Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Report
- Complete Remission of Drug-Induced Acute Dizziness Using Eight Constitution Acupuncture and the Barbecue Maneuver: A Case Report
- Younkuk Choi, Juhee Cho
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):51-56. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.007
- 1,004 View
- 47 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dizziness, often symptomatic of underlying conditions, presents management challenges especially when dealing with drug-induced vestibular disorders. Complementary therapies like acupuncture, specifically, Eight Constitution Acupuncture (ECA), offers a potential alternative to other management therapies. A 74-year-old female, experiencing sudden dizziness from medication for back pain, underwent a detailed examination, constitutional diagnosis, and targeted acupuncture involving 26 insertions over 4 sessions. The treatment for dizziness, which focused on constitutional differences, integrated ECA and the barbecue maneuver which resulted in significant efficacy. A 50% reduction in the Numeric Rating Scale score from 10 to 5 was observed after the 1st session. Subsequent sessions of ECA combined with the barbecue maneuver significantly reduced symptoms of dizziness and ultimately alleviated symptoms. This case underscored the potential of ECA when combined with the application of the barbecue maneuver in treating drug-induced vestibular disorders and residual benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. The ECA's constitutional approach allows for precise targeting and symptom resolution, and integrating the principles of Traditional Asian Medicine with biological mechanisms. Notably, this is the 1st case report of the efficacy of ECA and the barbecue maneuver in addressing drug-induced vestibular disorders. A holistic approach, considering constitutional differences, can offer insights and tailored solutions to present a promising avenue for patients experiencing such conditions. Rigorous research studies are essential to validate these findings.
Review Article
- Characteristics and Quality of Traditional Chinese Therapies and Integrative Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines for Musculoskeletal Disorders Published in Mainland China
- Xue-Feng Wang, Jing-Ling Zuo, Lin-Jian Li, Lan-Dan Xu, Xiao-Zhong Liu, Si-Si Ma, Jian-Ping Liu
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):7-17. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.002
- 713 View
- 17 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 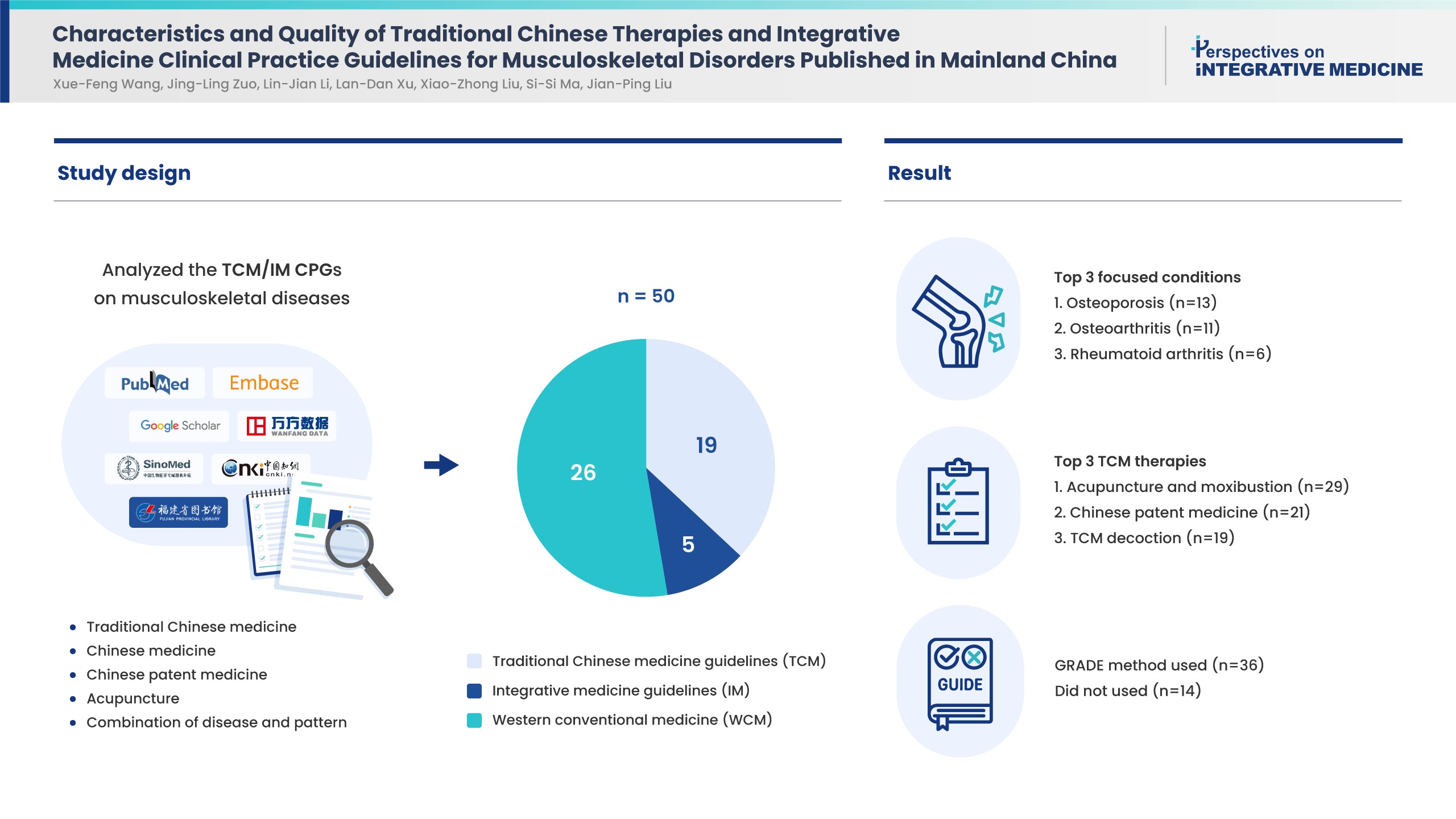
- Background
Musculoskeletal disorders are prevalent in adults. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and integrative medicine (IM) are commonly used treatments which have clinical practice guidelines (CPGs). This study aimed to determine the characteristics and quality of these CPGs.
Methods
CPGs which recommended TCM/IM therapies in musculoskeletal conditions/diseases published in Chinese or English between January 2018 to December 2022 in mainland China were retrieved and analyzed for guideline classification, funding source, conflict of interest, and methodology. Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ including 6 domains, was applied to assess CPG quality.
Results
Of the 50 CPGs included, there were 19 TCM, 5 IM, and 26 western conventional medicine (WCM) guidelines of which osteoporosis (13, 26%), osteoarthritis (11, 22%) and rheumatoid arthritis (6, 12%) were the most frequent diseases. The TCM therapies recommended by the CPGs successively were acupuncture and moxibustion, Chinese patent medicine, and TCM decoction based on syndrome differentiation. Nearly half of the CPGs reported funding source (52%) and conflict of interest (48%). Thirty-six CPGs used the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations method to present summaries of evidence, the remaining did not report the method. Based on Appraisal of Guideline for Research and Evaluation Ⅱ scores, “clarity of presentation” scored the highest (55%), while “applicability” was the lowest (6%). No CPG was recommended without change, and 23 CPGs were not recommended.
Conclusion
The quality of CPGs for musculoskeletal conditions/diseases in China is generally low. Future CPGs should pay more attention to standardized developing procedures.
Editorial
- A Pilot Trial of Integrative Medicine for Stroke Rehabilitation: Expert Recommendations for the Development and Sustainability of Integrative Medicine
- Chihyoung Son, Go-Eun Lee, Joo-Hee Seo, Inae Youn, Jin-Won Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2024;3(1):1-6. Published online February 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2024.02.001
- 791 View
- 19 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 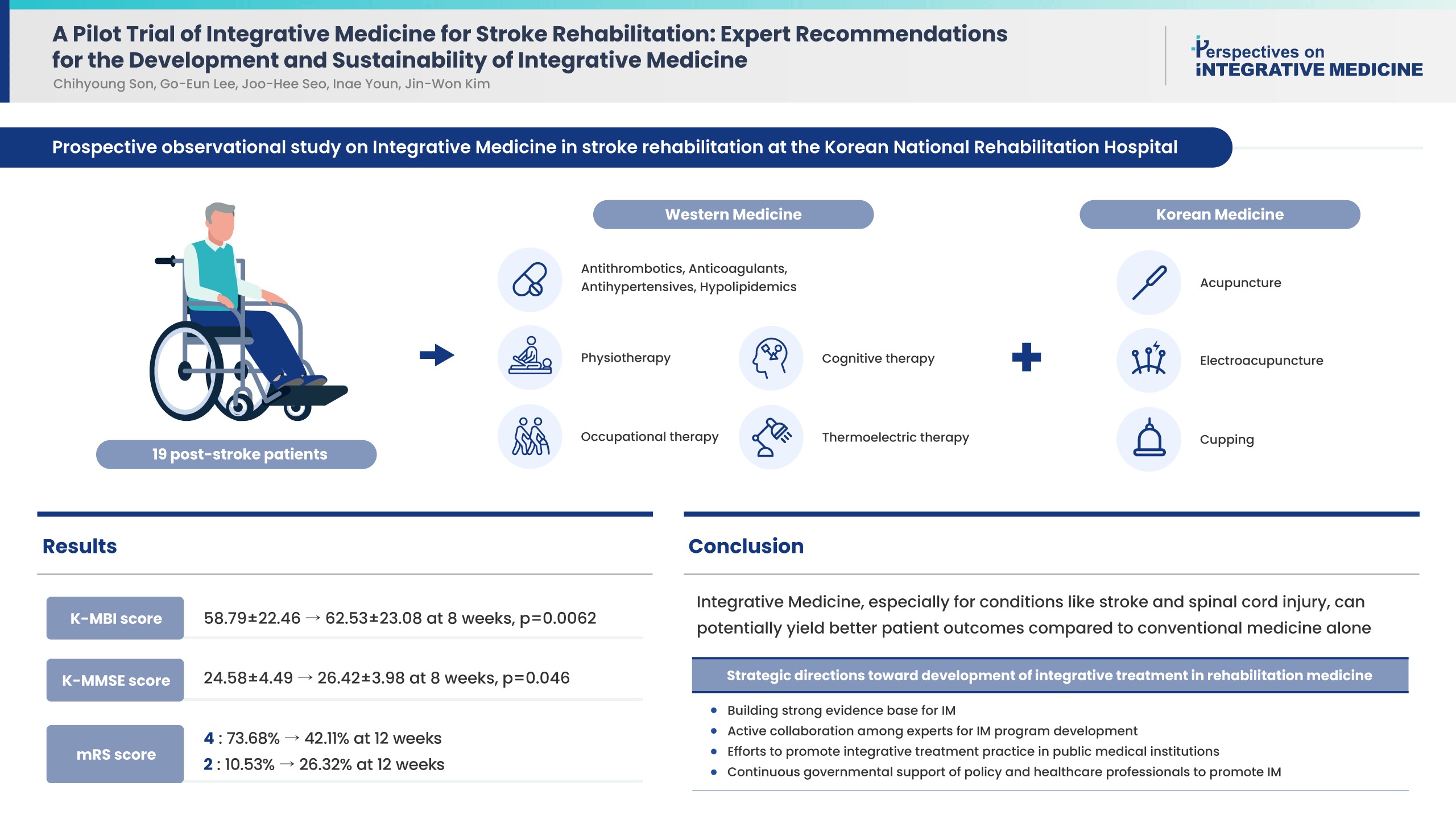
- Background
Strategies towards development and sustainability of integrative treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine are needed. National expert recommendations based on the implementation of Integrative Medicine (IM) in stroke rehabilitation and IM outcomes would be invaluable.
Methods
A pilot study was performed and the effectiveness of combining Korean traditional medicine and Western conventional medicine in post-stroke patients (ischemic stroke n = 15 and hemorrhagic stroke n = 4) was evaluated, and recommendations were developed through consensus with physicians in national centers of rehabilitative medicine. Outcome measures [Korean Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI), Korean Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), Modified Rankin Scale (mRS), and EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L) assessment were used at baseline, 4, 8 (K-MBI, K-MMSE, mRS, and EQ-5D-5L) and 12 weeks post treatment (EQ-5D-5L and mRS).
Results
Improvements were observed in functional and cognitive abilities at 8 weeks (K-MBI score p = 0.0062; K-MMSE score p = 0.046). Quality of life improvements (EQ-5D-5L) were observed but were not statistically significant. The disability assessment (mRS) indicated a gradual improvement from baseline to 12 weeks. No adverse events were reported. For effective, patient-centered IM treatment: (1) build a strong evidence base for IM as compared with Western medicine alone or traditional medicine alone; (2) active expert collaboration; (3) IM promotion in public medical institutions; and (4) continued government support.
Conclusion
Functional and cognitive abilities of stroke patients statistically significantly improved following 8 weeks of IM treatment. Strategies have been suggested towards the development and sustainability of IM treatment in stroke rehabilitation medicine.
Short Communication
- Perspectives and Ideas to Advance Integrative Medicine and Healthcare: Proceedings of the 4th Annual Jaseng Academic Conference
- Andrew Jang, Jinho Lee, Catherine Donahue, David Coggin-Carr, Mike Cummings, Kien Trinh, Myeong Soo Lee, Susan Wieland, Christopher Zaslawski, Lawrence Prokop, Joon Shik Shin
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):190-194. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.007
- 414 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The 4th Annual Jaseng Academic conference (August 13, 2023) in Seoul, South Korea, was a pivotal event in the realm of integrative medicine. Cohosted by Jaseng Hospital of Korean Medicine and Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine, over 500 professionals including Korean medicine doctors, medical doctors, doctors of osteopathic medicine, acupuncturists, researchers, and students gathered at the conference. The theme, “Perspectives on Integrative Medicine,” marked a departure from previous conference themes and embraced a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare. The event highlighted the importance of holistic patient care and cross-disciplinary collaboration within healthcare. It offered a comprehensive overview of the current state of integrative medicine approaches in manual medicine, evidence-based acupuncture treatment, and acupuncture research. The Annual Jaseng Academic conference continues to serve as a platform for healthcare professionals to exchange ideas and perspectives, and bridges the gap between diverse medical systems to promote improved patient outcome and wellbeing.
Editorial
- Strategy for Integration
- Nicola Robinson
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):1-2. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.001
- 672 View
- 25 Download


 First
First Prev
Prev


