Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Editorials
- Strategy for Integration
- Nicola Robinson
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):1-2. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.001
- 767 View
- 25 Download
- Integration of Acupuncture into UK Healthcare - A NICE Perspective: Why is Acupuncture Now Recommended for Chronic Pain but not for Back Pain or Osteoarthritis
- Mike Cummings
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):3-7. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.002
- 2,034 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In April 2021, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) published a guideline on chronic pain (NG193) with a recommendation to consider a single course of acupuncture treatment in patients with chronic primary pain. This positive recommendation came after the NICE guideline on low back pain and sciatica (NG59) announced in November 2016, that acupuncture treatment did not work for back pain, having previously recommended it in 2009 (CG88). This article attempts to explain this apparent contradiction in recommendations by tracing the history of acupuncture debates in the NICE guidelines over the last 2 decades.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
John McDonald, Sandro Graca, Claudia Citkovitz, Lisa Taylor-Swanson
Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine.2023; 29(8): 455. CrossRef
- A Review of Key Research and Engagement in 2022
Review Articles
- Clinical Research on Pharmacopuncture in Korea: A Scoping Review
- Me-riong Kim, Seong Min Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):8-23. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.003
- 2,792 View
- 74 Download
- 10 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- This scoping review was performed as an update on the effects and safety of pharmacopuncture clinical research for the treatment of multiple indications in Korea. Nine electronic databases were searched to identify comparative clinical studies and clinical practice guidelines on Korean pharmacopuncture from inception to December 31, 2022. In vivo and in vitro studies, and case reports were excluded. There were 226 studies identified, including randomized controlled trials, retrospective comparison observational studies, and single-subject crossover designs, of which 17 focused on clinical safety profiles. Most studies pertained to rehabilitation medicine, especially for musculoskeletal (n = 129) and nervous system disorders (n = 35). The evidence supported treatment of neoplasms, obesity, and stroke sequelae. Adverse events of pharmacopuncture were mostly mild and temporary, and occurred more frequently with bee venom compared with herb-derived solutions. Thirty-five clinical practice guidelines including recommendations on pharmacopuncture were included. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first scoping review of clinical pharmacopuncture use in Korea, and our findings support its use in clinical practice and research. Considering the diverse clinical applications of pharmacopuncture, additional pragmatic trials are required to further strengthen the evidence base and develop standard research methodology in Korean medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series
