Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Contributing Factors in the Decision to Study Korean Medicine and Satisfaction with the College Experience: A Quantitative Nationwide Study
- HyunSeok Kim, Hyunho Kim, Joohyun Lee, Hwimun Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):173-181. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.005
- 1,039 View
- 33 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 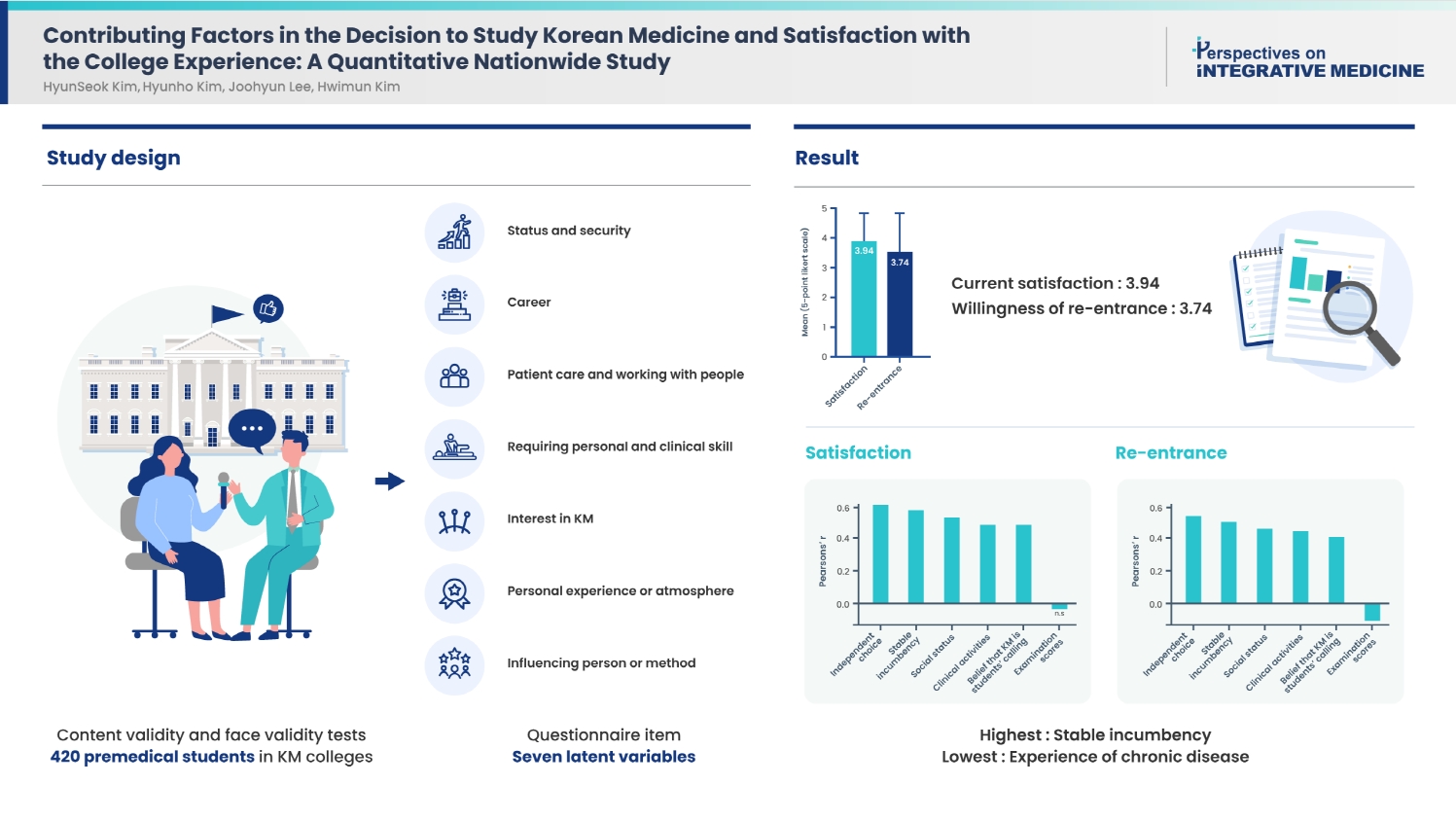
- Background
The practice of Korean medicine (KM) taught at KM colleges has equal legal rights and responsibilities as Western medicine in South Korea. To date, no research has been conducted on the factors which influence college students in their choice to study KM and satisfaction with the course.
Methods
Content validity and face validity tests were conducted while developing the questionnaires. Research was conducted amongst all KM colleges in South Korea and of the 744 premedical KM 2nd year students, 420 participated. Analysis was performed on how much the mean values changed between the items and sub-items. Factors were also correlated with the students’ satisfaction and willingness to reenter KM colleges.
Results
The means of stable incumbency items were the highest of all the items, while items concerning experience of chronic disease had the lowest mean values. For enrollment, the latent value that most questionnaire items were changed positively by was interest in KM. Items related to students’ choice or KM doctor status were closely tied to students’ current satisfaction with their choice to enroll at a KM college, rather than their college entrance examination scores.
Conclusion
Identifying which factors are considered before entering KM college and during the course can help students to be more satisfied with their academic progress. To satisfy the KM students, educators should focus on providing both qualified clinical training and guidance to enter diverse career fields. This study highlights factors that can be applied to college curriculum or subject teaching.
- Current Status of Korean Medicine Treatment for Post-acute COVID-19 Syndrome: A Survey of Korean Medicine Doctors
- Doori Kim, Seo-Hyun Park, Won-Suk Sung, Eun-Jung Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2022;1(1):34-44. Published online September 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2022.09.006
- 1,701 View
- 45 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The applicability of Korean medicine (KM) treatments for post-acute COVID-19 syndrome were investigated.
Methods
A cross-sectional, web-based survey of Korean medical doctors (KMDs) was conducted in June 2022. The 25-item questionnaire comprised of five parts: basic characteristics, prescribed post-COVID-19 KM treatments, treatment effect in patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, patient satisfaction, and awareness and utilization of the relevant KM Clinical Practice Guideline by the KMDs.
Results
In total, 1,063 completed questionnaires were collected, and 822 were analyzed. The most common symptoms in patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome treated by KMDs was weakness and fatigue (84.3%). Herbal decoctions (39.2%) and herbal powder (not covered by medical insurance; 25.8%) were primarily used. Among the KMDs, 95% (n = 781) responded that KM treatments, particularly herbal decoctions (82.6%) and herbal powder (not covered by medical insurance; 46.8%), were effective. Overall, 92.6% (n = 761) of KMD participants answered that the patients were satisfied with KM treatments, mostly due to symptomatic improvement (60.8%). The primary reason for dissatisfaction was the burden of cost for patients (78.4%). The main reasons for low uptake of KM services by patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome were lack of publicity and administrative issues such as no health insurance coverage.
Conclusion
KM is highly applicable for post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Health policies supporting the use of KM for post-acute COVID-19 syndrome are recommended.


 First
First Prev
Prev


