Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Perspect Integr Med > Volume 2(1); 2023 > Article
-
Review Article
Clinical Research on Pharmacopuncture in Korea: A Scoping Review -
Me-riong Kim1
 , Seong Min Lee1
, Seong Min Lee1 , Yoon Jae Lee1
, Yoon Jae Lee1 , In-Hyuk Ha2,*
, In-Hyuk Ha2,*
-
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine 2023;2(1):8-23.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.02.003
Published online: February 21, 2023
1Jaseng Hospital of Korean Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2Jaseng Spine and Joint Research Institute, Jaseng Medical Foundation, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- *Corresponding author: In-Hyuk Ha, Jaseng Spine and Joint Research Institute, Jaseng Medical Foundation, 2F Vision Tower, 540 Gangnam-daero, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea, E-mail: hanihata@gmail.com
©2023 Jaseng Medical Foundation
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
- 2,791 Views
- 74 Download
- 10 Crossref
Abstract
- This scoping review was performed as an update on the effects and safety of pharmacopuncture clinical research for the treatment of multiple indications in Korea. Nine electronic databases were searched to identify comparative clinical studies and clinical practice guidelines on Korean pharmacopuncture from inception to December 31, 2022. In vivo and in vitro studies, and case reports were excluded. There were 226 studies identified, including randomized controlled trials, retrospective comparison observational studies, and single-subject crossover designs, of which 17 focused on clinical safety profiles. Most studies pertained to rehabilitation medicine, especially for musculoskeletal (n = 129) and nervous system disorders (n = 35). The evidence supported treatment of neoplasms, obesity, and stroke sequelae. Adverse events of pharmacopuncture were mostly mild and temporary, and occurred more frequently with bee venom compared with herb-derived solutions. Thirty-five clinical practice guidelines including recommendations on pharmacopuncture were included. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first scoping review of clinical pharmacopuncture use in Korea, and our findings support its use in clinical practice and research. Considering the diverse clinical applications of pharmacopuncture, additional pragmatic trials are required to further strengthen the evidence base and develop standard research methodology in Korean medicine.
- Pharmacopuncture is a Korean medicine treatment that uses natural products or herbal medicines which are injected at various acupuncture points. Many variations of pharmacopuncture are used across Korea and China. The first records of the use of bee venom (BV), and herbal medicine extraction can be traced back to medical literature from the Han Dynasty. Pharmacopuncture, generally referred to as “aqua-puncture” or “acupoint injection” in China, started in the early 1950s [1,2]. In Korea, the first full-scale study on pharmacopuncture was performed by Nam Sang-Chun who introduced it to the Society of Korean Medicine in the 1960s. Subsequently, he published “Meridian Injection Treatment” in the Korean Pharmaceutical Industry News in 1965, and “Meridian” Volume 1 in 1967 [3]. Pharmacopuncture is thought to have been in use in Korea in the early 20th century, based on a report in the Kwonup newspaper in 1914 [4].
- Pharmacopuncture aims to maximize the treatment effects of acupuncture by delivering (injecting, inserting, or embedding) pharmacopuncture solution (extracted, purified, diluted, mixed, separated, proliferated, or fused) from natural/herbal medicines into meridians and acupoints. Using solution injection syringes or coated needles, pharmacopuncture solution is administered at various acupuncture points (including Ashi points, meridians (including cutaneous and muscle), lesion sites, or positive reaction points). This is based on meridian theory and disease, and acupuncture points may interchangeably correspond to tender points, trigger points (TPs), ligament and tendon insertions, bursae, intra-articular spaces, intra-cavities, blood vessels, and neoplasms [4,5]. These pharmacopuncture treatment techniques and solutions have been developed using a wide range of active materials and delivery devices. The techniques are being continually developed to further enhance the effectiveness and safety of pharmacopuncture as new drug delivery applications based on traditional Korean medicine theories. Pharmacopuncture treatment methods combine acupuncture based on meridian theories with natural/herbal medicine based on Qi and flavor theories [4–6].
- Regarding the history of and regulations governing pharmacopuncture use in Korea, legal provisions were largely initiated alongside the establishment of the Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute in 1990. Thereafter, since 1995, pharmacopuncture has been included in the educational course curriculum of Korean medicine colleges. In June 1998, pharmacopuncture was recognized as a Korean medicine treatment intervention by the Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare (MoHW) through authentic interpretation. In January 2001, pharmacopuncture was fully covered by the Korean National Health Insurance (NHI); however, since January 2006, it became a non-payment item under the NHI. It remains a non-payment item under the NHI, and all costs for pharmacopuncture are paid out-of-pocket. However, automobile insurance covers pharmacopuncture under the governance of the Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, with separate provisions for pharmacopuncture according to Article 5 (Range of approved medical treatment consultation charges), Section 2, Subdivision 2. Meanwhile, the MoHW has started the process of authorization of designated facilities as “external herbal dispensary pharmacopuncture preparation facilities” in 2019 [5,7].
- In Korea, patients have access to oral (e.g., decoction, pill, powder) or injectable (i.e., pharmacopuncture) herbal medicine solutions from Korean medicine institutions in the following forms as a prescribed medication by a Korean medicine doctor: (1) manufactured by a pharmaceutical company and authorized by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety; or (2) in the form of herbal medicine ingredients prepared internally, at a Korean medicine institution, or externally, through a contract with an external herbal dispensary [8,9]. The MoHW allowed the establishment of external herbal dispensaries in 2008 [10], and Korean medicine institutions are regulated in the use of herbs manufactured by “herb-good manufacture practice facilities” which are licensed by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety [11]. The amount of hazardous substances (e.g., heavy metals, pesticides, sulfur dioxide, aflatoxins, and benzopyrene) in herbs is governed by the Regulations on Limits and Test Methods for Residues and Contaminants in Herbal Medicines [12].
- The accreditation and certification criteria for external herbal dispensaries are assessed by the MoHW using the following 9 categories: (1) facilities; (2) clean area management; (3) business and organization operation; (4) employee management; (5) documentation; (6) quality control; (7) herbal material storage; (8) preparation; and (9) packaging [7]. The criteria for accreditation and certification were discussed by herbal medicine, Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, Korea Good Manufacturing Practice (KGMP), and accreditation specialists, and set through on-site opinion collection of administrators of the external facilities, policy research and public hearings. Deliberation was conducted and a resolution was reached by the External Herbal Dispensary Evaluation and Certification Committee [7]. Despite the consistency of the aforementioned 9 criteria across all herbal medicine and pharmacopuncture preparation facilities, the number of items for pharmacopuncture preparation facilities is greater than herbal medicine preparation facilities (165 vs. 81), reflecting KGMP, and KGMP and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points standards, respectively [13]. Currently, external herbal dispensaries accredited for the production of pharmacopuncture preparations by the MoHW include Nam Sang-Chun Korean Medicine Clinic external herbal dispensary, and the herbal dispensary of Jaseng Hospital of Korean Medicine [5,7].
- Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) are systematically developed statements intended to inform decisions made by healthcare providers, policymakers, and patients to improve the quality of care and patient safety practices. Development of CPGs in traditional medicine is currently being conducted in China, Japan, and Korea. In Korea, the National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency and the Korean Medical Guideline Information Center are the main organizations that are active in the development and dissemination of evidence-based CPGs. Furthermore, the Korean Medicine Leading Technology R&D project was initiated in 2008 by the Korean MoHW. Thereafter, CPGs on Hwabyung (Korean somatization disorder) and musculoskeletal diseases were published in 2013. The Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine and the Association of Korean Medicine further collaborated to establish methodologies for the development of Korean medicine CPGs in 2015, and the Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guidelines Development Project Group selected and developed CPGs for 30 diseases. Further, they implemented clinical research to strengthen the clinical evidence of Korean medicine treatments (2016–2022). This work is being continued through the Korean Medicine Innovative Technologies Development Project (2020–2029) to further improve the quality of Korean medicine services, increase coverage through standardization and scientific validation covering de novo CPG development and updates, and implement clinical research for the development of Korean medicine clinical technology, identification of herbal medicine and drug interactions, and execution of translational research [14].
