth Aged 19–39 Years: Based on the microdata of national survey on Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption, 2017. J Soc Prevent Korean Med 2021;25(2):85−98. https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO202125761138573.page.
- [14] Cheon C. Traditional Korean medicine treatment patterns in patients with low back pain: A cross-sectional study based on the 2017 Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey. Eur J Integr Med 2020;36:101124. Article
- [15] National Development Institute of Korean Medicine. Report of Korean Medicine Utilization Survey - User, 2020. Seoul (Korea), National Development Institute of Korean Medicine, 2021.
- [16] Cheon C, Kim J, Cho Y, Choi D, Yoon S, Cha J, et al. The analysis on the use experience of other medical institution for the same symptoms and the frequent diseases of outpatients of Korean medical institution: Based on the 2017 Korean Medicine Utilization and Herbal Medicine Consumption Survey. J Soc Prevent Korean Med 2019;23(3):13−20. https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201909165770259.page.
- [17] Choi JH, Kang S, You CH, Kwon YD. The Determinants of Choosing Traditional Korean Medicine or Conventional Medicine: Findings from the Korea Health Panel. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015;2015:147408. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [18] Jung B, Kim J, Ha I-H, Lee J. Factors affecting utilisation of traditional Korean medical services by privately insured persons: a retrospective study using Korean Health Panel Survey (KHPS). BMJ Open 2020;10(1):e033159. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [19] Kim D, Sung S-H, Shin S, Park M. The effect of cancer on traditional, complementary and alternative medicine utilization in Korea: a fixed effect analysis using Korea Health Panel data. BMC Complement Med Ther 2022;22(1):137. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [20] Kim JY, Cho SM, Yoo Y, Lee T, Kim JK. Association between Stroke and Abdominal Obesity in the Middle-Aged and Elderly Korean Population: KNHANES Data from 2011–2019. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022;19(10):6140. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [21] Jin T, Park EY, Kim B, Oh JK. Non-Linear Association between Serum Folate Concentration and Dyslipidemia: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2016–2018. Epidemiol Health 2022;44:e2022046. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [22] Kim Y, Kim DW, Kim K, Choe JS, Lee HJ. Usual intake of dietary isoflavone and its major food sources in Koreans: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018 data. Nutr Res Pract 2022;16(Suppl 1):S134−46.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [23] Kim H, Lee E, Lee SW. Association between oral health and frailty: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. BMC Geriatr 2022;22(1):369. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [24] Lee JW, Hyun MK, Lee JH. Determinants of concurrent use of Biomedicine and Korean Medicine on the hypertension patients: a cross-sectional study. Integr Med Res 2021;10(1):100429. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [25] Cheon C, Park J-S, Park S, Nam K-W, Lee J-Y, Jo J-K, et al. The Relationship between Yangsaeng and General Health Status: Based on 2008 –2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Soc Prevent Korean Med 2012;16[in Korean] https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201208138129172.page.
- [26] Cheon C, Jang BH. Trends for weight control strategies in Korean adults using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2017. Explore (NY) 2021;17(4):320−6.ArticlePubMed
- [27] Kim H, Koo JH, Choi Y, Shin J. A Study on the Determinants of Outpatient Medical Service Satisfaction Based on “Medical Service Experience Survey”. Health Welf 2021;23(3):179−98.Article
- [28] Lee A-Y, Yu J-W, Lee S-H, Lee J, Jung D. A Study on Factors Affecting Outpatient Care Satisfaction According to the Types of Medical Institution: Findings from the Health Care Experience Survey 2019. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc 2021;22(9):505−13.Article
- [29] Sasaki Y, Park JS, Park S, Cheon C, Shin YC, Ko SG. Factors influencing use of conventional and traditional Korean medicine-based health services: a nationwide cross-sectional study. BMC Complement Med Ther 2022;22(1):162. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [30] Lee J, Lee JS, Park SH, Shin SA, Kim K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46(2):e15. ArticlePubMed
- [31] Seong SC, Kim YY, Park SK, Khang YH, Kim HC, Park JH, et al. Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open 2017;7(9):e016640. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [32] Kim YI, Kim YY, Yoon JL, Won CW, Ha S, Cho KD, et al. Cohort Profile: National health insurance service-senior (NHIS-senior) cohort in Korea. BMJ Open 2019;9(7):e024344. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [33] Koh W, Kang K, Lee YJ, Kim M-R, Shin J-S, Lee J, et al. Impact of acupuncture treatment on the lumbar surgery rate for low back pain in Korea: A nationwide matched retrospective cohort study. PLoS One 2018;13(6):e0199042. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [34] Gang BG, Shin JS, Lee J, Lee YJ, Cho HW, Kim MR. Association Between Acupuncture and Knee Surgery for Osteoarthritis: A Korean, Nationwide, Matched, Retrospective Cohort Study. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020;7:524628. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [35] Huang CW, Hwang IH, Lee YS, Hwang SJ, Ko SG, Chen FP, et al. Utilization patterns of traditional medicine in Taiwan and South Korea by using national health insurance data in 2011. PLoS One 2018;13(12):e0208569. ArticlePubMedPMC
- [36] Huang CW, Hwang IH, Yun YH, Jang BH, Chen FP, Hwang SJ, et al. Population-based comparison of traditional medicine use in adult patients with allergic rhinitis between South Korea and Taiwan. J Chin Med Assoc 2018;81(8):708−13.ArticlePubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations
- Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
Ye-Seul Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101000. CrossRef - Trends in the treatment of fibromyalgia in South Korea between 2011 and 2018: a retrospective analysis of cross-sectional health insurance data
Jin-Sil Yu, Eun-San Kim, Kyoung Sun Park, Yoon Jae Lee, Yeon Cheol Park, Dongwoo Nam, Eun-Jung Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
BMJ Open.2023; 13(12): e071735. CrossRef




 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite