Funded articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Funded articles
Editorials
- Reporting Overviews of Reviews: PRIORitizing a Reporting Guideline
- Lisa Hartling, David Moher
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):65-68. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.001
- Funded: Canada Research Chairs
- 358 View
- 21 Download
- Korean Medicine Innovative Technologies Development Project: Integrative Advances and Comprehensive Overview of the National R&D Initiative
- Yoon Jae Lee, Seungwon Shin, Junhyeok Yi, Minjung Park
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):69-73. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.002
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 342 View
- 19 Download
Review Articles
- Current Status and Challenges of the Evidence for Cupping Therapy in Clinical Practice Guidelines in Korea
- Seungwon Shin
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):74-85. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.003
- Funded: Sangji University
- 238 View
- 16 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) published in Korea were reviewed to evaluate up-to-date evidence and the recommendations for cupping therapy (CT) to inform clinicians and researchers for future studies. There were 14 CPGs (allergic rhinitis, ankle sprain, cervical pain, chronic low back pain, cold hands and feet, facial nerve palsy, Hwabyung, knee osteoarthritis, lumbar herniated intervertebral disk, migraine, osteoporosis, postoperative syndrome, shoulder pain, and traffic accident injury) with 29 recommendations for CT determined from “low” to “moderate” rated evidence. The levels of evidence were mostly downgraded due to the risk of bias and imprecision. The majority of recommendations for CT were graded as B or C. This comprehensive analysis underscores the imperative need for robust clinical research, including randomized controlled trials and observational studies using real-world data to enhance the quality of the evidence for CT. In addition, recommendations providing definite phases or scope of the target conditions/diseases and treatment regimens should be employed. This work lays a foundational step towards integrating CT into evidence-based clinical practice, emphasizing strategic directions for future research to bridge the gap between evidence and practice.
- Addressing the Challenges of Traditional, Complementary, and Integrative Medicine Research: An International Perspective and Proposed Strategies Moving Forward
- Maheen Raja, Holger Cramer, Myeong Soo Lee, L. Susan Wieland, Jeremy Y. Ng
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):86-97. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.004
- Funded: National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
- 537 View
- 26 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine (TCIM) encompasses a broad range of healthcare practices beyond conventional Western medicine. Despite its use globally and increased research, many TCIM research challenges persist impeding its progress and integration into clinical practice. Key challenges involve financial constraints, insufficient research training and educational support, and the methodological barriers which arise from a lack of standardization. Financial limitations hinder investment into crucial research limiting both the quantity and quality of TCIM research. Inadequate training in research and educational support limit the development of TCIM research, hindering growth and recognition of TCIM in academic and clinical settings. The inherent dynamic nature of TCIM therapies poses additional challenges for applying standardized biomedical research models. These challenges not only impede the advancement of TCIM research but also perpetuate negative attitudes and biases within the healthcare and research communities. To overcome these challenges, a comprehensive strategy is necessary to increase funding, improve literacy, and the promotion of open science practices in TCIM. Addressing these confounding factors will enable well-informed TCIM research literacy and the development of TCIM skills and facilitate the integration of evidence based TCIM therapies into a more inclusive healthcare domain, ultimately reducing negative attitudes and biases towards TCIM.
Original Articles
- The Status of Nationwide Implementation of Integrative Medicine Programs by Japanese Local Government from a “Social Model” Viewpoint
- Hui-Yu Chung, Masaki Moroi, Yasutaka Hojo, Fu-Shih Chen, Keiko Yukawa, Yoshiharu Motoo, Ichiro Arai
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):98-105. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.005
- Funded: Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- 241 View
- 18 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
The world's demographics are transitioning, prompting governments globally to adopt diverse health promotion and disease prevention programs to enhance people's quality of life. While several integrative medicine (IM) programs, including traditional or alternative medicine, may be in place, the level of implementation nationwide is unknown. This research represents the first nationwide study in Japan, conducted in 2018 before local government health programs were cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The study examines the use of IM by local government in Japan and its safety and effectiveness as a “social model.”
Methods
IM programs for disease prevention and health promotion of all 1,944 Japanese local governments in 2018, were retrieved the using the Web Archive Project of the National Diet Library, which is a maintained website repository for all Japanese local government including IM and health programs.
Results
A total of 1,739 IM programs were implemented in 537 local governments (27.6% among all Japanese local governments). These included programs for Yoga (1,242; 71.4% of the projects), Qigong (211; 12.1%), and Aromatherapy (145; 8.3%). Among the providers of the programs, only 16 (0.9%) were national medical-related license holders. The purpose of disease prevention or health promotion was not described with scientific basis (safety and effectiveness).
Conclusion
Japanese local government conduct health-promoting IM programs, but untrained providers administer many of them. There needs to be more evidence to support the alleged health promotion objectives. Local governments require better support and evidence-based planning to rectify this situation.
- Shilajit, a Natural Phytocomplex Acts as a Neuroprotective Agent Against Amyloid Beta-induced Cytotoxicity and Inflammation
- Seoyoung Kim, Changon Seo, HyeJin Park, Jin Gwan Kwon, Jin Kyu Kim, Hyoun Jong Moon, Sunki Lim, Yujeong Gho, Wang Jun Lee, Yongmun Choi, Sanghun Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):114-122. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.007
- Funded: Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 181 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Shilajit is a natural phytocomplex known for centuries in Ayurveda traditional medicine for its antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective properties. However, there is little published scientific evidence to support these acclaimed properties.