- Regarding the use of pharmacopuncture in Korea, a 2016 study conducted in 12 Korean medicine medical institutions reported that among 33,145 in-patients and 373,755 out-patients, 32,947 (98.6%) and 289,860 (77.6%) were treated with pharmacopuncture, respectively [15]. A large-scale retrospective study conducted on 80,523 patients with musculoskeletal diseases revealed that the number of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs were low despite its prevalent use. Further, among 5,966 in-patients and 74,557 out-patients, the number of pharmacopuncture treatment sessions was 23.0 ± 15.6 times for in-patients and 7.8 ± 11.5 times for out-patients. Moreover, the number of BV pharmacopuncture treatment sessions was 15.4 ± 11.3 times for in-patients and 10.0 ± 12.3 times for out-patients [16]. A study conducted on car accident patients who visited Korean medicine medical institutions in 2014 reported that 1,550,000 pharmacopuncture treatment sessions were administered to 168,089 patients [17]. Furthermore, the analysis of 5,510,000 car insurance claims filed in 2014 revealed that a total of 1,410,500 claims included pharmacopuncture as an intervention, which constituted 25.7% of the total claims, and amounted to 12.8 billion Korean Won [18]. While research and clinical use of pharmacopuncture is prominent in Korea and China, its clinical use has also been approved in 8 states of the US [5].
- Regulations, indications, and use of pharmacopuncture differ across countries, but are diverse and time-dependent even within Korea. To understand the effects and harms related to the use of pharmacopuncture in Korea, we searched the published literature and CPGs in this scoping review to further expand on a systematic review (SR) published previously [19], and to update the effectiveness, safety profile, and evidence-based use of pharmacopuncture.
Introduction
- 1. Research questions
- The primary research question for this scoping review was regarding the use of pharmacopuncture in Korean medicine, which evolved into a more structured and detailed format as follows:
The types of clinical research conducted on pharmaco-puncture.
The main indications for pharmacopuncture.
Predominant types of pharmacopuncture.
The clinical effects and safety profile of pharmacopuncture.
- 2. Data sources and searches
- PubMed (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online [MEDLINE]), Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), Cochrane Library, Korean studies Information Service System (KISS), Korean Medical Database (KMbase), Oriental Medicine Advanced Searching Integrated System (OASIS), Research Information Sharing Service (RISS), and ScienceON were searched for comparative clinical studies on the effects or safety of Korean pharmacopuncture use from inception to December 31, 2022.
- The National Clearinghouse for Korean Medicine (https://nikom.or.kr/engnckm) for CPGs published from 2015 to December 31, 2022 including recommendations on the use of Korean pharmacopuncture was searched.
- Studies that were conducted in Korea and published in either English or Korean were included. Moreover, references cited in the articles were examined for additional relevant studies. Keywords and MeSH terms referring to pharmacopuncture were employed. In vivo, in vitro studies, veterinary research, study protocols, and case reports were excluded.
- 3. Study selection
- All comparative clinical studies that evaluated pharmacopuncture treatment for various conditions were included. This covered thread embedding acupuncture (TEA) and intravenous injections, prospective and retrospective studies, and single-subject crossover study designs. Studies that included healthy participants (to study effectiveness or safety) were also eligible. Each disorder or disease, with the exception of studies on healthy individuals, was categorized for analysis according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision [20]. Studies assessing the combined effects or the safety of pharmacopuncture with other interventions (e.g., pharmacopuncture plus acupuncture) were also considered (if identical interventions were administered to the intervention and control groups, or when the study determined the effects or safety of pharmacopuncture as a combined or sole intervention).
- Under the purview of a scoping review, this study aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the comparative clinical studies on pharmacopuncture conducted in Korea. Additionally, non-randomized controlled trials (non-RCTs), retrospective comparison studies, and quasi-RCTs (where the method of allocating participants to groups is not truly random, e.g., hospital record number or alternating allocation of consecutive patients) were also included.
- In vivo studies, in vitro studies, literature reviews, survey studies, case reports, study protocols, single arm observational studies, and case series studies were excluded from this review. Studies where pharmacopuncture was not the main intervention (i.e., used only as part of a regimen administered identically to the intervention and treatment groups) were excluded.
- 4. Data extraction
- All the retrieved articles were reviewed to evaluate eligibility for inclusion in this review. The following data were extracted from the selected studies: author(s), year of publication, study design, study population (sample size, age, sex), condition and symptoms, symptom duration, interventions and controls including concurrent treatments, outcome measures, main results regarding the effect of treatment, AEs, length of treatment, frequency, doses, and follow-up period, if applicable. The format and outcomes of this study are an extension of the results of a previously published (2016) SR and meta-analysis of RCTs on pharmacopuncture in Korea [19].
- 5. Data analyses
- Between-group comparisons were based on the results of the original study and assigned to 1 of 4 categories in order to classify the results for interpretation. The categories are as follows: (1) positive, when the results of the intervention group were statistically significantly better than that of the control group; (2) negative, when the results of the control group were statistically significantly better than the intervention group; (3) neutral, when there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups, i.e., no significant difference between groups (NS); and (4) not applicable (NA), when the results were not relevant to the effectiveness, not quantifiable, or not quantified.
Material and Methods
3.1. Inclusion criteria
3.2. Exclusion criteria
- 1. Research articles
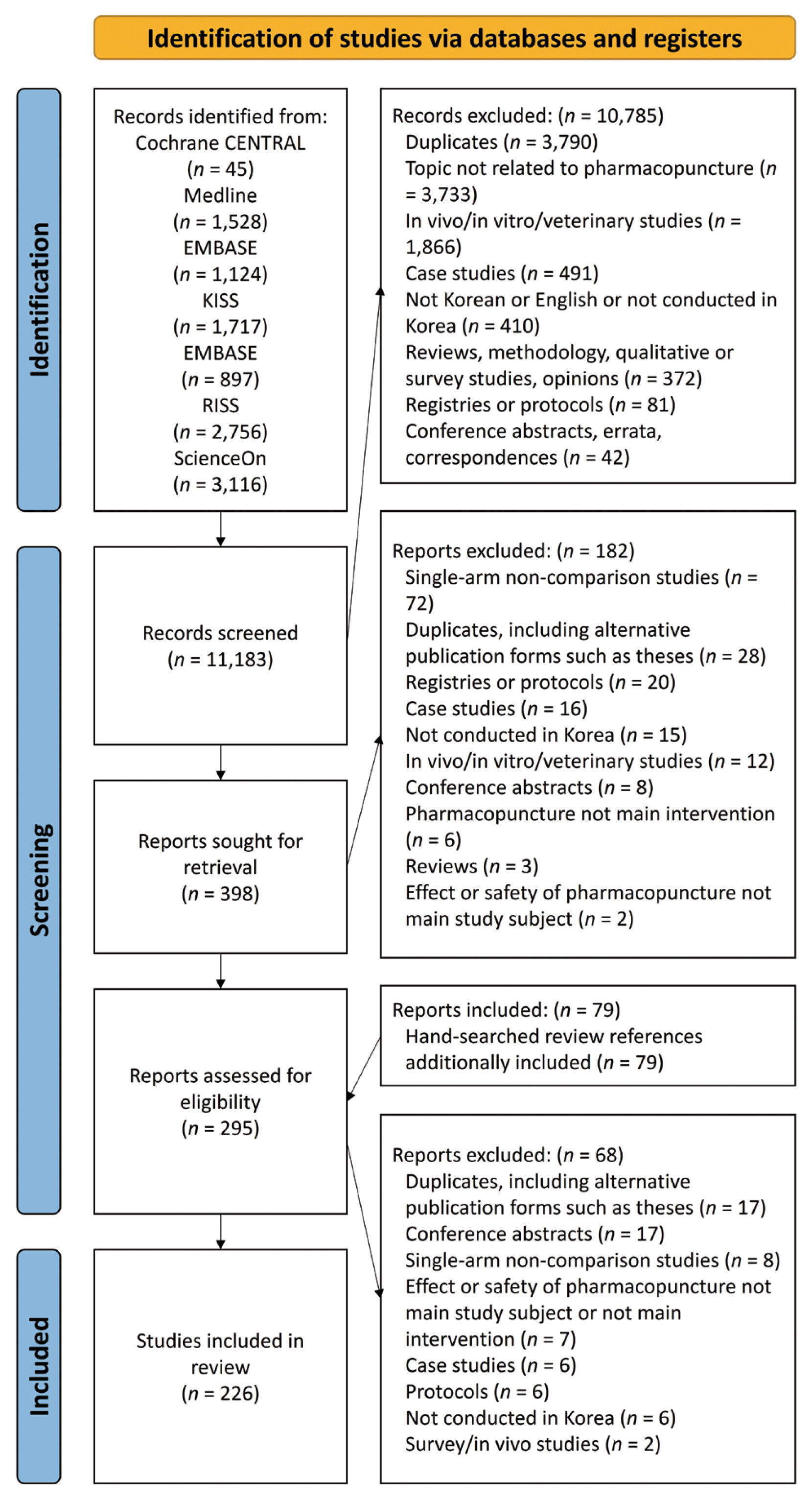
- Two hundred and twenty-six studies that employed various research methodologies were included in this review. The studies comprised of 132 RCTs, 30 retrospective comparison observational studies, 55 non-randomized trials, and 7 single-subject crossover designs (Fig. 1, Supplementary Table 1). The studies which were conducted prospectively were mostly parallel-group (n = 189) compared with crossover studies (n = 7) which were mostly 2-armed studies (n = 159), including RCTs (n = 108), non- or quasi-randomized studies (n = 49), and 2 non-equivalent design studies. However, several RCTs did not adequately report the randomization process, and were categorized as non-randomized studies or quasi-RCTs if the relevant study methodology was specified.
- Regarding the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th revision codes, clinical studies were conducted in patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (n = 129); diseases of the nervous systems (n = 35); endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases (n = 8); diseases of the genitourinary system (n = 5); neoplasms (n = 3); diseases of the digestive system (n = 2); diseases of the circulatory system (n = 2); diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (n = 2); and pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium (n = 1), in descending order. Several studies on healthy participants (n = 39) were also reported.
- The types of natural/herbal solutions most frequently used for pharmacopuncture interventions (including the intervention and control groups) were BV (n = 144), including combined use with other pharmacopuncture types, acupuncture or herbal medicine (n = 83), sweet BV (n = 24), skin tests (n = 5), and essential BV (n = 2); Hominis Placenta (n = 22); Hwangryunhaedok-tang (n = 21, including one study where it was mixed for dilution, and three studies which used it in combination with other types of pharmacopuncture such as Shinbaro or BV); Jungsongouhyul (n = 19); wild Ginseng (n = 17, including one arm where it was used as part of a complex pharmacopuncture intervention); Carthami Flos/Semen (n = 17); TEA (n = 16); Cervi Pantotrichum Cornu (n = 11, including two studies where it was used as a complex pharmacopuncture intervention); Soyeom (n = 11); Shinbaro (n = 9); Calculus Bovis · Fel Ursi (n = 9, including two studies where it was used as a complex pharmacopuncture solution); Calculus Bovis · Fel Ursi · Moschus (n = 7, including 2 arms where it was used as a complex pharmacopuncture intervention); Rehmannia glutinosa (n = 6); Scolopendrid (n = 5); and Dioscoreae Rhizoma (n = 4), in descending order. Supplementary Table 2 lists the raw ingredients of pharmacopuncture solution prescriptions included in the studies.
- The included studies primarily used (1) a placebo as a comparative group (n = 67) including normal saline pharmacopuncture (NSP; n = 38), distilled water (n = 1), or sham TEA alone (n = 4), or NSP with other active treatments including usual care as administered in all groups (n = 22), with 2 arms using both NSP and sham acupuncture. Alternatively, other studies employed various Korean medicine treatments; (2) acupuncture, electroacupuncture or auricular acupuncture (n = 27); (3) Chuna (n = 6); (4) herbal medicine (n = 1); (5) cupping (n = 1); (6) physical therapy (n = 2); (7) different pharmacopuncture solutions using various ingredients (n = 59); (8) varying preparations (e.g., solvent, cultivated vs. natural), application methods (e.g., guided vs. blind, injection depth, region, amount or concentrations), or results (i.e., response to BV skin test) from the same ingredients (n = 47); (9) usual care as administered in all groups (n = 56); (10) other conventional interventions (n = 3); or (11) single treatment (e.g., acupuncture, NSAIDs) administered in all groups (n = 12) as an active control or additional intervention group; or (12) no treatment (n = 5). Each comparative arm was tallied individually (total n = 284, allowing for 2 duplicates). Of the 116 study arms, 1 or more of the treatment comparators (2) – (11) were applied as a common treatment which were administered to all the groups.
- The most frequently used meridian and acupuncture points were the Bladder meridian and GB21 and GB20, respectively. While Korean medicine CPGs often referred to meridians collectively as needling points, the research articles almost exclusively cited specific acupoints or anatomical structure targets, and those most frequently used for pharmacopuncture treatment were: GB21 (n = 51), GB20 (n = 34), Ashi points (n = 29), ST36 (n = 28), BL23 (n = 27), GB34 (n = 22), and BL25 (n = 22), in descending order.
- Eighty-four studies included safety outcomes, and seventeen of the examined studies focused on clinical safety profiles. AEs are summarized and classified according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events scale [21], outcomes, and allergic reactions according to Mueller [22], and treatment decision after an AE to BVP (Supplementary Table 3). AEs associated with pharmacopuncture were mostly mild and temporary, and occurred more frequently with BV compared with herb-derived pharmacopuncture solutions.
- 2. CPGs
- Out of the 41 Korean medicine CPGs that have been published since 2015, the 35 Korean medicine CPGs that include recommendations regarding pharmacopuncture are summarized in Table 1 [23–57] and Supplementary Tables 4 and 5.
- Recommendation grades were moderate (n = 24), low (n = 44), or very low (n = 15), with 2 recommendations based on Good Practice Point / Classical Text-based, and 1 recommendation was inconclusive.
- The most frequently studied pharmacopuncture natural/herbal solutions were TEA (n = 29) and BV (n = 21); followed by Hominis Placenta (n = 9); Astragali Radix (n = 6, including a mixed formula with Salviae miltiorrhizae Radix); Carthami Flos (n = 5); Hwangryunhaedok-tang (n = 4, including combined use with Fel Ursi in Regulating Ascending Kidney Water and Descending Heart Fire pharmacopuncture); Salviae miltiorrhiza Radix (n = 4, including 2 mixed formulae with Astragali Radix, and Dalbergiae odoriferae Lignum); Dalbergiae odoriferae Lignum (n = 3, including 1 mixed formula as stated above); and Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma (n = 3).
- Pharmacopuncture use was evaluated for integrative (n = 11, including 1 duplicate), add-on (n = 37, including 1 duplicate), and sole use (n = 26) recommendations. The operational definition of “integrative” was when the Korean medicine treatment was added to the conventional treatment, and the definition of “add-on” was when a Korean medicine treatment was added to a different Korean medicine treatment to enhance treatment effects or safety.
- The most frequently used meridian and acupuncture points were the Bladder meridian and SP6 and ST36, respectively. The meridians and collective acupoints assessed in the studies included: Bladder meridian or points (n = 45), Stomach meridian points (n = 34), Spleen meridian points (n = 29), Extra points (n = 27), Gallbladder meridian or points (n = 26), Conception Vessel points (n = 23), Governor Vessel points (n = 18), Ashi points (n = 14), Small Intestine meridian points (n = 12), Triple Energizer meridian points (n = 10), Large Intestine meridian points (n = 10), Baesu points (n = 4), Liver meridian points (n = 2), Kidney meridian points (n = 2), Pericardium meridian points (n = 2), and Bogmo points (n = 1), in descending order. Single acupoints used, in descending order were; SP6 (n = 14), ST36 (n = 14), BL23 (n = 10), and CV4 (n = 8).
Results
1.1. Study designs
1.2. Participants
1.3. Pharmacopuncture interventions
1.4. Comparators
1.5. Acupuncture points and meridians
1.6. Adverse events
2.1. Recommendation grades
2.2. Interventions
2.3. Concomitant treatments
2.4. Acupuncture points and meridians
- Pharmacopuncture has a documented historical medical use for the treatment of a diverse array of medical conditions. The majority of the clinical trials published in the current scientific literature address the indications and effects of pharmacopuncture for musculoskeletal disorder pain. This highlights the major aspects of the current clinical application of pharmacopuncture.
- Recently, pharmacopuncture has also been indicated for management of pain caused by nerve entrapment [5]. In addition to pain, pharmacopuncture is used to treat internal disorders of the digestive system (e.g., indigestion, gastroesophageal reflux, diarrhea, enteritis, and constipation); circulatory disorders (e.g., palpitation, and chest pain); liver diseases (e.g., hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and fatty liver); respiratory diseases and disorders (e.g., cough, asthma, and common colds); gynecological diseases and disorders (e.g., dysmenorrhea, climacteric syndrome and postmenopausal syndrome, and infertility); and genitourinary diseases, including prostate diseases [5]. In addition, pharmacopuncture is also used to treat Hwabyung (Korean somatization disorder), stress, and anxiety [5]. According to in vitro experiments and clinical trials conducted at Gachon University Hospital, wild Ginseng pharmacopuncture is being widely implemented to manage regional obesity [5]. Recently, pharmacopuncture is finding use in the therapeutic management of cancer, Parkinson’s disease, and rheumatoid arthritis [5].