Hee-seung Choi, Yoon Jae Lee, Dae-Hyun Hahm, Hyangsook Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2024; 20(1): 130. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up of inpatients with meniscus tears who received integrative Korean medicine treatment: A retrospective analysis and follow-up survey
June Haeng Lee, Jin Young Song, Kyoung Sun Park, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Yoon Jae Lee
Medicine.2024; 103(6): e36917. CrossRef - Pragmatic randomized controlled trial of pharmacopuncture therapy for adhesive capsulitis: A pilot study
Doori Kim, Kyoung Sun Park, Sun-A Kim, Ji Yeon Seo, Hyun-Woo Cho, Yoon Jae Lee, Changsop Yang, In-Hyuk Ha, Chang-Hyun Han
Integrative Medicine Research.2024; : 101065. CrossRef - Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine Clinics and Hospitals
Ju Yeon Kim, Jung Min Yun, Sook-Hyun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Dong Kun Ko, In Heo, Woo-Chul Shin, Jae-Heung Cho, Byung-Kwan Seo, In-Hyuk Ha
Medicine.2024; 103(14): e37659. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of hominis placental pharmacopuncture for chronic temporomandibular disorder: A multi-center randomized controlled trial
Kyoung Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Koh-Woon Kim, Jae-Heung Cho, Yoon Jae Lee, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2024; 13(2): 101044. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Trends on the Korean Medicine Treatments of Subacromial-Subdeltoid Bursitis
Hyunsuk Park, Dong-Jin Jang, Jonghyun Lee, Sungjae Yoo, Minji Sun, Junsoo Kim, Yongjun Kim, Jeong-Hee Noh, Si-Hyoung Kim, Jung-Min Yun
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2024; 34(2): 85. CrossRef - A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effectiveness and Safety of Pharmacopuncture for Chronic Lower Back Pain
Kyoung Sun Park, Changnyun Kim, Joo Won Kim, Sang‐Don Kim, Jee Young Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Jinho Lee, Min Ji Kim, Young Eun Choi, Changsop Yang, Chang-Hyun Han, In-Hyuk Ha
Journal of Pain Research.2023; Volume 16: 2697. CrossRef - Long-Term Follow-Up of Inpatients with Rotator Cuff Tear Who Received Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis and Questionnaire Survey
Dong-Hwi Yoo, Jae-Yong Choi, Sang-Gun Lee, Ki-Won Choi, Han-Bin Park, Ho Kim, Hyunwoo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Domestic Clinical Research Trends of Shinbaro Pharmacopuncture: Scoping Review
Yeongmin Kim, Yunhee Han, Seungkwan Choi, Jungho Jo, Byeonghyeon Jeon, Hyeonjun Woo, Wonbae Ha, Junghan Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2023; 33(4): 125. CrossRef
- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series
- Proposal of a Case Reporting Draft Guideline for Pharmacopuncture: Literature Review of Pharmacopuncture Case Reports
- Soohyun Jeong, Chaeyeon Son, Hyunjin Kim, Gapsik Yang, Hongmin Chu, Jungtae Leem
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):24-35. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.004
- 1,555 View
- 42 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Pharmacopuncture is a popular treatment that combines the advantages of both herbal medicine and acupuncture. However, pharmacopuncture care reporting guidelines have not yet been developed. This study aimed to propose a reporting guideline draft for pharmacopuncture case reports. Pharmacopuncture case reports were retrieved from 4 databases (KCI, RISS, ScienceON, OASIS) to analyze the items reported and their fidelity. We analyzed 5 existing reporting guidelines related to Korean medicine case reporting to identify the items to be included in the extension of pharmacopuncture reporting guidelines. From 3,684 studies, 29 case reports were included and 4 items were identified as not reported in enough detail: “direction and depth of pharmacopuncture” (89.5%); “method of manufacturing the syringe needle” (82.8%); “posture of the patient during the therapy” (75.9%); and “pharmacopuncture recipe” (69.5%). As a result of analyzing moxibustion and acupuncture clinical trial reporting guidelines, it was determined that detailed reporting guidelines on the type of pharmacopuncture, manufacturing method, and treatment method were required and we propose that a pharmacopuncture reporting guideline draft should include these details. Further investigations are warranted using the Delphi technique to reach agreement with clinical practitioners and clinical research experts.
- Trends in the Development of Sham Acupuncture-Related Technologies Focused on Patents Applied for in South Korea
- Sung Min Lim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):36-41. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.005
- 2,365 View
- 22 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 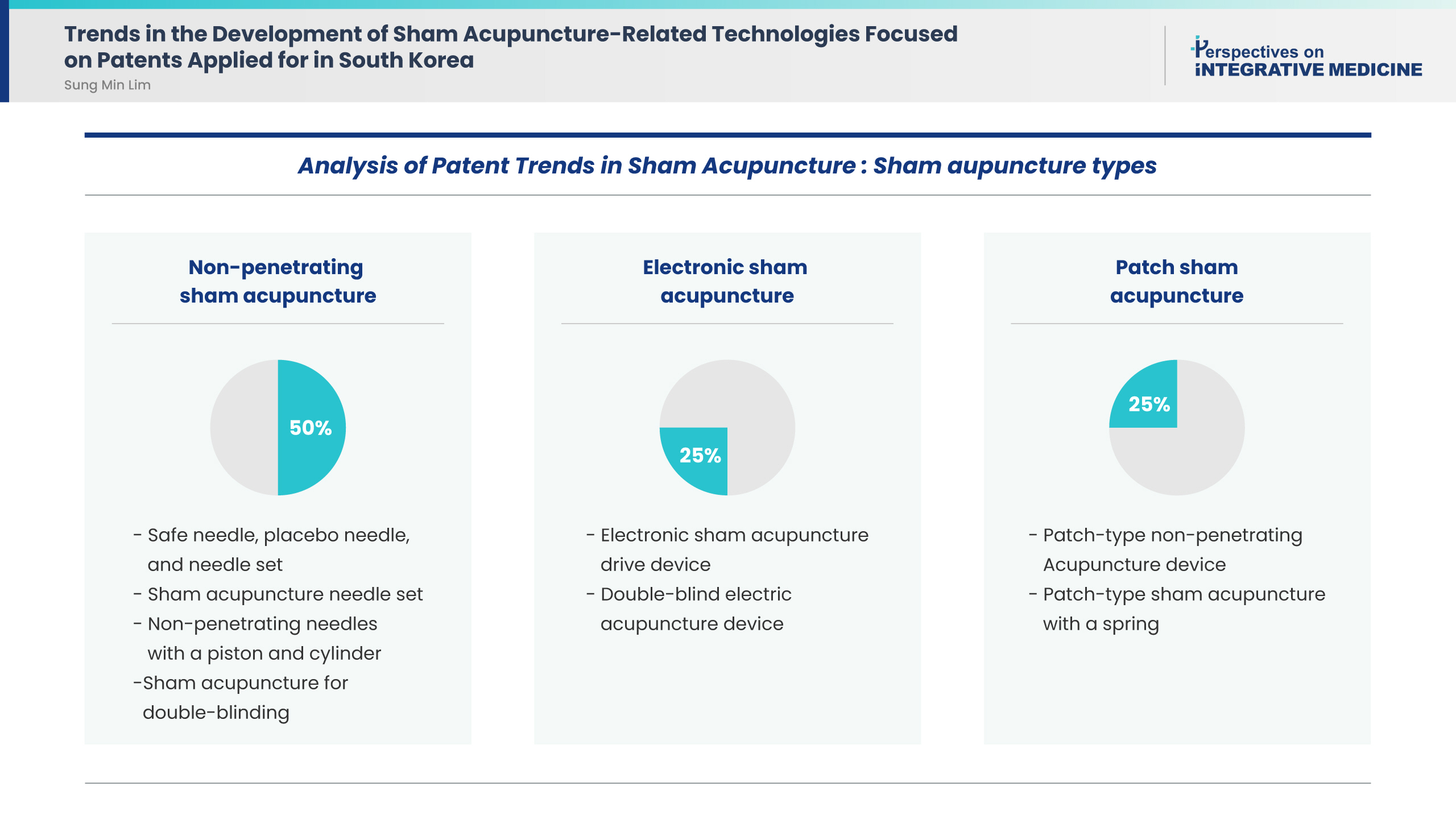
- Background
This study aimed to analyze the trends in Korean patents for sham acupuncture.
Methods
The electronic database of the Korea Intellectual Property Rights Information Service was searched for Korean patents for sham acupuncture from inception till September 2020. Patents, which were not related to sham acupuncture, were excluded. The applicant, application date, International Patent Classification, and technological content of sham acupuncture were analyzed.
Results