Methods
The safety, regarding the heavy metal content, component analysis, the neuroprotective effects and amyloid beta (Aβ)-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation of 3 samples of Shilajit derived from different geographical origins were assessed. Neuroprotective effects of Shilajit were examined using neuroblastoma cell lines (SH-SY5Y and IMR-32) and cell viability assays. The inhibitory effect on the proinflammatory cytokine derived from macrophage cells was assessed using bone marrow-derived macrophage cells in vitro and in a murine model of Aβ-induced inflammation (ex vivo analysis).
Results
The results showed that a daily dose of each Shilajit sample were within the permissible heavy metal limit established by the United States Food and Drug Administration. The 3 Shilajit samples alleviated Aβ-induced toxicity in neuronal cells. One sample derived from the Altai Mountains suppressed Aβ-induced processing of pro-interleukin (pro-IL)-1β into mature, biologically active IL-1β in macrophages. This Shilajit sample inhibited Aβ-induced production of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β in the brain (ex vivo analysis). In component analysis, this sample was enriched in salicyluric acid.
Conclusion
Shared and distinct properties were observed among the 3 Shilajit samples concerning their neuroprotective effects, and regarding safety, the daily dose of each Shilajit had a safe level of heavy metal content. Salicyluric acid in Shilajit may be important in mitigating Aβ-induced inflammatory cytokine but more research is necessary.
Protocol
- Protocol for a Scoping Review of Traditional and Complementary Medicine Governance Across Sub-Saharan Africa
- Tendayi R. Chihaka, Nadine Ijaz, Ossy M.J. Kasilo, Peter B. James, Daniel F. Gallego Pérez, Jon Wardle, Razak M. Gyasi
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(2):123-128. Published online June 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.06.008
- Funded: Carleton University
- 298 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Since 1978, the World Health Organization (WHO) has repeatedly called on Member States to recognize the role of traditional and complementary medicine (T&CM) in primary healthcare, improve safety, and accessibility by governing T&CM. In the 2019 Global Report on T&CM, the WHO reported that 40 out of 47 (85%) Member States from African Region had enacted governance policies, and 20 out of 47 (43%) had regulatory policies on herbal medicines. The primary barriers to implementing T&CM policy were identified as an absence of data and inadequate financial support for research. The objective of this protocol was to detail how to perform a scoping review that will examine the policy, legislative, and regulatory landscape for T&CM practitioners and products in sub-Saharan Africa.
Methods
Databases will be searched (AMED, CINAHL Plus with Full Text, MEDLINE Plus with Full text, Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, Google Scholar) for relevant articles. Searches will be limited to English, French, Portuguese, and Spanish language studies in peer-reviewed journals (1963-2023) that substantively report on legislation, bills, policies, governance approaches and regulations on T&CM (including successes and/or challenges in their design and implementation). Actual legislation, policies, and regulatory documents on T&CM and peer-reviewed studies with emphasis on integrating T&CM and biomedicine into healthcare systems will be excluded.
Expected Outcomes
This protocol has formulated the objectives for a scoping review to identify, map, and synthesize evidence on the governance of T&CM in sub-Saharan Africa.
Editorial
- A Pilot Trial of Integrative Medicine for Stroke Rehabilitation: Expert Recommendations for the Development and Sustainability of Integrative Medicine
- Chihyoung Son, Go-Eun Lee, Joo-Hee Seo, Inae Youn, Jin-Won Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):1-6. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.001
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 1,368 View
- 22 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 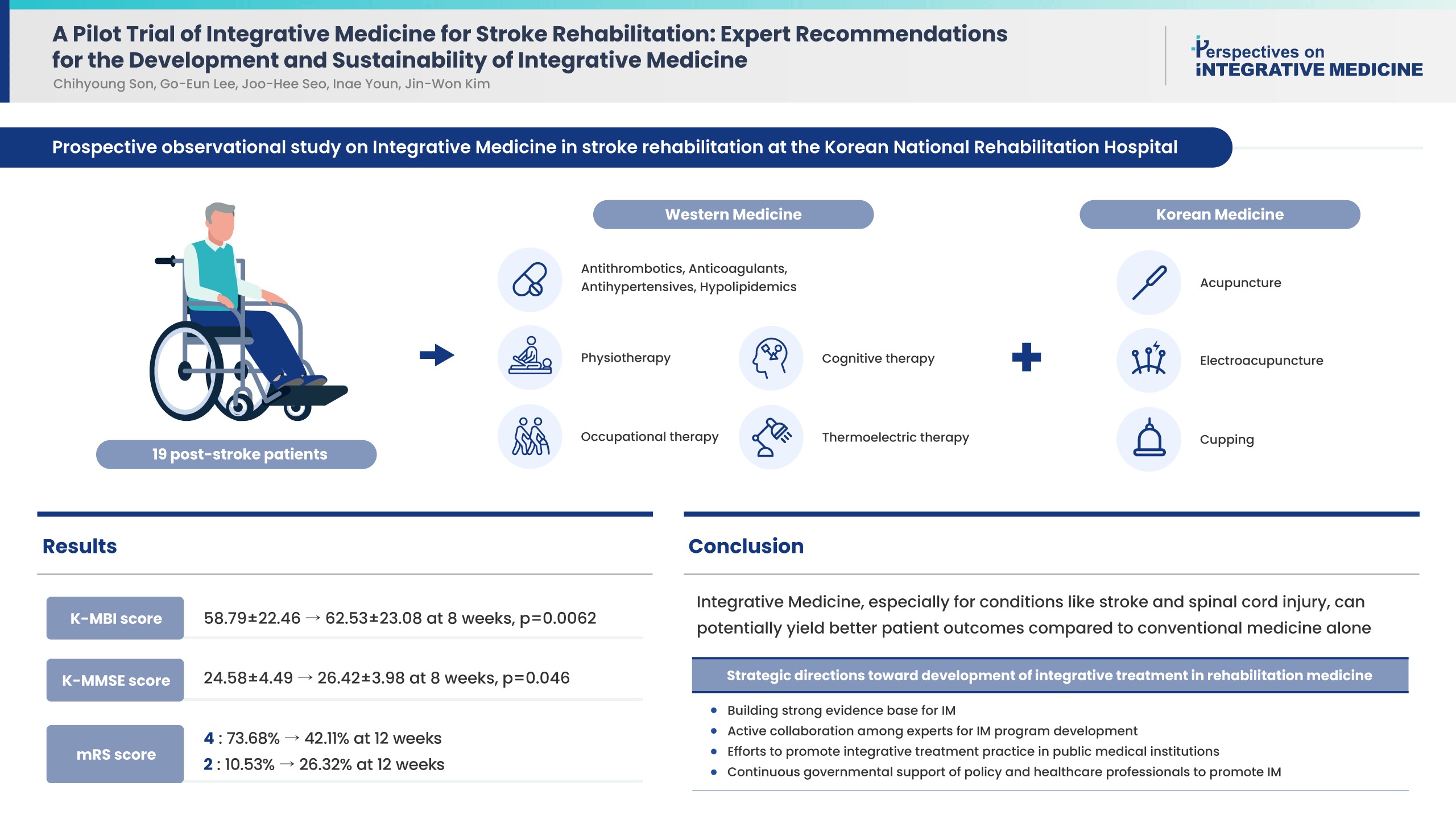
- Background
Strategies towards development and sustainability of integrative treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine are needed. National expert recommendations based on the implementation of Integrative Medicine (IM) in stroke rehabilitation and IM outcomes would be invaluable.
Methods
A pilot study was performed and the effectiveness of combining Korean traditional medicine and Western conventional medicine in post-stroke patients (ischemic stroke n = 15 and hemorrhagic stroke n = 4) was evaluated, and recommendations were developed through consensus with physicians in national centers of rehabilitative medicine. Outcome measures [Korean Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI), Korean Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), Modified Rankin Scale (mRS), and EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L) assessment were used at baseline, 4, 8 (K-MBI, K-MMSE, mRS, and EQ-5D-5L) and 12 weeks post treatment (EQ-5D-5L and mRS).
Results
Improvements were observed in functional and cognitive abilities at 8 weeks (K-MBI score p = 0.0062; K-MMSE score p = 0.046). Quality of life improvements (EQ-5D-5L) were observed but were not statistically significant. The disability assessment (mRS) indicated a gradual improvement from baseline to 12 weeks. No adverse events were reported. For effective, patient-centered IM treatment: (1) build a strong evidence base for IM as compared with Western medicine alone or traditional medicine alone; (2) active expert collaboration; (3) IM promotion in public medical institutions; and (4) continued government support.
Conclusion
Functional and cognitive abilities of stroke patients statistically significantly improved following 8 weeks of IM treatment. Strategies have been suggested towards the development and sustainability of IM treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine.
Review Articles
- Characteristics and Quality of Traditional Chinese Therapies and Integrative Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines for Musculoskeletal Disorders Published in Mainland China
- Xue-Feng Wang, Jing-Ling Zuo, Lin-Jian Li, Lan-Dan Xu, Xiao-Zhong Liu, Si-Si Ma, Jian-Ping Liu
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):7-17. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.002
- Funded: National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 1,027 View
- 19 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 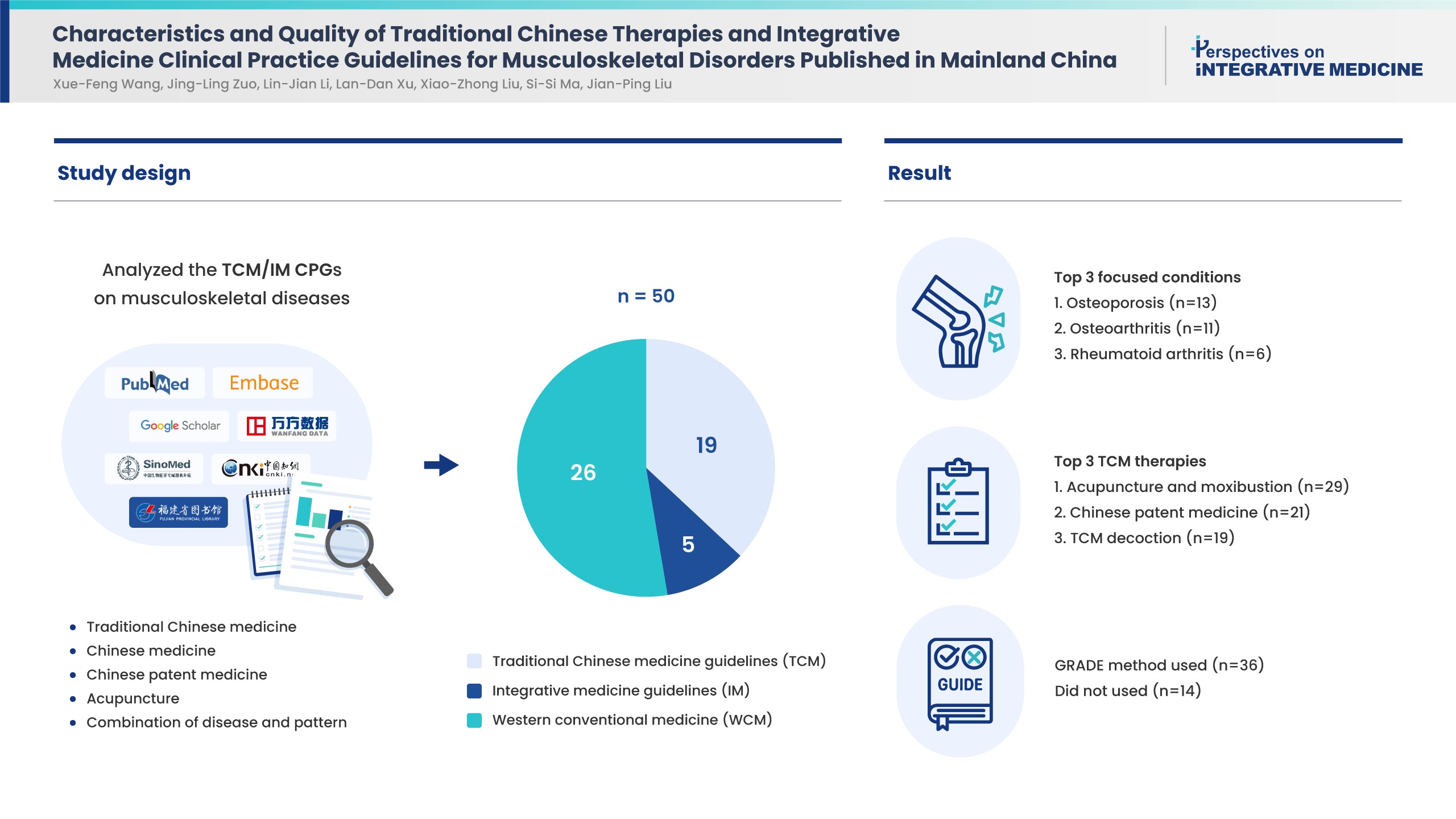
- Background
Musculoskeletal disorders are prevalent in adults. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and integrative medicine (IM) are commonly used treatments which have clinical practice guidelines (CPGs). This study aimed to determine the characteristics and quality of these CPGs.
Methods
CPGs which recommended TCM/IM therapies in musculoskeletal conditions/diseases published in Chinese or English between January 2018 to December 2022 in mainland China were retrieved and analyzed for guideline classification, funding source, conflict of interest, and methodology. Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ including 6 domains, was applied to assess CPG quality.
Results
Of the 50 CPGs included, there were 19 TCM, 5 IM, and 26 western conventional medicine (WCM) guidelines of which osteoporosis (13, 26%), osteoarthritis (11, 22%) and rheumatoid arthritis (6, 12%) were the most frequent diseases. The TCM therapies recommended by the CPGs successively were acupuncture and moxibustion, Chinese patent medicine, and TCM decoction based on syndrome differentiation. Nearly half of the CPGs reported funding source (52%) and conflict of interest (48%). Thirty-six CPGs used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations method to present summaries of evidence, the remaining did not report the method. Based on Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ scores, “clarity of presentation” scored the highest (55%), while “applicability” was the lowest (6%). No CPG was recommended without change, and 23 CPGs were not recommended.
Conclusion
The quality of CPGs for musculoskeletal conditions/diseases in China is generally low. Future CPGs should pay more attention to standardized developing procedures.
- A Modern Interpretation of Cold-Heat Pattern in Traditional Medicine with a Focus on Thermo-Regulation
- Younggwang Kim, Jee Young Lee, Joongho Lee, Sanghun Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):18-28. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.003
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 1,084 View
- 22 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 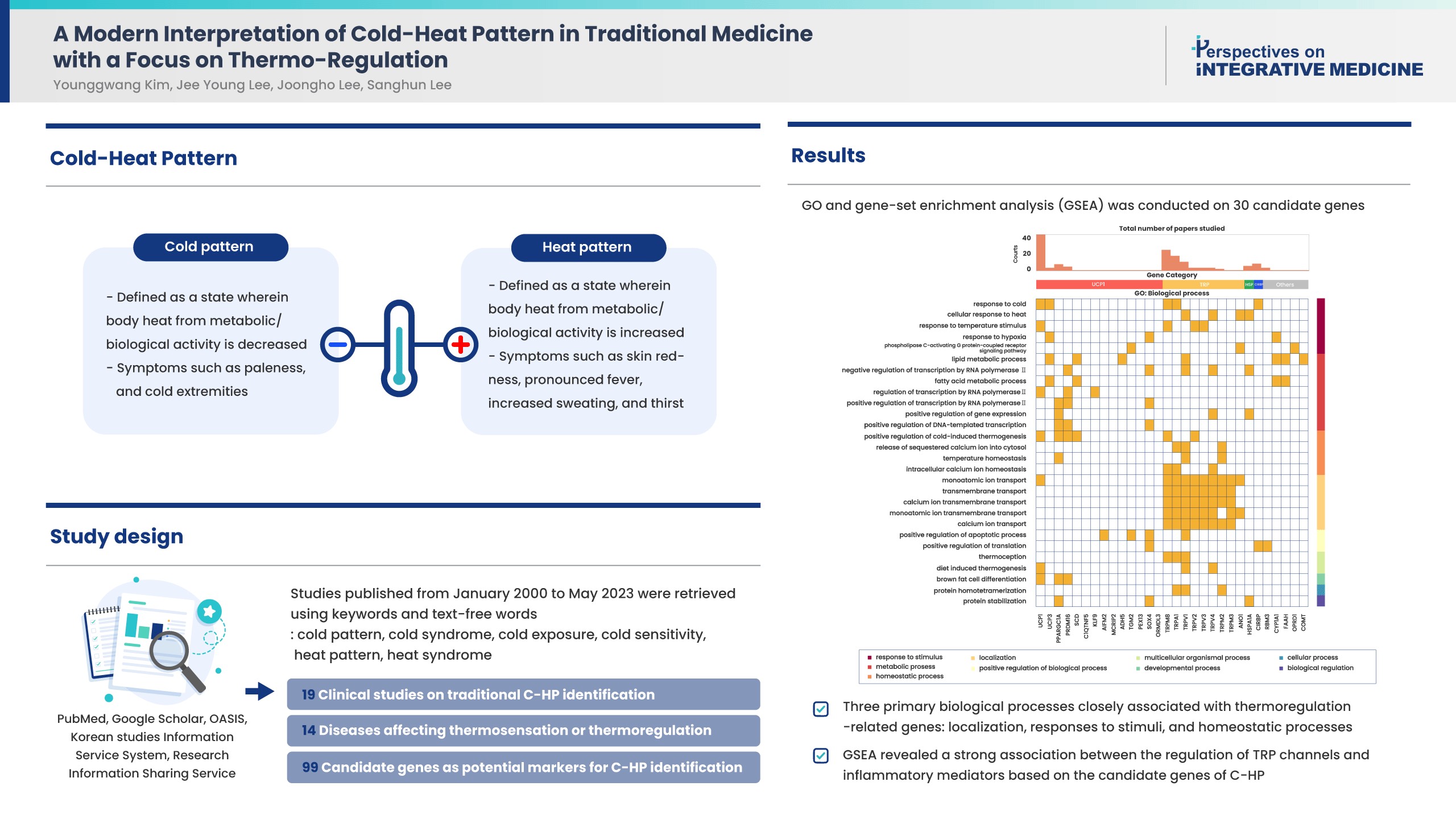
- Cold-heat patterns (C-HPs) in Traditional East Asian Medicine are essential for individually diagnosing and treating patients. However, the concept of C-HPs and their biological mechanisms (thermoregulation) remains unclear. C-HPs studies published between January 2000 and May 2023 were retrieved from 5 databases (PubMed, Google Scholar, OASIS, Korean studies Information Service System, and Research Information Sharing Service). Among the 8,373 articles screened, 132 were included in the review and categorized. Nineteen articles were clinical studies related to traditional concept of C-HP identification, 14 studies investigated diseases affecting thermosensation or thermoregulation, and 99 studies identified candidate genes as potential markers for C-HP identification. Further analysis, including gene ontology, and gene set enrichment analysis of the candidate genes, revealed 3 primary biological processes closely associated with thermoregulation-related genes, including localization, responses to stimuli, and homeostatic processes. Notably there was a significant association between the candidate genes and inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential channels (p < 0.001). A significant association between C-HPs and inflammation-related pathways across thermosensation-related and thermoregulation-related clinical and preclinical studies was observed, suggesting that the traditional concept of C-HPs should be studied further from an immunological perspective.
Original Articles
- Acupuncture Needles and the Risk of Lymphedema After Breast Cancer Surgery: A Retrospective National Cohort Study
- Ye-Seul Lee, Yucheol Lim, Jiyoon Yeo
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):29-36. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.004
- Funded: Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 1,864 View
- 28 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 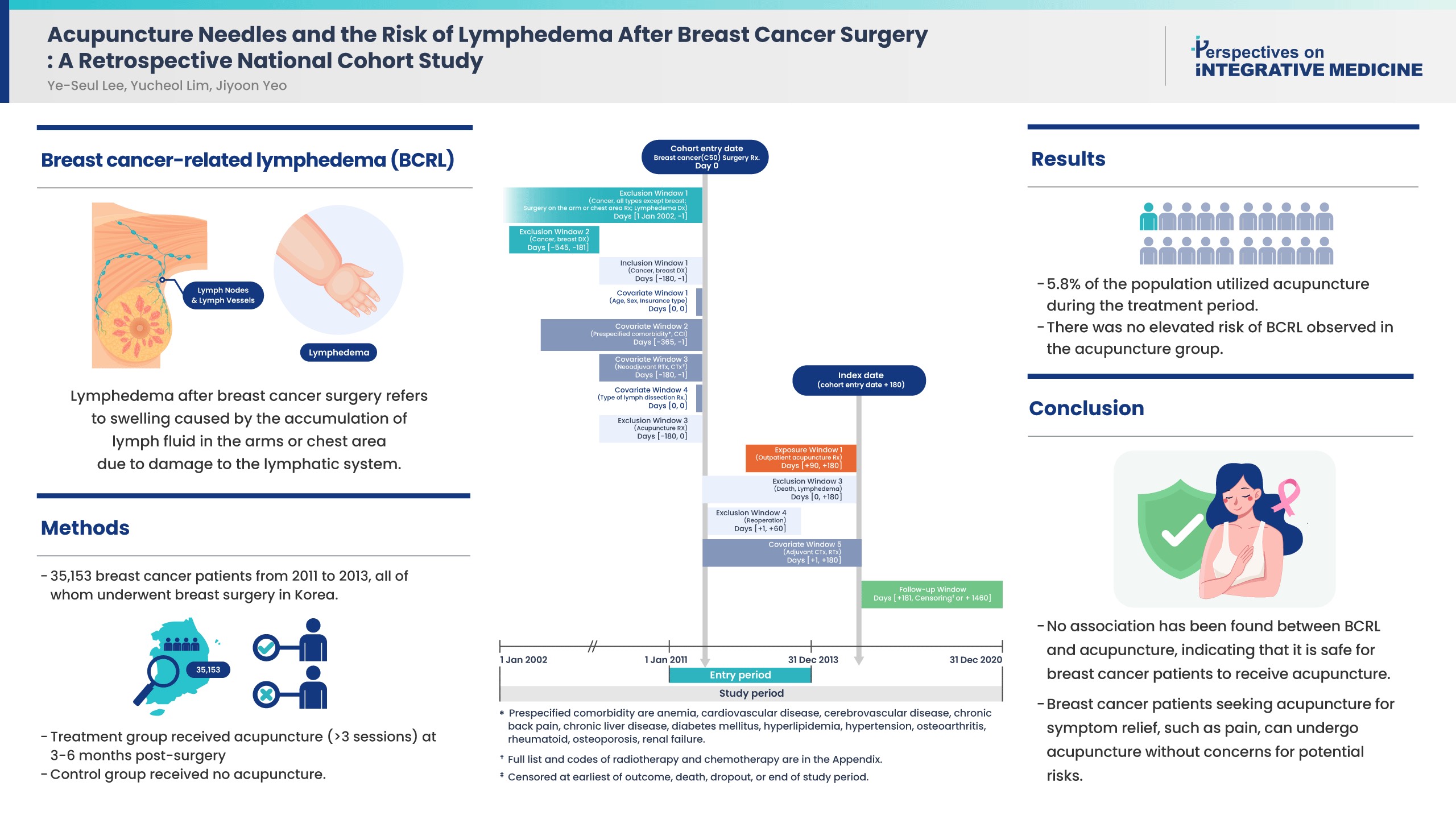
- Background
Controversies remain over the impact of using needles on breast cancer patients after surgery due to risk of breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL). While recent literature suggests that vascular access during the postsurgical stage does not affect the risk of BCRL, the impact of acupuncture on the risk of BCRL during the postsurgical stage has not been studied.
Methods
This study included 35,153 patients from 2011 to 2013 who were newly diagnosed with breast cancer in a population-based cohort from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. All patients received breast surgery, and the treatment group received acupuncture for more than 3 sessions in the 3-6 months post-surgery. The control group did not receive acupuncture. The incidence rate ratio, Kaplan-Meier curve, and Cox proportional hazards models were used to compare the risk of BCRL, and death between groups.
Results
About 5.8% of the study population received acupuncture during the 3-6 months post-surgery treatment window. After propensity score matching, the acupuncture treatment group did not show an increased risk of BCRL (IRR 1.017, 95% CI 0.868-1.193; unadjusted HR 1.018, 95% CI 0.868-1.193). This risk was robust in all multivariate Cox proportional hazards models.
Conclusion
An association of BCRL with acupuncture was not observed. Patients who received acupuncture to manage symptoms such as pain during the 3-6 months postsurgical stage did not have a higher risk of developing BCRL. Breast cancer patients who seek acupuncture to alleviate post-surgery symptoms such as pain, can receive acupuncture without concerns for potential risk of BCRL.
- Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy and Photontherapy in Cervicobrachialgia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Bianca dos Santos Bobadilha, Talita Bonato de Almeida, Maria Imaculada de Lima Montebello, Maria da Luz Rosário de Sousa
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):37-44. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.005
- Funded: Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 1,066 View
- 19 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 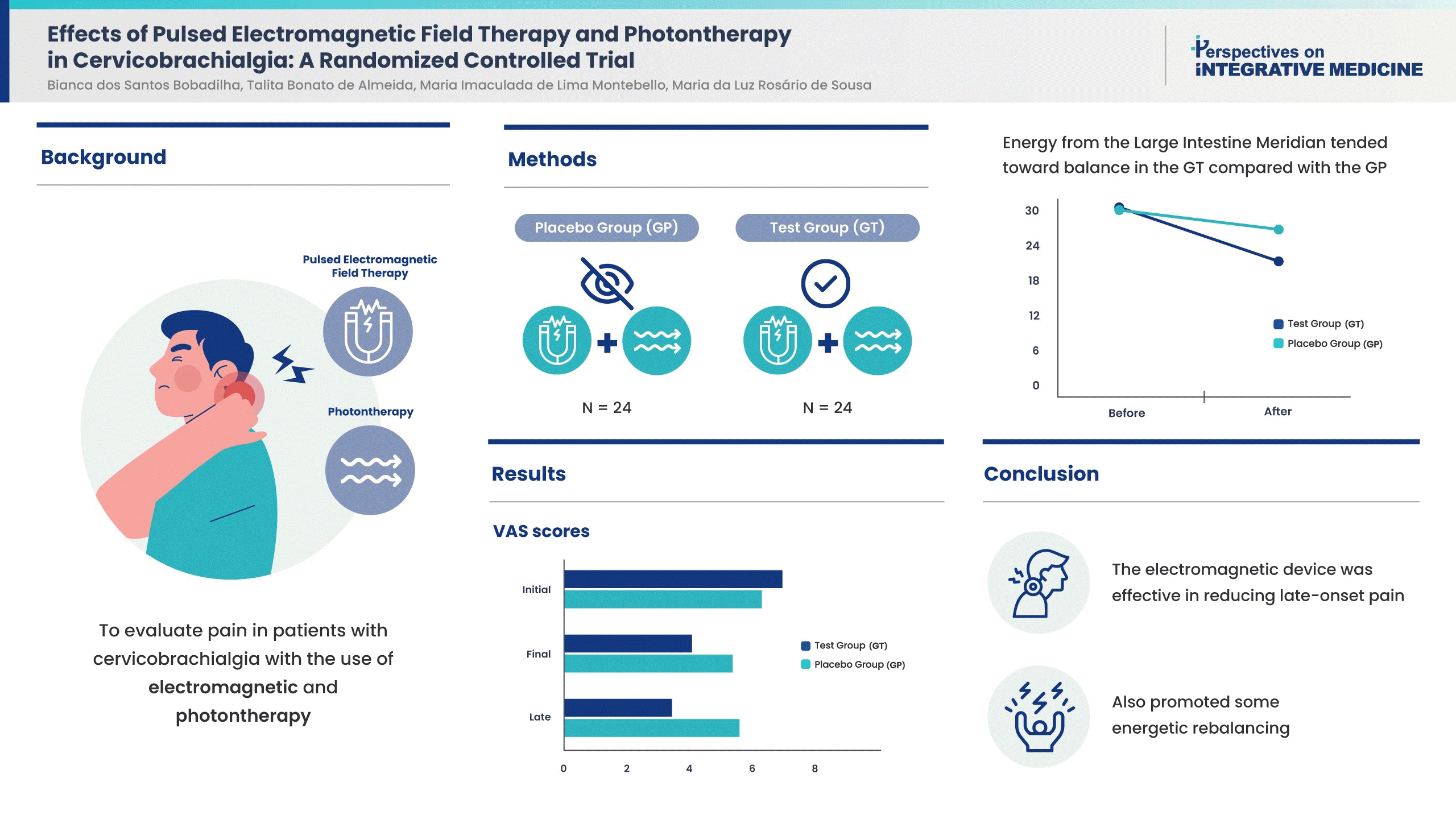
- Background
Cervicobrachialgia is a painful condition commonly treated with medication and physiotherapy. The aim was to evaluate pain following electromagnetic and photontherapy, and examine patient energy profiles.
Methods
There were 48 patients experiencing pain [Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score ≥ 4] who were not receiving medication and physiotherapy and were randomized into Test Group (GT); electromagnetism using a Kenkobio device (intensity = 0.055 mT/frequency = 60 Hz) and photon therapy; a photon therapy blanket, and Placebo Group (GP); the Kenkobio device was turned off and the blanket was not used. Pain was assessed using the VAS, before, immediately after treatment, and the following day. Algometry was also carried out before and after the treatment to understand the pain threshold at bilateral acupoints GB20 and GB21. The energy profile was assessed using Ryodoraku measurements before and after the session.
Results
The GT achieved a greater reduction in pain the following day than GP. Both groups were equal for left GB20 and right GB21 points considering algometry and, after the intervention, a reduction in pain in the GT was noticed only in the left GB20 (CI [95%]: 0.09-0.99, p = 0.019). The average energy level was low and dropped further following treatment. Furthermore, energy from the Large Intestine Meridian tended towards balance in the GT compared with the GP [CI (95%): 0.58-15.75, p = 0.035]. No adverse effects were reported.
Conclusion
The combined use of electromagnetic and photontherapy were effective in reducing pain in patients and promoted energy rebalancing.
Protocol
- Validation of a New Sham Acupuncture Needle for Double-Blind Trials: A Study Protocol
- Sung Min Lim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):57-60. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.008
- Funded: National Research Foundation of Korea, Ministry of Science and ICT
- 1,920 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
To establish efficacy in acupuncture treatment, rigorous randomized controlled trials (RCT) are needed. Non-invasive sham acupuncture needles are an effective tool for practitioner/participant blinding. This study presents a protocol for the validation of a newly developed sham acupuncture needle.
Methods
A double-blind RCT will be conducted on 66 healthy adults who will be randomly assigned (using computer-generated random numbers) to either the verum (n = 33) or sham (n = 33) acupuncture needle group. The needles will be inserted at 2 acupuncture points: LI4 (upper limb) and ST36 (lower limb). The primary outcome measure is the practitioner/participants belief that they received verum or sham acupuncture. The secondary outcome measures are participant-rated sensations (penetration, pain, and de qi). Adverse events will be recorded with detailed explanations, categorizing occurrences according to related or unrelated to acupuncture. As the newly developed sham acupuncture has not been studied before, an exploratory approach has been adopted. Descriptive statistics, t test, and χ² test will be applied appropriately.
Results
This study is intended to provide a protocol for the validation of a sham acupuncture needle by using a double-blind RCT setting, and the results will hopefully contribute to the standardization of the needles used for sham acupuncture. The outcomes aim to determine the reliability of practitioner/participant blinding, participant experience of sensations, and lay groundwork for a standardized control group for clinical trials in the future. The newly developed non-invasive sham acupuncture needle may reduce bias and improve reliability in the size effect of acupuncture treatment.
Review Article
- Effectiveness and Safety of Low-Level Laser Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sang Jun Lee, Seung Jin Noh, Jeong Rock Kim, Kyung Bok Park, Sae-rom Jeon, Yejin Hong, Dongwoo Nam
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):155-163. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.003
- Funded: Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- 1,965 View
- 61 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Low-level laser treatment (LLLT) is used to treat low back pain (LBP) however, its effects on lumbar disc herniation (LDH) remain unclear. The safety and effectiveness of LLLT for LDH was determined using a systematic review of randomized clinical trials.
Methods
Studies on LLLT in adults with LDH were identified from 12 worldwide databases. A risk of bias assessment and a meta-analysis with categorization according to the type of control used (inactive, active, or add-on) was performed. The quality of evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation.
Results
The quantitative analyses included five studies. LLLT was significantly more effective at treating LDH [leg pain visual analog scale (VAS) mean difference (MD): -1.90, 95% confidence interval (CI): -2.01, -1.80, I2 80%; LBP VAS MD: -0.79, 95% CI: -0.87, -0.71, I2 80%] than inactive controls (placebo or sham). The quality of the evidence ranged from “low” to “very low.” As an add-on to usual care, LLLT significantly improved pain intensity and disability compared with usual care (leg pain VAS MD: -2.52, 95% CI: -2.65, -2.40, I2 97%; LBP VAS MD: -1.47, 95% CI: -1.58, -1.36; Oswestry Disability Index MD: -4.10, 95% CI: -4.55, -3.65, I2 6%). However, the quality of the evidence ranged from “moderate” to “low.”
Conclusion
LLLT significantly improved outcomes compared with the inactive controls, but was not more effective than usual care for LDH. In combination with usual care, LLLT was significantly more effective than usual care alone highlighting the potential of LLLT.
Original Article
- Improvement in Growth in Adolescents with Average Height Using A Massage Chair: A Prospective Single Arm Pre-Post and National Standard Data Comparison Study
- Sul Gi Park, Gyu Tae Chang, Jin Yong Lee, Sun Haeng Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):164-172. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.004
- Funded: Bodyfriend, Inc.
- 759 View
- 13 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
This study aimed to examine the changes in height, weight, and bone age between pre- and post-intervention when using a BEG-100 massage chair daily.
Methods
Thirty-five children aged 11 years who were close to the average height (145-155 cm) were included in the study. There were 34 participants who used the BEG-100 massage chair for 24 weeks. Daily intervention consisted of 20 minutes of lower body massage and 10 minutes of whole-body massage. Height, weight, and adverse events were checked every five visits, while a hand X-ray was used before and after massages. The height percentile and height standard deviation score (SDS) were calculated using the 2017 Korean growth chart. The bone age and predicted adult height using radiographs were computed using the Tanner-Whitehouse method. The paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used according to normality of data to determine statistical significance.
Results
A total of 31 children were included in the final analysis. The height percentile and height SDS significantly increased after BEG-100 massage chair use (2.39; p = 0.032, and 0.07; p = 0.036, respectively). However, these changes were not significant in children whose baseline height was shorter than the average. There were no significant differences in bone age, height for bone age, predicted adult height, or sitting height/height ratio. None of the participants complained of adverse events.
Conclusion
The height percentile and SDS of teenagers increased after use of massage chair therefore, it is necessary to perform larger randomized controlled clinical studies. Trial registration: KCT0004673.




 First
First Prev
Prev