- In this scoping review, we identified 226 published comparative studies pertaining to clinical effectiveness or safety, and the majority of the studies were controlled trials, with a few single-subject crossover study designs. Although beyond the scope of this study, uncontrolled studies provided the earliest and most clinically-oriented evidence on pharmacopuncture. The extensive range and number of relevant case reports and case series highlighted that pharmacopuncture has been used and studied for an increasing set of clinical indications. However, this study is limited in that many of the included studies did not report the randomization process in detail and therefore, the research methodology was categorized exclusively based on the information made available in the articles. Moreover, while the research articles included in this study were primarily Korean articles pertaining to pharmacopuncture use, effectiveness, and safety in Korea, the CPGs were broader and more comprehensive in their scope and included case reports and studies from China (Fig. 2). As the inclusion criteria (e.g., country, study design) differ among guidelines and research articles, and the regulations, indications, and uses differ across countries, and these results need to be interpreted with caution.
- Strengths of this study include that it is the first scoping review of clinical pharmacopuncture use in Korea. Further, it builds upon a previously published SR in 2016 [19], and it includes the latest Korean medicine CPGs. While SRs aim to produce a critically appraised and synthesized result or answer to a particular question, the current study aimed to provide an overview or map of the evidence regarding the effects and safety of the clinical use of pharmacopuncture as a scoping review, which may act as precursor to future SRs. The diverse clinical research reflects the extensive indications of pharmacopuncture use in clinical practice, and provides evidence in support of treatment for musculoskeletal disorders and pain, neoplasms, obesity, and stroke sequelae. Furthermore, this study illustrates the effectiveness and safety of pharmacopuncture by analyzing various imaging guides [58–60] and by drawing comparisons between intra-acupoints and intra-articular points [61]. Regarding the comparison between guided and blind pharmacopuncture administration, the between-group results were non-specific in one study [59], and statistically significantly superior for certain outcome measures in the other two studies [58,60].
- Regarding the study design, the prospective comparative studies were mostly 2-armed, and the multi-arm studies were conducted in healthy participants for the collection of information regarding safety (2 arms, n = 159; 3 arms, n = 19; 4 arms, n = 8; and 6 arms, n = 3, respectively). Furthermore, most of the studies (n = 266) employed more than one treatment in the intervention and control groups, which reflects “usual care” in clinical practice. “Usual care” generally consisted of various Korean medicine treatments (n = 255), with a few studies using an integrative combination of both conventional and Korean medicine (n = 8), while some used conventional medicine treatment exclusively (n = 3). However, many studies that compared different types of pharmacopuncture (with or without co-interventions) reported statistically significant improvement in within-group differences, but non-significance in between-group differences, suggesting the need for further careful consideration of comparators. Allowing continued intake of previously prescribed medications, and provision of educational programs, information leaflets, or rescue medicine (in all groups), was not considered “usual care” or integrative medicine in this current review study.
- Management of diseases and disorders with pharmaco-puncture encompasses injecting natural/herbal solutions at acupuncture points or specific surface reaction points, and as such combines acupuncture with natural/herbal medicine [5]. Acupuncture treatment effects are mainly induced by applying physical stimulation to acupuncture points, whereas pharmacopuncture constitutes simultaneous application of the physical stimulation of acupuncture along with physical (e.g., irrigation, hydrodissection) and chemical stimulation of pharmacological action of the pharmacopuncture solution. Pharmacopuncture has the additional advantage over acupuncture by stimulating the acupuncture points and simultaneously providing a prolonged therapeutic window for absorption of the pharmacopuncture solution. For a pharmacopuncture solution containing large molecules, a smaller dosage should be administered at a slower injection rate, since the patient may report discomfort or pain. On the contrary, a larger dosage can be used for smaller molecules [19]. Notably, TEA is a special form of acupuncture that is also classified as a type of pharmacopuncture, and involves the insertion and embedding of an absorbable thread at select acupoints to provide continuous stimulation. TEA produces strong, long-term stimulation at the insertion site.
- The general mechanisms of pharmacopuncture are not yet fully understood. For instance, the role of prolonged stimulation of acupoints in exchange of the change in volume characteristics remains unclear [62]. Furthermore, a therapeutic effect of the product formed depots may occur similar to prolotherapy; however, the main mechanism of action is possibly an interaction between the mechanical properties of acupoint stimulation and chemical stimulation via the injected solution. Regarding drug-delivery pathways, the natural/herbal medicine solution injected at acupoints may flow along the meridians or primo-vessels, following the epi-, peri-, and endoneurium of peripheral nerves, and mater of the spinal cord, or be absorbed directly into the bloodstream or lymphatic flow without passing through the gastrointestinal tract [63,64].
- Some large molecule pharmacopuncture solutions may have similar indications and characteristics as prolotherapy. Prolotherapy is the injection of a solution known to cause a local inflammatory cascade involving chemical mediators and growth factors that promote symptom relief and tissue regeneration in several chronic musculoskeletal pain disorders, especially degenerative disorders [65,66]. The agents used in prolotherapy have been hypothesized to initiate wound healing by inducing collagen synthesis and fibroblast proliferation, which lead to stronger hypertrophied ligaments that aid in the stabilization of hypermobile joints. Injected solutions (“proliferants”) have been postulated to cause local irritation, with subsequent inflammation and tissue healing, resulting in strengthening of injured ligaments, tendons, and intra-articular structures [67,68]. These processes are presumed to improve joint stability, biomechanics, and function, and result in a decreased level of pain [69,70]. Although various mechanisms for individual herbal pharmacopuncture solutions have been proposed based on the active ingredients and main constituents (through in vitro and in vivo research), better design and execution of high-quality research is crucial to determine the mechanisms of pharmacopuncture.
- Pharmacopuncture is generally categorized according to the pharmacopuncture solution content [e.g., Meridian field (Gyungrakyakchim), Eight principles (Palgangyakchim), BV, single compound] [4]; however, the solutions may vary depending on the preparation facilities and methods. Supplementary Table 6 summarizes the systematic management of pharmacopuncture solutions prepared using rigorous standards that are in line with the MoHW accreditation of herbal dispensary facilities.
- Twenty-three Korean medicine CPGs and 221 clinical research articles pertaining to pharmacopuncture reported acupoints that are effective for pharmacopuncture [25–27,29,30,33,35,36,38,40,42–51,53–55]. Although various meridians, collective acupoints, and single acupoints were reported, the majority were located around the specific region of pain or lesion, including Ashi points. Standardization, wider application, and study of various acupoints including Ashi points of the primary area of pain, primary points pertaining to specific disorders, diseases, or symptoms, and five phase (transport) points are needed. The concept of Ashi points is closely associated to tender points, because they induce tenderness (i.e., painful or sensitive reactions) when pressed firmly. Furthermore, the concept of Ashi points also overlap with the concept of TPs that are caused by muscle tightness, which refer pain. The rationales for tender points or TPs to treat pain and symptoms can be found in “Huangdi Neijing,” which states “the area of pain is used as an acupuncture point.” As the locations of Ashi points change, unlike other acupuncture points which remain fixed, Ashi points are also known as “variable points” or “time corresponding points.” Ashi points are regarded “variable points” because their location points continue to change, and therefore should be checked at the time of treatment. The first person to use the term “Ashi point” was Sun Simiao, a renowned physician of the Tang dynasty, in “Qianjin Yaofang.” The concept of Ashi points corresponding to TPs due to muscle shortening, was established by Im Heo, a prominent physician of the mid-Joseon dynasty (17th century). He emphasized the significance of accurate localization, fixture, and needling (penetration) of the tissue mass in “Chimgugyeongheom-bang (Empirical Prescriptions in Acupuncture and Moxibustion)” for successful treatment as reviewed by Shin and Choi [5], which is also relevant and applicable in enhancing the effectiveness of pharmacopuncture treatment in clinical practice.
- This is the first scoping review of clinical pharmaco-puncture use in Korea, and our findings support its use in clinical practice and research. Pharmacopuncture has been used and studied for an extensive range of clinical indications; however, the heterogeneity of pharmacopuncture types, conditions, and study designs were high due to lack of firmly established research methodology for pharmacopuncture studies. Future studies may want to examine the validity of pharmacopuncture based on the recommendations of standardized guidelines for more effective dissemination and incorporation of pharmacopuncture into clinical practice.
Discussion
- Considering the diverse clinical applications of pharmacopuncture, more RCTs and pragmatic trials should be conducted to further substantiate its evidence and develop standard research methodology in Korean medicine to support the evidence-based use of pharmacopuncture.
Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
-
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: YJL and IHH. Methodology: MRK, SML, YJL and IHH. Formal investigation: MRK, SML, YJL and IHH. Data analysis: MRK and SML. Writing original draft: MRK. Writing - review and editing: MRK, SML, YJL and IHH.
-
Conflicts of Interest
In-Hyuk Ha and Yoon Jae Lee are the editors of Perspectives on Integrative Medicine but this had no influence in the decision to publish this article. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
Ethical Statement
This research did not involve any human or animal experiments.
-
Data Availability
All relevant data are included in this manuscript.
-
Funding
None.
Article information
| CPG | ICD main code(s) | Recommendation grade / level of evidence | Alone / add-on | Recommendation no. | Recommendation contents regarding pharmacopuncture | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tension-type headache [23] | G44.2 | C | Very low | Add-on (complex Korean medicine) | R12 | Pharmacopuncture combined with herbal medicine may be considered in patients with tension-type headache as pharmacopuncture combined with herbal medicine is more effective for symptom improvement than Western medicine treatment. |
|
|
||||||
| Gout [24] | M10 | GPP | CTB | Alone | R8 | Pharmacopuncture can be considered in adults to improve symptoms of acute gout. |
|
|
||||||
| Irritable bowel syndrome [25] |
K58.0 K58.9 |
B | Moderate | Alone | R6 | Acupuncture should be considered over conventional Western medicine treatment to improve symptoms in patients with IBS. |
| C | Low | Integrative | R8 | Integrative treatment of acupuncture and conventional Western medicine may be considered over conventional Western medicine alone to improve symptoms in patients with IBS. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Osteoporosis [26] | M81 | C | Low | Alone | R9 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered to improve BMD and osteoporotic pain. |
| C | Low | Add-on | R10 | Pharmacopuncture combined with conventional treatment may be considered to improve BMD, pain, and indicators of osteoporosis. | ||
| C | Low | Alone | R15 | Thread embedding may be considered to improve related indicators of osteoporosis. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R16 | Thread embedding in combination with conventional treatment should be considered to improve BMD, pain, and related indicators of osteoporosis. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Postoperative treatment of lumbar musculoskeletal disease [27] |
Z54.0 Z98.8 |
C | Low | Integrative (with conventional rehabilitation) | R6 | Concurrent treatment of pharmacopuncture or BVP and conventional rehabilitation, or integrative traditional Korean medicine treatments may be considered for patients in postoperative rehabilitation or patients postoperatively presenting with persistent or recurrent pain. |
|
|
||||||
| Postoperative treatment of knee musculoskeletal disease [28] | Z96.64 | C | Very low | Integrative (with conventional rehabilitation) | R6 | Evidence for the efficacy and safety of the combined treatment of pharmacopuncture and conventional rehabilitation in patients in the rehabilitation phase after total knee arthroplasty could not be obtained. Pharmacopuncture combined with conventional rehabilitation may be considered. |
|
|
||||||
| Postoperative treatment of rotator cuff muscle musculoskeletal disease [29] |
Z54.0 Z98.8 |
C | Very low | Integrative (with conventional rehabilitation) | R10 | Pharmacopuncture or BVP combined with conventional rehabilitation may be considered over conventional rehabilitation alone for patients in rehabilitation after rotator cuff surgery. |
|
|
||||||
| Migraine [30] | G43 | B | Moderate | Alone | R19 | Pharmacopuncture can be considered for migraine symptoms as it may be more effective than placebo pharmacopuncture or general conventional medicine in patients with migraine. |
|
|
||||||
| Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis [31] | M48.00 | C | Very low | Add-on (complex Korean medicine) | R6 | For pain relief in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis, complex Korean medicine may be considered over single Korean medicine. |
|
|
||||||
| Dementia [32] |
F00 F06.7 |
C | Moderate | Alone | R25 | Hominis placenta pharmacopuncture may be considered for depression, anxiety, anger, and insomnia in patients with mild cognitive impairment over placebo. |
|
|
||||||
| Dysmenorrhea [33] | N94.4 | B | Low | R3 | Other acupuncture treatments (thread embedding, warm acupuncture, auricular acupuncture) used alone or as add-on should be considered over other treatments (Western medicine or placebo) to improve symptoms of menstrual pain in patients with primary dysmenorrhea. | |
| Inconclusive | Alone | R3-1 | Recommendation inconclusive regarding the clinical question "Does administering thread embedding in primary dysmenorrhea patients result in menstrual pain-related scale improvement compared to Western medicine (NSAIDs)?" | |||
| C | Low | R4 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered over other treatments (e.g., normal saline pharmacopuncture, acupuncture alone, conventional medicine) to improve menstrual pain in patients with primary dysmenorrhea. | |||
| C | Low | Alone | R4-1 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered over normal saline pharmacopuncture to improve symptoms of menstrual pain and abdominal temperature in patients with primary dysmenorrhea. | ||
| B | Moderate | Alone | R4-2 | Pharmacopuncture should be considered over conventional medicine to improve symptoms of menstrual pain in patients with primary dysmenorrhea. | ||
| C | Very low | Add-on | R4-3 | Combined treatment of acupuncture and pharmacopuncture may be considered over acupuncture alone to improve symptoms of menstrual pain in patients with primary dysmenorrhea. | ||
| C | Low | Add-on | R8-6 | Combined treatment of thread embedding and Chuna may be considered over no treatment to improve symptoms of menstrual pain in patients with primary dysmenorrhea. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Insomnia disorders [34] |
F510 G470 |
C | Low | Alone | R2-4-1 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered to treat insomnia over sleeping pills. |
|
|
||||||
| Anxiety disorders [35] | F41.1 | B | Moderate | Integrative (for generalized anxiety disorder) | R10-5 | Thread embedding combined with anxiety disorder treatment drugs should be considered over anxiety disorder treatment drugs alone in adults to improve symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder. |
| C | Low | Alone (for panic disorder) | R15 | Thread embedding may be considered over anxiety disorder treatment drugs in adults to improve symptoms of panic disorder. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Allergic rhinitis [36] | J303 | C | Very low | Alone | R17 | Thread embedding may be considered in patients to improve the main symptoms of allergic rhinitis. |
| C | Low | Add-on | R18 | The combination of thread embedding, acupuncture and moxibustion may be considered in patients to improve the main symptoms and quality of life of allergic rhinitis. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Hypertension [37] | I10 | C | Moderate | Integrative | R12 | Antihypertensives combined with pharmacopuncture over antihypertensives alone may be considered to lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. |
|
|
||||||
| Climacteric and postmenopausal syndrome [38] | N95.1 | B | Low | (For hot flush menopausal and postmenopausal symptoms) | R4 | Thread embedding may be more effective than hormone replacement therapy for treating menopausal, postmenopausal facial flushing and other menopause-related symptoms, and should be considered as a treatment option. |
| GPP | CTB | (For hot flush menopausal and postmenopausal symptoms) | R5 | Pharmacopuncture is recommended as an auxiliary therapy for menopausal and postmenopausal syndrome based on expert group consensus. | ||
| B | Very low | Complex (for hot flush menopausal and postmenopausal symptoms) | R8 | Thread embedding combined with electroacupuncture may be more effective than hormone replacement therapy in treatment of hot flushes and other menopause-related symptoms, and should be considered. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Stroke [39] | I60 | C | Low | Add-on | R90 | BVP may be considered to improve motor disability in patients with stroke sequelae. |
| C | Low | Add-on | R91 | BVP may be considered to improve shoulder pain in patients with stroke sequelae. | ||
| C | Very low | Add-on | R92 | BVP may be considered to improve spasticity in patients with stroke sequelae. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Chronic fatigue [40] |
R53 R54 |
B | Moderate | R10 | Pharmacopuncture should be considered for improving symptoms in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome/idiopathic chronic fatigue. | |
| B | Moderate | Alone (for global symptom severity) | R10-1 | Pharmacopuncture should be considered for improving global symptom severity in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome /idiopathic chronic fatigue. | ||
| C | Low | Alone (for fatigue) | R10-2 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered for relieving fatigue in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome/idiopathic chronic fatigue. | ||
| C | Low | R11 | Additional thread embedding combined with other Korean medicine treatments or symptomatic drug treatment may be considered over other Korean medicine treatments or symptomatic drug treatment alone in patients to improve the main symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome/idiopathic chronic fatigue. | |||
| C | Low | Add-on/integrative (for global symptom severity) | R11-1 | Additional thread embedding combined with Korean medicine treatments (acupuncture/moxibustion)/symptomatic drug treatment (anti-inflammatory analgesics/antiviral drugs/sleep inducing agents) may be considered over Korean medicine treatments or symptomatic drug treatment alone in patients to improve the main symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome/idiopathic chronic fatigue. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Autism spectrum disorder [41] |
F84.0 F84.1 |
C | Low | Add-on | R9 | The combination of herbal medicine, meridian point acupuncture, pharmacopuncture and behavioral/educational treatment may be considered to improve symptoms of patients with autism. |
| C | Low | Add-on | R15 | Thread embedding combined with behavioral/educational treatment may be considered in pediatric patients to improve symptoms of autism. | ||
| C | Low | Add-on | R21 | The combination of manual acupuncture, thread embedding, auricular acupressure and behavioral/educational treatment may be considered in pediatric patients to improve symptoms of autism. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Cold hypersensitivity in hands and feet [42] |
I73.0 I73.8 |
B | Low | R7 | Pharmacopuncture treatment should be considered to improve symptoms in adults with cold hypersensitivity in hands and feet. | |
|
|
||||||
| Functional dyspepsia [43] | K30 | B | Low | Add-on | R16 | Korean medicine add-on treatment (e.g., herbal medicine, acupuncture, moxibustion, pharmacopuncture, and plaster therapy) should be considered to improve symptoms in adults with functional dyspepsia. |
|
|
||||||
| Knee osteoarthritis [44] |
M17 M23 |
B | Low | Alone | R15 | Compared to sham pharmacopuncture, Chinemys reevesii Gray pharmacopuncture showed significant functional improvement and effects in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Pharmacopuncture should therefore be considered for patients with knee osteoarthritis. |
| C | Low | Alone | R16 | Compared to usual conventional care, pharmacopuncture showed significant treatment effects in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Pharmacopuncture may therefore be considered for patients with knee osteoarthritis. | ||
| B | Low | Alone | R17 | Compared to sham pharmacopuncture, BVP showed significant pain relief and functional improvement in patients with knee osteoarthritis. BVP should therefore be considered for patients with knee osteoarthritis. | ||
| C | Very low | Integrative | R18 | Pharmacopuncture combined with usual conventional care may be considered for pain relief and functional improvement for patients with knee osteoarthritis. | ||
| B | Low | Add-on | R19 | Pharmacopuncture combined with other Korean medicine care should be considered for pain relief and effects for patients with knee osteoarthritis. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Breast cancer [45] |
R53 R52 |
C | Very low | R6 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered to improve pain symptoms for patients with breast cancer. | |
|
|
||||||
| Lumbar disc herniation [46] | M51 | B | Moderate | Add-on | R10 | Pharmacopuncture combined with usual care should be considered for overall symptoms of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation in adults. |
| B | Moderate | Alone | R13 | Thread embedding should be considered in adults to improve overall symptoms of lumbar disc herniation. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R14 | Thread embedding combined with usual care should be considered in adults to improve overall symptoms of lumbar disc herniation. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Facial palsy [47] | G510 | C | Low | Alone | R19 | BVP may be considered over general acupuncture for facial palsy patients with delayed treatment response. |
| C | Very low | Add-on | R20 | General Korean medicine treatments with BVP may be considered over general Korean medicine treatments alone for patients with idiopathic facial palsy. | ||
| C | Low | Add-on | R21 | General Korean medicine treatments with Hominis placenta pharmacopuncture may be considered over general Korean medicine treatments alone for patients with idiopathic facial palsy. | ||
| B | Low | Add-on | R22 | General Korean medicine treatments along with pharmacopuncture may be considered over general Korean medicine treatments alone for idiopathic facial palsy patients with postauricular pain. | ||
| C | Low | Add-on | R23 | General Korean medicinal treatments* combined with thread embedding may be considered in patients to improve facial palsy symptoms of idiopathic facial palsy over general Korean medicinal treatments* alone. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R24 | When 3+ months after onset of facial palsy have passed and general treatment does not show clear improvement, general Korean medicine treatments* combined with thread embedding may be considered over general Korean medicine treatments* alone. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Nonspecific chronic low back pain [48] |
M545 M5456 |
B | Moderate | Alone | R13 | BVP should be considered to improve pain and function in adults with chronic nonspecific low back pain. |
| B | Moderate | Alone | R14 | Thread embedding should be considered to improve pain and function in adults with chronic nonspecific low back pain. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R15 | Thread embedding combined with other Korean medicine treatments should be considered to improve pain and function in adults with chronic nonspecific low back pain. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Neck pain [49] |
M542 M501 |
A | Moderate | Alone | R16 | Pharmacopuncture was shown to significantly relieve neck pain in adults compared to usual care. Pharmacopuncture is therefore recommended for symptom alleviation in patients with neck pain. |
| B | Low | Alone | R17 | Pharmacopuncture was shown to significantly relieve neck pain in adults compared to acupuncture. Pharmacopuncture should therefore be considered for symptom alleviation in patients with neck pain. | ||
| B | Low | Integrative | R18 | Concurrent treatment with pharmacopuncture and usual care was shown to significantly relieve pain and improve quality of life compared to usual care alone for adults with neck pain. Integrative treatment with pharmacopuncture should therefore be considered for symptom alleviation in adults with neck pain receiving usual care. | ||
| B | Low | Add-on | R19 | Concurrent treatment with pharmacopuncture and acupuncture was shown to significantly relieve pain compared to acupuncture alone for adults with neck pain. Concurrent treatment with pharmacopuncture treatment should therefore be considered for symptom alleviation in adults with neck pain receiving acupuncture. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R20 | Concurrent treatment with BVP and acupuncture was shown to significantly relieve pain and improve function for neck pain in adults. Concurrent treatment with BVP should therefore be considered for symptom alleviation in adults with neck pain receiving acupuncture. | ||
| C | Low | R25 | Compared to nonactive controls, thread embedding was shown in adults to significantly relieve pain for neck pain. Thread embedding may therefore be considered for symptom improvement in clinical treatment of neck pain patients. | |||
|
|
||||||
| Hwabyung [50] | U22.2 | C | Very low | Alone | R3 | Pharmacopuncture may be considered to improve physical symptoms in patients with Hwabyung. |
|
|
||||||
| Temporomandibular joint disorder [51] |
S03.0 S03.4 |
A | Moderate | Alone | R5 | Pharmacopuncture showed significant improvement in pain and quality of life compared to usual conservative treatment in adults with temporomandibular joint disorder. Consideration of pharmacopuncture treatment is therefore recommended for improvement of symptoms in patients with temporomandibular joint disorder. |
|
|
||||||
| Dizziness [52] | R42 | B | Moderate | Add-on (for dizziness) | R (I-C-1) | Collaborative treatment with herbal medicine and pharmacopuncture should be considered over herbal medicine alone for patients with vertigo. |
| C | Low | Add-on (for cervical vertigo) | R (IIIa-A-13) | Combined treatment of thread embedding and herbal medicine may be considered over herbal medicine alone for symptom improvement in patients with cervical vertigo. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on (for cervical vertigo) | R (IIIa-C-1) | Combined treatment with pharmacopuncture, electrical stimulation and traction should be considered over electrical stimulation and traction for patients with cervical vertigo. | ||
| C | Low | Integrative (for vasovagal syncope) | R (IIIb-C-1) | Collaborative treatment with pharmacopuncture and beta-blockers may be considered over beta-blocker treatment alone for patients with vasovagal syncope. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Cancer-related symptoms [53] |
R52 R53 |
C | Low | Integrative | R9 | BVP combined with analgesics may be considered over analgesics alone to improve cancer-related pain. |
|
|
||||||
| Traffic injuries [54] |
S0000 T009 |
C | Very low | Alone | R4-1 | Pharmacopuncture according to syndrome differentiation may be considered for symptom alleviation of neck pain and low back pain over acupuncture alone in adult WAD 1, 2 patients. |
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R4-2 | Pharmacopuncture combined with usual care (KMT) according to syndrome differentiation should be considered for symptom improvement over acupuncture treatment alone in adult WAD 1, 2 patients with neck pain. | ||
| C | Very low | Add-on | R4-3 | Pharmacopuncture combined with usual care (KMT) according to syndrome differentiation may be considered for symptom improvement in adult WAD 1, 2 patients with low back pain. | ||
| C | Very low | Add-on | R12-1 | Chuna manual therapy combined with pharmacopuncture may be considered for symptom improvement of neck pain and low back pain over Chuna manual therapy or pharmacopuncture alone in adult WAD 1, 2 patients. | ||
| C | Low | Add-on | R12-2 | Pharmacopuncture combined with usual care (KMT, including Chuna manual therapy) may be considered for symptom improvement over usual care (KMT, including Chuna manual therapy) in adult WAD 1, 2 patients with neck pain. | ||
| B | Moderate | Add-on | R12-3 | Chuna manual therapy combined with usual care (KMT, including pharmacopuncture) should be considered for symptom improvement over usual care (KMT, including pharmacopuncture) alone in adult WAD 1, 2 patients with neck pain. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Ankle sprain [55] |
S9340 S9341 |
C | Low | Add-on | R13 | Acupuncture combined with BVP may be considered to reduce pain in adults with acute ankle sprain. |
| C | Low | Add-on | R14 | Acupuncture combined with BVP may be considered to reduce pain and improve the range of motion in adults with chronic ankle sprain. | ||
|
|
||||||
| Shoulder pain [56] |
M750 M751 |
C | Low | R17 | Thread embedding may be considered to improve quality of life associated with SF-36 in adults with shoulder pain. | |
| B | Moderate | R18 | BVP should be considered for adults with shoulder pain. | |||
| C | Low | R19 | Pharmacopuncture including Scolopendrid, and Juglandis Semen pharmacopuncture may be considered for adults with shoulder pain presenting with a main complaint of pain. | |||
|
|
||||||
| Obesity [57] | E66 | B | Low | Pharmacopuncture should be considered in the treatment of obesity as it shows significant effects on body weight and waist circumference. | ||
* General Korean medicine treatments include treatments such as acupuncture, electroacupuncture, herbal medicine, and physical therapy.