This study included eight patents. Application analysis identified the following sham acupuncture types: four (50%), two (25%), and two (25%) patents were for non-penetrating sham acupuncture, electronic sham acupuncture, and patch sham acupuncture, respectively. All patents aimed to use sham acupuncture as a control for rigorous double-blind clinical trials to verify the efficacy of real acupuncture treatment.
Conclusion
The present findings suggest that technological advances were focused on developing various types of sham acupuncture methods for double-blind studies. Further large-scale studies using rigorous designs are needed to investigate new sham acupuncture applications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validation of a New Sham Acupuncture Needle for Double-Blind Trials: A Study Protocol
Sung Min Lim
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine.2024; 3(1): 57. CrossRef - A systematic review of sham acupuncture validation studies
Sung Min Lim, Eunji Go
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in the Development of Acupuncture-Related Technologies Based on Patents in South Korea
Sung Min Lim, Eunji Go, Carmen Mannucci
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medic.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Systematic Review Protocol for Sham Acupuncture Validation Research
Sung Min Lim
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine.2023; 2(2): 131. CrossRef
- Validation of a New Sham Acupuncture Needle for Double-Blind Trials: A Study Protocol
Original Articles
- In Vitro Effect of Herbal Medicines with Thermal Characteristics on Heat Sensitivity in Cancer Cells
- Chae Ryeong Ahn, Sumin Jung, Seeun Kwon, Seung Ho Baek
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):42-48. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.006
- 1,120 View
- 35 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 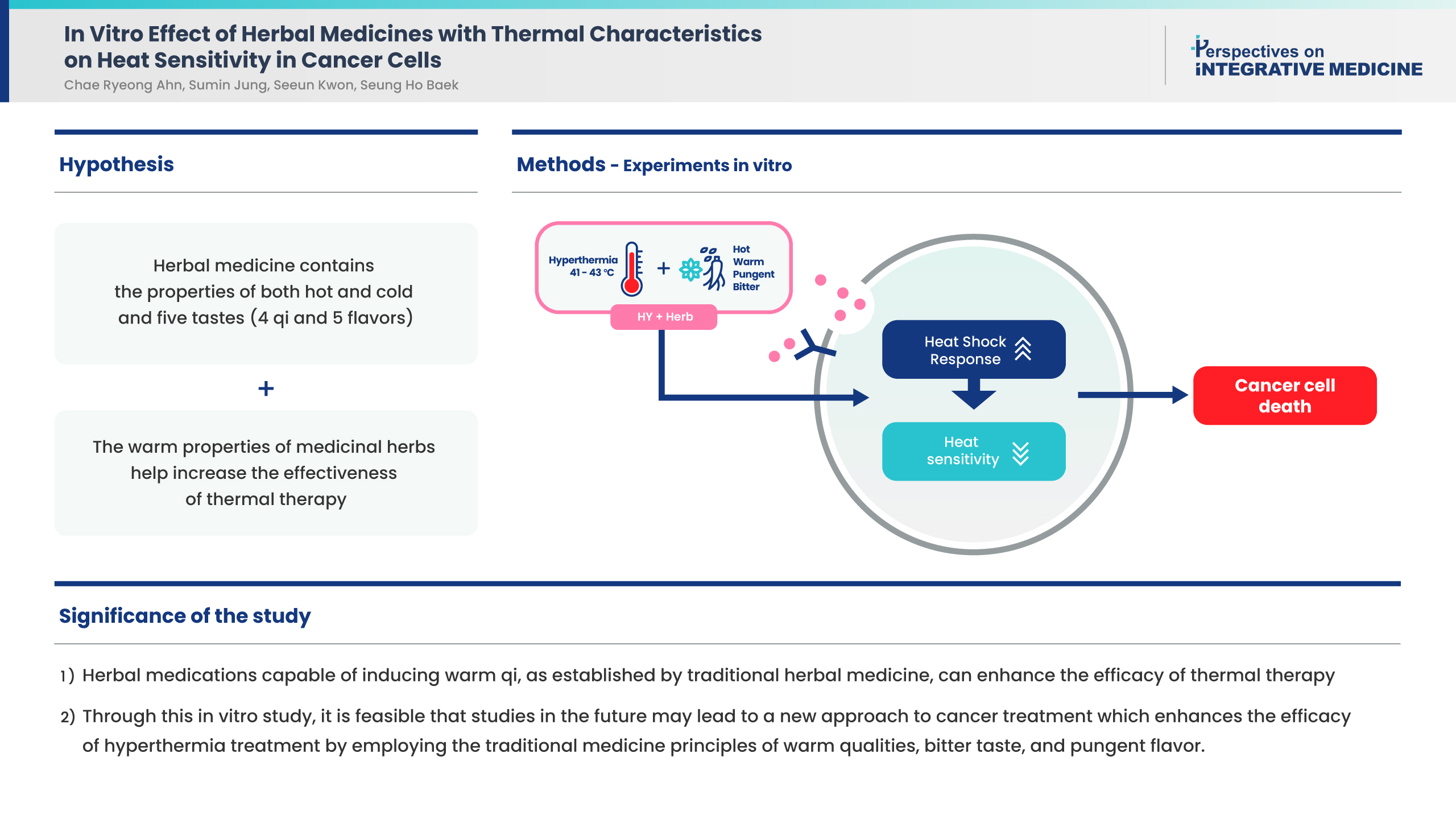
- Background
Cancer remains a major public health threat even though there have been breakthroughs in conventional diagnostics and therapies. Alternatively, treatment with mild hyperthermia and herbal medicine treatment [selected using traditional Korean medicine theory 4 qi (cold, cool, warm and hot) and using the 5 senses of taste (sour, bitter, sweet, pungent and salty)], may be an option to promote cancer cell death in patients where the cancer is accessible.
Methods
To investigate effect of combination treatment of herbal medicines and hyperthermia in vitro on cancer cell lines (ACHN, AGS, A549 and U937), the qualities of 38 medicinal herbs and sensitivity to mild hyperthermia (42 and 43°C) treatment were examined. An assay was performed to detect cell viability and proliferation (MTT) following exposure to medicinal herbs and hyperthermia.
Results
Heat sensitizing herbal medicines were determined to be larger in the warm and hot groups of medicinal herbs (29.6%) than the groups which were neither warm nor hot (18.2%). In addition, the proportion of heat sensitizing effect with bitter and pungent flavors was 33.3 % and 32.1 %, respectively, greater than the average (26.3 %).
Conclusion
In conditions of mild hyperthermia in cancer cell lines, incubation with herbal medicines caused cancer cell death in vitro. These results suggest that the use of traditional herbal medicines with warm, hot, pungent and bitter characteristics may be a useful treatment for cancer using conditions to induce mild hyperthermia and this requires further investigation.
- An Observational Study on the Anatomical Characteristics of Acupoint CV23 (Lianquan) with Ultrasonography
- Hongmin Chu, Seongjun Park, Jaehyo Kim, Wonbae Ha, Seung Bum Yang, Kyungho Kang, Jongho Kim, Jungtae Leem, Sanghun Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):49-55. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.007
- 1,461 View
- 37 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 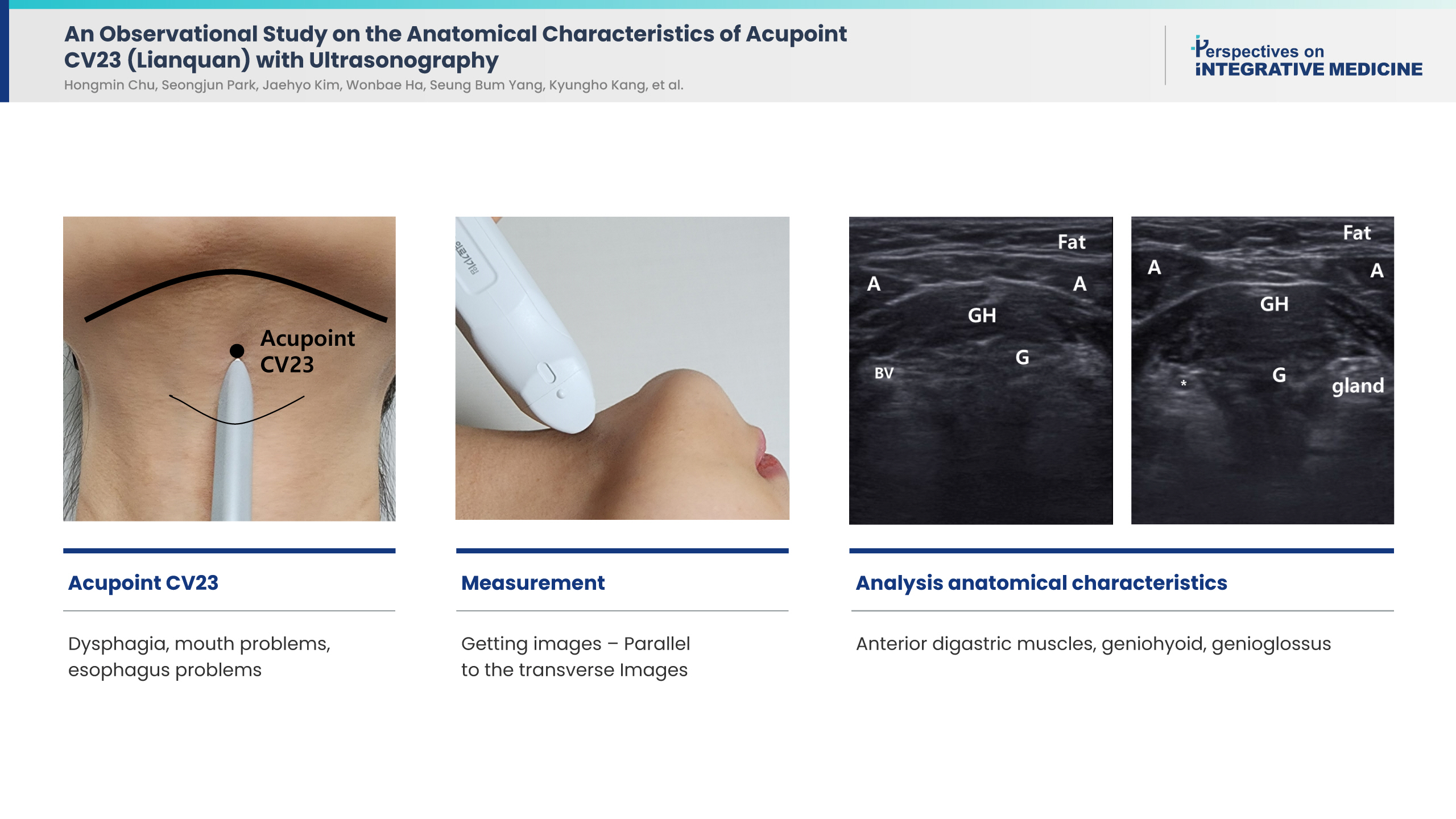
- Background
Acupoint CV23 is one of the most commonly used acupoints for the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia and tongue pain. However, care must be taken during the procedure to consider the position of glands and blood vessels in the subcutaneous space of the acupoint. Needling depths to the geniohyoid muscle reportedly range from 0.4 to 3.3 cm. Using ultrasound imaging, we aimed to observe the anatomical characteristics around acupoint CV23 to derive a safe needling depth.
Methods
Ultrasound images of acupoint CV23 accessed from the Standard Ultrasound Image of Acupoint database were retrospectively analyzed for 30 participants aged in their 20s and 30s (15 male, 15 female), and the depth from the skin to the geniohyoid muscle was measured. Correlations between the needling depth and anthropometric factors (such as neck circumference) were analyzed.
Results
The average needling depth to the geniohyoid muscle was 1.59 ± 0.49 cm (male; 1.43 ± 0.52 cm, female, 1.75 ± 0.42 cm, p = 0.03). The geniohyoid muscle, anterior digastric muscles, and genioglossus muscle were observed in the subcutaneous area of acupoint CV23, and a risk of sublingual gland damage needs to be considered for oblique insertion of the acupuncture needle. No statistically significant correlations between the needling depth and anthropometric factors were observed.
Conclusion
Acupoint CV23 has a relatively shallow needling depth, and considering the presence of blood vessels and glands in the sublingual space, visualizing the surrounding anatomical structures using ultrasound was helpful to ensure safe needling practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine Clinics and Hospitals
Ju Yeon Kim, Jung Min Yun, Sook-Hyun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Dong Kun Ko, In Heo, Woo-Chul Shin, Jae-Heung Cho, Byung-Kwan Seo, In-Hyuk Ha
Medicine.2024; 103(14): e37659. CrossRef
- Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine Clinics and Hospitals
Protocols
- A Protocol for the Overview of Systematic Reviews of Aromatherapy for Management of Health
- Ki Jung Kil, Myeong Soo Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):56-58. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.008
- 1,067 View
- 36 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Aromatherapy has been reported to have a positive effect on various health conditions. While these studies show positive results, many of them have limited evidence. The aim of this study was to develop a protocol to evaluate all systematic reviews (SRs) that have evaluated the efficacy of aromatherapy (for any health condition) as a therapeutic treatment (protocol registration number INPLASY202280089).
Methods
We will include aromatherapy through different therapeutic application methods such as inhalation, massage, and bathing. Seven international databases (including PubMed, AMED, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library), and three Korean medical databases (Korean Studies Information, Research Information Service System, KoreaMed), will be searched. The SR process, including study selection, data extraction, and assessment, will be performed by two independent reviewers. Methodological assessment will be performed using AMSTAR-2.
Discussion
The benefits of aromatherapy for health management are evaluated to provide useful information to patients and therapists and inform decisions on further studies on this topic.
- A Study Protocol for a Multicenter, Pragmatic, Randomized Controlled, Parallel-Grouped Pilot Clinical Trial: Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Versus Pharmacological Treatments for Non-Acute Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Hui Yan Zhao, Purumea Jun, Chaewon Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Chang-Hyun Han
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(1):59-64. Published online February 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.009
- 765 View
- 25 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 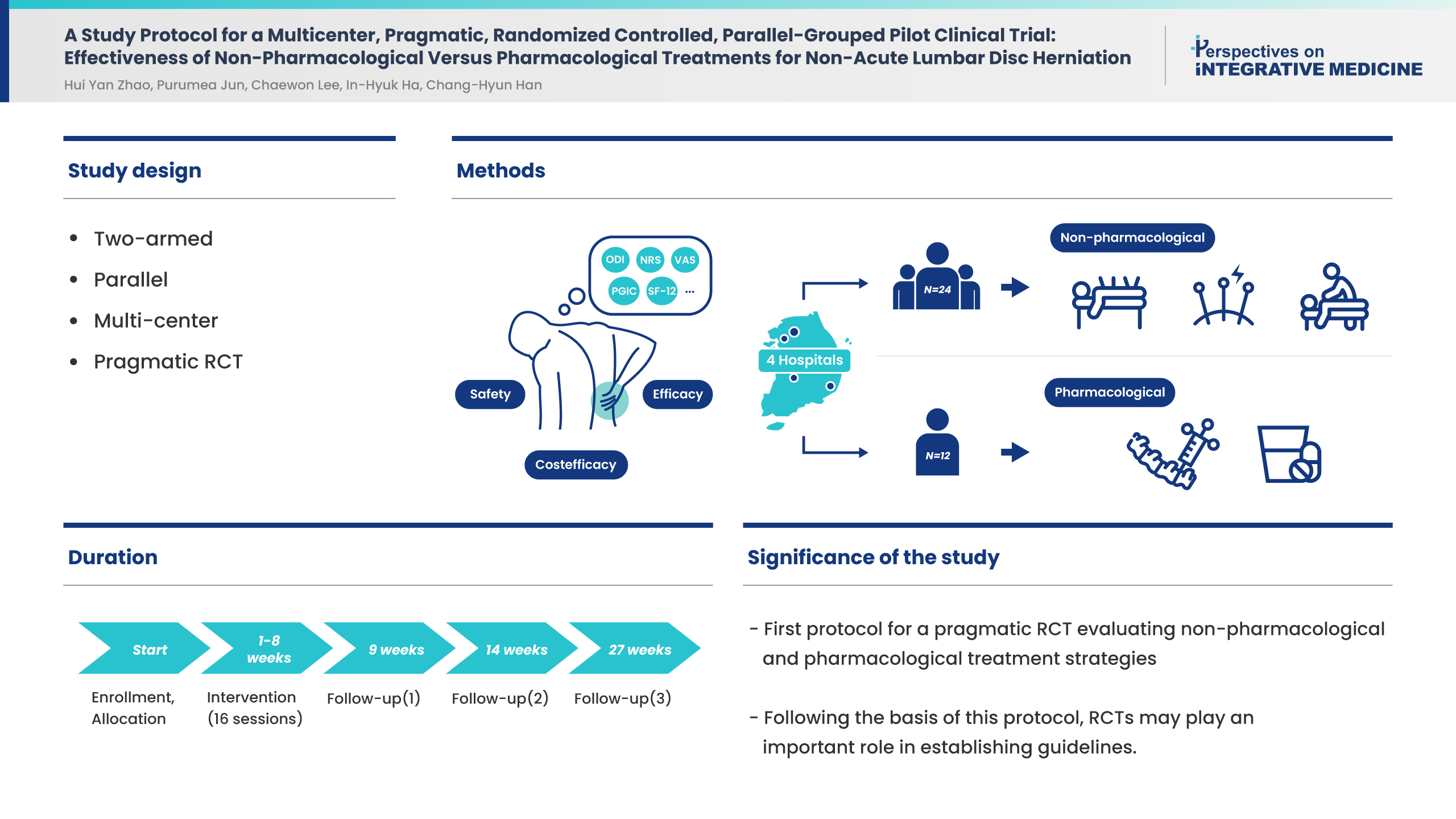
- Background
This study was the development of a protocol for the comparison between the efficacy of non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment approaches for lumbar disc herniation in a pragmatic environment to obtain real-world based study data.
Methods
The protocol sets out a two-armed, parallel, multicenter pragmatic, randomized-controlled trial (RCT) which will be conducted in four spine specialist hospitals in Korea to determine cost-efficiency.
Results
The study will enroll 36 participants and allocate patients into either the non-pharmacological treatment group or the pharmacological treatment group in a 1:2 ratio. Patients must have evidence of disc-related disease diagnosed using MRI, as well as having lower back pain or radiating leg pain (numeric rating scale score ≥ 5). The treatment will last for 8 weeks with a 26-week follow-up. The primary outcome will be measured using the Oswestry Disability Index score from Week 9. Secondary outcomes related to lower back pain and radiating leg pain will be measured using the scores from the numeric rating scale, the visual analogue scale, the European Quality of Life 5 Dimensions 5 Level Version), the 12-item Short Form Survey, and the patient global impression of change.
Conclusion
This is the first protocol for a pragmatic RCT evaluating the efficacy, safety, and cost-efficiency of non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatment strategies in a clinical setting. Following the basis of this protocol, RCTs may play an important role in establishing guidelines for treating radiating leg pain and lower back pain and provide effective information to clinicians in practical settings.





 First
First Prev
Prev