BMD = bone mineral density; BVP = bee venom pharmacopuncture; CPG = clinical practice guideline; CTB = classical text-based; GPP = good practice point; IBS = irritable bowel syndrome; ICD = International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems; KMT = Korean medicine treatment; NSAID = non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; SF-36 = short form-36 health survey; WAD = whiplash associated disorders
- [1] Lee HJ. Introduction to phamacopuncture and its clinical use. Seoul (Korea), Il-Chung-Sa, 1999.
- [2] Yin CS, Koh HG. The first documental record on bee venom therapy in Oriental medicine: 2 prescriptions of bee venom in the ancient Mawangdui books of Oriental medicine. J Korean Acupunct Moxibution Soc 1998;15(1):143−7. https://www.e-jar.org/journal/view.html?pn=vol&uid=405&vmd=Full.
- [3] Nam SC. Meridian. Seoul (Korea), Hang-Lim-Seo-Won Publications, 1967.
- [4] Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute. Pharmacopuncturology: Principles and clinical applications. Seoul (Korea), Elsevier Korea LLC, 2012.
- [5] Shin MS, Choi SW. Pharmacopuncturology in musculoskeletal disease. Seoul (Korea), Gaonhae Media, 2021.
- [6] Lee MH, Son IC. Introduction to the aqua-acupuncture therapy and problems. J Acupunct Res 1998;15(2):511−8. https://www.e-jar.org/journal/view.html?pn=vol&uid=470&vmd=Full.
- [7] Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare [Internet]. Certification standard criteria established for 2nd term of external herbal dispensaries: 2022 [cited 2022 Dec 31]. Available from: http://www.mohw.go.kr/react/al/sal0301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=04&MENU_ID=0403&page=1&CONT_SEQ=371676
- [8] Choi DW, Kim JH, Cho SY, Kim DH, Chang SY. Regulation and quality control of herbal drugs in Korea. Toxicology 2002;181–182:581−6.Article
- [9] Kim JD, Kang DI. A descriptive statistical approach to the Korean pharmacopuncture therapy. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2010;3(3):141−9.ArticlePubMed
- [10] Sung SH, Han JE, Ryu JY, Sung ADM, Park JY, Ha IH, et al. Current status and future perspective of external herbal dispensaries preparing traditional herbal medicine in South Korea: The first national-wide survey results. BMC Complement Med Ther 2020;20(1):354. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [11] Korea Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety white paper. Osong (Korea), Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, 2015.
- [12] Lee YJ, Park CG. A study on the collection of Oriental herbal medicine and the production of standardized items. Osong (Korea), Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, 2015, https://scienceon.kisti.re.kr/srch/selectPORSrchReport.do?cn=TRKO201600010697.
- [13] Sung SH, Shin BC, Park MJ, Kim KH, Kim JW, Ryu JY, et al. Current status of management on pharmacopuncture in Korea through introduction of an accreditation system. J Pharmacopunct 2019;22(2):75−82.ArticlePubMedPMC
- [14] National Institute for Korean Medicine Development (NIKOM) - National Agency for Korean Medicine Innovative Technologies Development (IT-KoM) [Internet]. National Clearinghouse for Korean Medicine: 2022 [cited 2022 Dec 31]. Available from: https://nikom.or.kr/engnckm/html.do?menu_idx=33
- [15] Lee YJ, Shin JS, Lee JH, Kim MR, Park KB, Lee HD, et al. Usage report of pharmacopuncture in musculoskeletal patients visiting Korean medicine hospitals and clinics in Korea. BMC Complement Altern Med 2016;16(1):292. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [16] Kim MR, Shin JS, Lee JH, Lee YJ, Ahn YJ, Park KB, et al. Safety of acupuncture and pharmacopuncture in 80,523 musculoskeletal disorder patients: A retrospective review of internal safety inspection and electronic medical records. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016, 95(18):p e3635.. PubMedPMC
- [17] Kim DH, Cho SJ, Ko JA. Policy improvement plan based on Korean medicine use. Wonju (Korea), Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, 2015.
- [18] Suh CY, Lee YJ, Kim MR, Bae YH, Kim HS, Kim NH, et al. A web-based survey for assessment of Korean medical treatment clinical practice patterns for neck pain and cervical intervertebral disc displacement. J Acupunct Res 2016;33(4):65−72.ArticlePDF
- [19] Park JM, Lee HS, Shin BC, Lee MS, Kim BR, Kim JI. Pharmacopuncture in Korea: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016;2016:4683121. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- [20] World Health Organization. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems, 10th revision. 5th ed. Geneva (Switzerland), World Health Organization, 2016.
- [21] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services [Internet]. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE), version 5.0: Washington DC (WA); National Institutes of Health: 2017 [cited 2022 Dec 31]. Available from: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcae_v5_quick_reference_5x7.pdf
- [22] Mueller HL. Diagnosis and treatment of insect sensitivity. J Asthma Res 1966;3(4):331−3.ArticlePubMed
- [23] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Medicine on Tension-Type Headache. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2022 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=233&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=%EA%B8%B4%EC%9E%A5%EC%84%B1&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [24] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Medicine on Gout. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2022 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=234&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [25] The Society of Internal Korean Medicine. Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Medicine on Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2022 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=218&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B3%BC%EB%AF%BC&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [26] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Osteoporosis. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2022 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=219&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B3%A8%EB%8B%A4%EA%B3%B5%EC%A6%9D&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [27] The Society of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Post-Operative Treatment of Spinal Disorders. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=175&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%88%98%EC%88%A0%ED%9B%84&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [28] The Society of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Post-Operative Treatment of Total Knee Arthroplasty. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=174&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%88%98%EC%88%A0%ED%9B%84&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [29] The Society of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Post-Operative Treatment of Rotator Cuff Surgery. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=173&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%88%98%EC%88%A0%ED%9B%84&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [30] The Society of Stroke on Korean Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Migraine. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=171&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%ED%8E%B8%EB%91%90%ED%86%B5&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [31] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=170&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%ED%98%91%EC%B0%A9%EC%A6%9D&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [32] The Society of Korean Medicine Neuropsychiatry. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Dementia. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=169&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%B9%98%EB%A7%A4&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [33] The Society of Korean Medicine Obstetrics and Gynecology. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Dysmenorrhea. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=168&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%9B%94%EA%B2%BD&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [34] The Society of Korean Medicine Neuropsychiatry. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Insomnia Disorder. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=164&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=&sortType=&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EB%B6%88%EB%A9%B4&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [35] The Korean Society of Oriental Neuropsychiatry. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline on Anxiety Disorders. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2022 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=165&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=INT&code_gubun=mds&agency=%EB%8C%80%ED%95%9C%ED%95%9C%EB%B0%A9%EC%8B%A0%EA%B2%BD%EC%A0%95%EC%8B%A0%EA%B3%BC%ED%95%99%ED%9A%8C&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [36] The Society of Korean Medicine Ophthalmology Otolaryngology & Dermatology. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline on Allergic Rhinitis. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=167&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EB%B9%84%EC%97%BC&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [37] The Society of Stroke on Korean Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Hypertension. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=163&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B3%A0%ED%98%88%EC%95%95&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [38] The Society of Korean Medicine Obstetrics and Gynecology. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Climacteric Syndrome and Postmenopausal Syndrome. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=162&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B0%B1%EB%85%84&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [39] The Society of Stroke on Korean Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Stroke. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=159&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%A4%91%ED%92%8D&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [40] The Society of Korean Medicine Diagnostics. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Chronic Fatigue. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=157&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%ED%94%BC%EB%A1%9C&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [41] The Association of Korean Oriental Pediatrics. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=156&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%9E%90%ED%8F%90&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [42] The Society of Sasang Constitutional Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Cold Hypersensitivity of Hands and Feet. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=155&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%88%98%EC%A1%B1&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [43] The Society of Internal Korean Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Functional Dyspepsia. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=154&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B8%B0%EB%8A%A5%EC%84%B1&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [44] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Knee Osteoarthritis. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2020 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=153&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B4%80%EC%A0%88&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [45] The Society of Korean Medicine Obstetrics and Gynecology. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Breast Cancer. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2020 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=152&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%9C%A0%EB%B0%A9%EC%95%94&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [46] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Herniation of Lumbar Disk. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2020 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=151&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%B6%94%EA%B0%84%ED%8C%90&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [47] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Facial Palsy. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2019 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=150&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%95%88%EB%A9%B4&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [48] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Chronic Low Back Pain. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2020 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=149&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%9A%94%ED%86%B5&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [49] The Korean Society of Chuna Manual Medicine for Spine and Nerves. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Neck Pain. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=148&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B2%BD%ED%95%AD&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [50] The Society of Korean Medicine Neuropsychiatry. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Hwabyung. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=147&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%ED%99%94%EB%B3%91&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [51] The Society of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=146&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%ED%84%B1%EA%B4%80%EC%A0%88&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [52] The Society of Sasang Constitutional Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Dizziness. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=145&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%ED%98%84%ED%9B%88&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [53] Korean Association of Traditional Oncology. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Cancer-Related Symptoms. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=144&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%95%94&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [54] The Society of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Traffic Injuries. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2021 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=143&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B5%90%ED%86%B5&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [55] Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Ankle Sprain. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2020 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=142&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EC%97%BC%EC%A2%8C&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [56] The Society of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline for Shoulder Pain. Gyeongsan (Korea); National Institute for Korean Medicine Development: 2020 https://nikom.or.kr/nckm/module/practiceGuide/view.do?guide_idx=141&progress=&mds_code=&disease_code=&gubun=&code_gubun=mds&agency=&continent=&sortField=agency&sortType=asc&language=kor&search_type=all&search_text=&viewPage=1&guide_idx=&progress_jq=&title=%EA%B2%AC&disease_code_etc1=&agency_jq=&country=&cert_yn=&release_date=&menu_idx=14
- [57] Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine. Korean Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline on Obesity. Seoul (Korea); Elsevier Korea LLC: 2016 https://www.kiom.re.kr/brdartcl/boardarticleView.do?menu_nix=WUNNW2Aq&brd_id=BDIDX_o9YEVvNb40b134N1Rt17aq
- [58] Yang JE, Oh MS. Comparison of ultrasound guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy effect and unguided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy effect on cervical facet joint of acute cervical pain patient caused by traffic accidents: A retrospective study. J Korean Med Rehabilitation 2022;32(3):109−17.Article
- [59] Park JW, Kim SW, Jeon DH, Kim BJ, Oh MS. Comparison the Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy effects of ultrasound guided group and unguided group on the patients' facet joint with acute low back pain caused by traffic accidents: A retrospective study. J Korean Med Rehabilitation 2021;31(3):85−93.Article
- [60] Kim YH, Oh TY, Lee EJ, Oh MS. A comparative study on the pain and treatment satisfaction between Korean medical treatment combined with ultrasound guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy in thoracic paravertebral space and non-guided Soyeom pharmacopuncture therapy on patients with ribs fracture: A retrospective study. J Korean Med Rehabil 2019;29(3):103−12.Article
- [61] Kim SW, Bae EJ, Lee JH, Seo JC, Lim SC, Han SW. The clinical review of intra-articular herbal-acupuncture by using fluoroscopy. J Acupunct Res 2003;20(6):182−9. https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO200326662305868.page.
- [62] Agasarov LG. Pharmacopuncture in dorsopathy treatment. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2008;1(2):110−3.ArticlePubMed
- [63] Soh KS. Hypothesis on the treatment of gliomas with acupuncture at the primo node corresponding to Zusanli (ST 36). Med Acupunct 2015;27(3):144−50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- [64] Jia ZF, Lee BC, Eom KH, Cha JM, Lee JK, Su ZD, et al. Fluorescent nanoparticles for observing primo vascular system along sciatic nerve. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2010;3(3):150−5.ArticlePubMed
- [65] Jensen KT, Rabago DP, Best TM, Patterson JJ, Vanderby R Jr. Early inflammatory response of knee ligaments to prolotherapy in a rat model. J Orthop Res 2008;26(6):816−23.ArticlePubMedPMC
- [66] Covey CJ, Sineath MH Jr, Penta JF, Leggit JC. Prolotherapy: Can it help your patient? J Family Pract 2015;64(12):763−8.
- [67] Liu YK, Tipton CM, Matches RD, Bedford TG, Maynard JA, Walmer HC. An in situ study of a sclerosing solution in rabbit medial collateral ligaments and its junction strength. Connect Tissue Res 1983;11(2–3):95−102.ArticlePubMed
- [68] Maynard JA, Pedrini VA, Pedrini–Mille A, Romanus B, Ohlerking F. Morphological and biochemical effects of sodium morrhuate on tendons. J Orthop Res 1985;3(2):236−48.ArticlePubMed
- [69] Linetsky FS, Rafael M, Saberski L. Pain management with regenerative injection therapy (RIT). Boca Raton (FL), CRC Press, 2002.
- [70] Hackett GS, Hemwall GA, Montgomery GA. Ligament and tendon relaxation treated by prolotherapy. 5th ed. Oak Park (IL), Gustav A. Hemwall, 1993.
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations
- The effect of integrative Korean medicine treatment on symptomatic lumbar facet joint cysts: A case series
Hee-seung Choi, Yoon Jae Lee, Dae-Hyun Hahm, Hyangsook Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2024; 20(1): 130. CrossRef - Long-term follow-up of inpatients with meniscus tears who received integrative Korean medicine treatment: A retrospective analysis and follow-up survey
June Haeng Lee, Jin Young Song, Kyoung Sun Park, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha, Yoon Jae Lee
Medicine.2024; 103(6): e36917. CrossRef - Pragmatic randomized controlled trial of pharmacopuncture therapy for adhesive capsulitis: A pilot study
Doori Kim, Kyoung Sun Park, Sun-A Kim, Ji Yeon Seo, Hyun-Woo Cho, Yoon Jae Lee, Changsop Yang, In-Hyuk Ha, Chang-Hyun Han
Integrative Medicine Research.2024; : 101065. CrossRef - Effectiveness of lumbar motion style acupuncture treatment on inpatients with acute low back pain: A pragmatic, randomized controlled trial
Oh-Bin Kwon, Dong Wook Hwang, Dong-Hyeob Kang, Sang-Joon Yoo, Do-Hoon Lee, Minjin Kwon, Seon-Woo Jang, Hyun-Woo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Kyong Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Doori Kim, In-Hyuk Ha
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2024; 82: 103035. CrossRef - Survey on the current usage of ultrasound-guided procedures in Korean Medicine Clinics and Hospitals
Ju Yeon Kim, Jung Min Yun, Sook-Hyun Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Dong Kun Ko, In Heo, Woo-Chul Shin, Jae-Heung Cho, Byung-Kwan Seo, In-Hyuk Ha
Medicine.2024; 103(14): e37659. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of hominis placental pharmacopuncture for chronic temporomandibular disorder: A multi-center randomized controlled trial
Kyoung Sun Park, Eun-San Kim, Koh-Woon Kim, Jae-Heung Cho, Yoon Jae Lee, Jinho Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2024; 13(2): 101044. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Trends on the Korean Medicine Treatments of Subacromial-Subdeltoid Bursitis
Hyunsuk Park, Dong-Jin Jang, Jonghyun Lee, Sungjae Yoo, Minji Sun, Junsoo Kim, Yongjun Kim, Jeong-Hee Noh, Si-Hyoung Kim, Jung-Min Yun
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2024; 34(2): 85. CrossRef - A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effectiveness and Safety of Pharmacopuncture for Chronic Lower Back Pain
Kyoung Sun Park, Changnyun Kim, Joo Won Kim, Sang‐Don Kim, Jee Young Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, Jinho Lee, Min Ji Kim, Young Eun Choi, Changsop Yang, Chang-Hyun Han, In-Hyuk Ha
Journal of Pain Research.2023; Volume 16: 2697. CrossRef - Long-Term Follow-Up of Inpatients with Rotator Cuff Tear Who Received Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment: A Retrospective Analysis and Questionnaire Survey
Dong-Hwi Yoo, Jae-Yong Choi, Sang-Gun Lee, Ki-Won Choi, Han-Bin Park, Ho Kim, Hyunwoo Cho, Sang Don Kim, Doori Kim, Yoon Jae Lee, Kyoung Sun Park, In-Hyuk Ha
EXPLORE.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Domestic Clinical Research Trends of Shinbaro Pharmacopuncture: Scoping Review
Yeongmin Kim, Yunhee Han, Seungkwan Choi, Jungho Jo, Byeonghyeon Jeon, Hyeonjun Woo, Wonbae Ha, Junghan Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2023; 33(4): 125. CrossRef






 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite