Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and issues > Previous issues
Editorial
- Best Evidence for Best Care
- Nicola Robinson
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):139-141. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.001
- 964 View
- 31 Download
Review Articles
- An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews for Chuna (or Tuina) Manual Therapy on Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Doori Kim, Gil Geun Baek, Byung-Cheul Shin
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):142-154. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.002
- 1,090 View
- 33 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 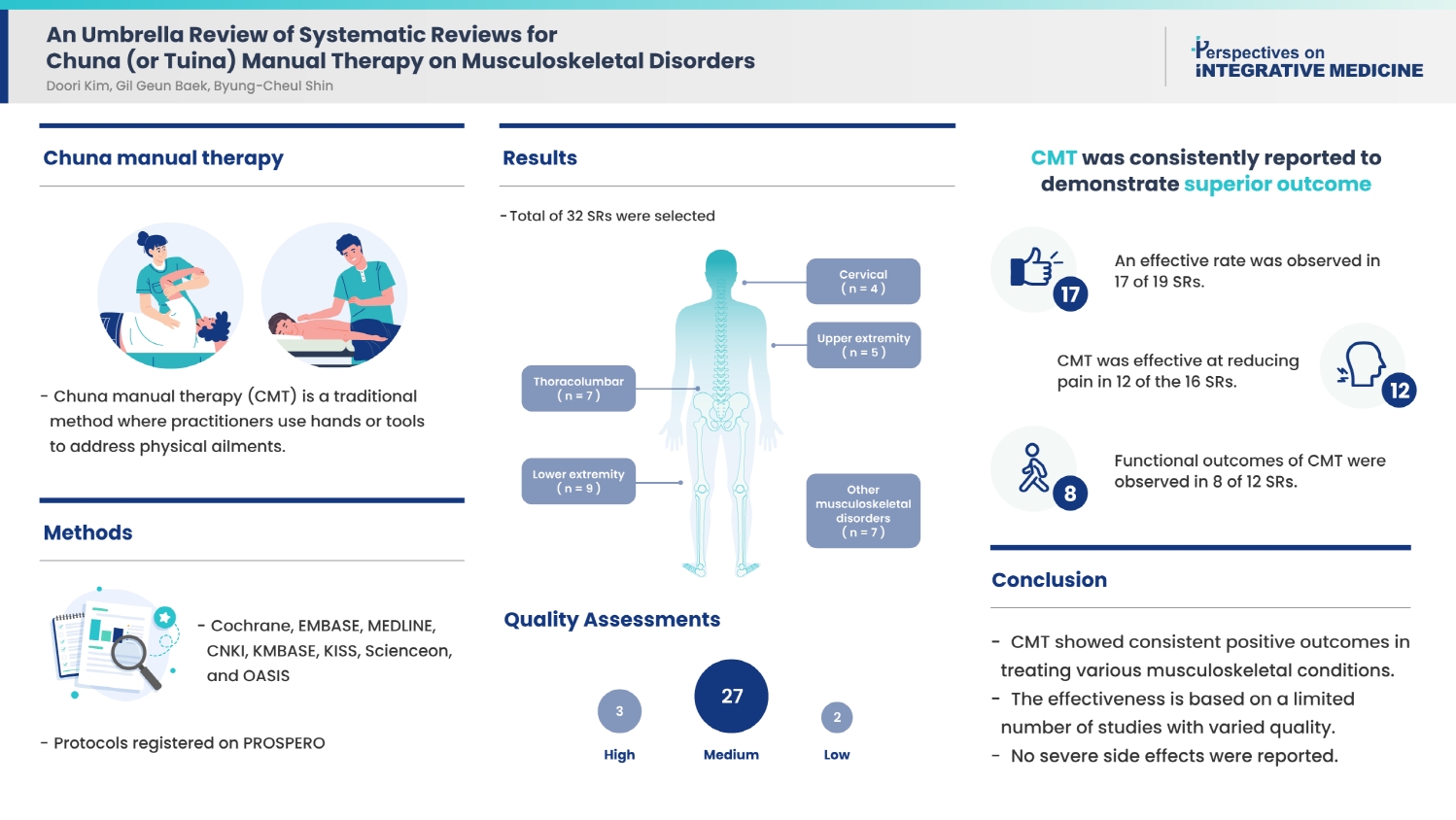
- Background
To provide clinicians with reliable evidence an umbrella review of systematic reviews (SRs) on Chuna manual therapy (CMT) for musculoskeletal disorders was performed to synthesize important outcomes.
Methods
There were eight databases (Cochrane, EMBASE, MEDLINE, CNKI, KMBASE, KISS, Scienceon, and OASIS) searched as well as the international database Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews in health and social care until August 2023. SRs of randomized controlled trials involving patients with musculoskeletal conditions, limited to interventions explicitly labeled as “Chuna” or “Tuina” in English, Chinese, or Korean language were retrieved. Two reviewers independently conducted selection and data extraction, and SR quality was assessed using A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews tool (low, medium, or high quality).
Results
This review included 32 SRs, categorized by cervical (n = 4), thoracolumbar (n = 7), upper extremity (n = 5), lower extremity (n = 9), and other musculoskeletal disorders (n = 7). Quality assessments determined that three SRs were of “high” quality, two were “low” quality, and the remaining SRs were of “medium” quality. CMT was consistently reported to demonstrate superior outcomes: an effective rate was observed in 17 of 19 SRs, CMT was effective at reducing pain in 12 of the 16 SRs, and functional outcomes of CMT were observed in 8 of 12 SRs. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion
CMT may be a safe and effective treatment for various musculoskeletal disorders based on the limited number of studies and the low quality of included SRs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reporting Overviews of Reviews: PRIORitizing a Reporting Guideline
Lisa Hartling, David Moher
Perspectives on Integrative Medicine.2024; 3(2): 65. CrossRef
- Reporting Overviews of Reviews: PRIORitizing a Reporting Guideline
- Effectiveness and Safety of Low-Level Laser Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Sang Jun Lee, Seung Jin Noh, Jeong Rock Kim, Kyung Bok Park, Sae-rom Jeon, Yejin Hong, Dongwoo Nam
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):155-163. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.003
- 1,965 View
- 61 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Background
Low-level laser treatment (LLLT) is used to treat low back pain (LBP) however, its effects on lumbar disc herniation (LDH) remain unclear. The safety and effectiveness of LLLT for LDH was determined using a systematic review of randomized clinical trials.
Methods
Studies on LLLT in adults with LDH were identified from 12 worldwide databases. A risk of bias assessment and a meta-analysis with categorization according to the type of control used (inactive, active, or add-on) was performed. The quality of evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation.
Results
The quantitative analyses included five studies. LLLT was significantly more effective at treating LDH [leg pain visual analog scale (VAS) mean difference (MD): -1.90, 95% confidence interval (CI): -2.01, -1.80, I2 80%; LBP VAS MD: -0.79, 95% CI: -0.87, -0.71, I2 80%] than inactive controls (placebo or sham). The quality of the evidence ranged from “low” to “very low.” As an add-on to usual care, LLLT significantly improved pain intensity and disability compared with usual care (leg pain VAS MD: -2.52, 95% CI: -2.65, -2.40, I2 97%; LBP VAS MD: -1.47, 95% CI: -1.58, -1.36; Oswestry Disability Index MD: -4.10, 95% CI: -4.55, -3.65, I2 6%). However, the quality of the evidence ranged from “moderate” to “low.”
Conclusion
LLLT significantly improved outcomes compared with the inactive controls, but was not more effective than usual care for LDH. In combination with usual care, LLLT was significantly more effective than usual care alone highlighting the potential of LLLT.
Original Articles
- Improvement in Growth in Adolescents with Average Height Using A Massage Chair: A Prospective Single Arm Pre-Post and National Standard Data Comparison Study
- Sul Gi Park, Gyu Tae Chang, Jin Yong Lee, Sun Haeng Lee
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):164-172. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.004
- 759 View
- 13 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Background
This study aimed to examine the changes in height, weight, and bone age between pre- and post-intervention when using a BEG-100 massage chair daily.
Methods
Thirty-five children aged 11 years who were close to the average height (145-155 cm) were included in the study. There were 34 participants who used the BEG-100 massage chair for 24 weeks. Daily intervention consisted of 20 minutes of lower body massage and 10 minutes of whole-body massage. Height, weight, and adverse events were checked every five visits, while a hand X-ray was used before and after massages. The height percentile and height standard deviation score (SDS) were calculated using the 2017 Korean growth chart. The bone age and predicted adult height using radiographs were computed using the Tanner-Whitehouse method. The paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used according to normality of data to determine statistical significance.
Results
A total of 31 children were included in the final analysis. The height percentile and height SDS significantly increased after BEG-100 massage chair use (2.39; p = 0.032, and 0.07; p = 0.036, respectively). However, these changes were not significant in children whose baseline height was shorter than the average. There were no significant differences in bone age, height for bone age, predicted adult height, or sitting height/height ratio. None of the participants complained of adverse events.
Conclusion
The height percentile and SDS of teenagers increased after use of massage chair therefore, it is necessary to perform larger randomized controlled clinical studies. Trial registration: KCT0004673.
- Contributing Factors in the Decision to Study Korean Medicine and Satisfaction with the College Experience: A Quantitative Nationwide Study
- HyunSeok Kim, Hyunho Kim, Joohyun Lee, Hwimun Kim
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):173-181. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.005
- 1,039 View
- 33 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 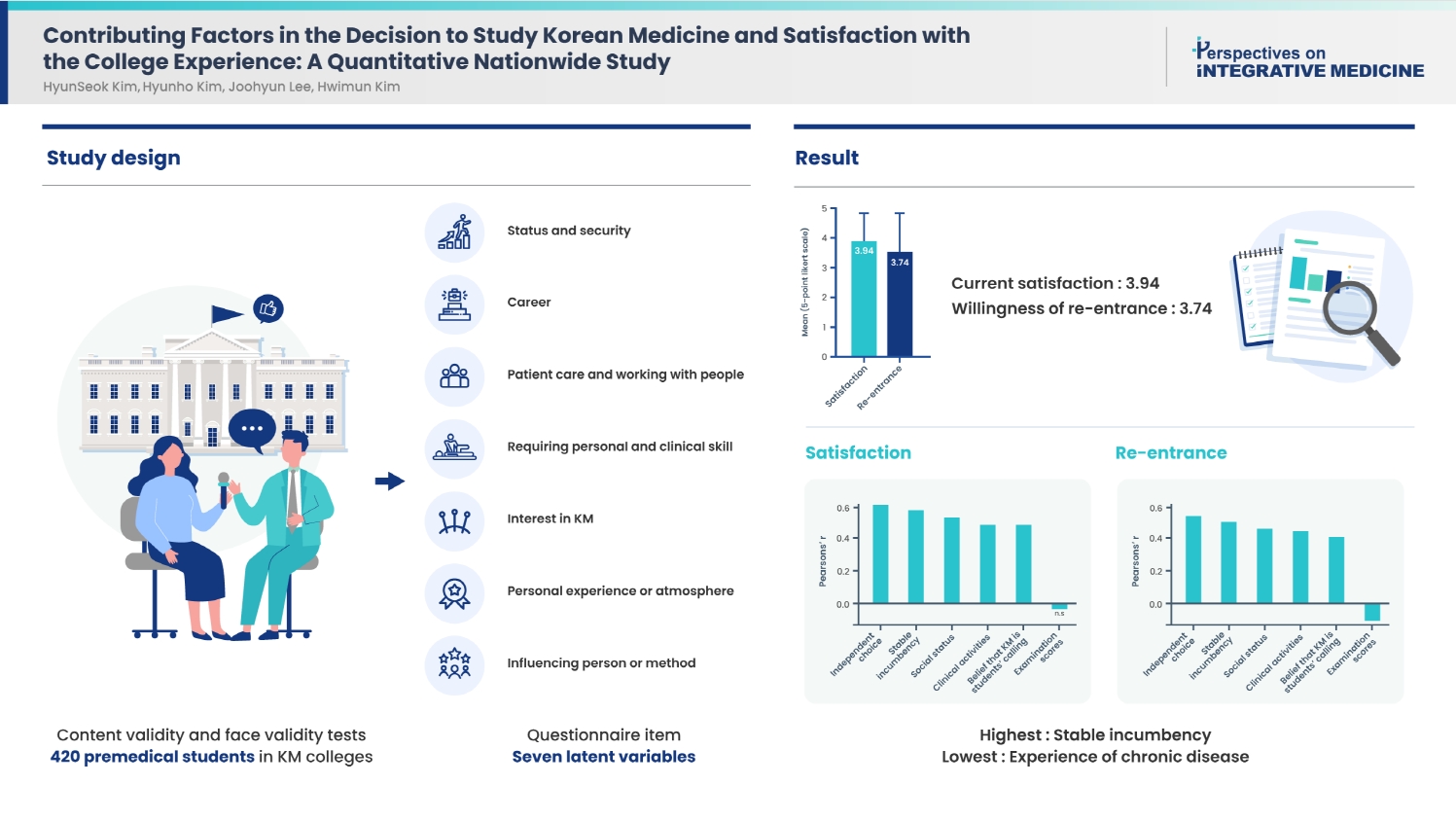
- Background
The practice of Korean medicine (KM) taught at KM colleges has equal legal rights and responsibilities as Western medicine in South Korea. To date, no research has been conducted on the factors which influence college students in their choice to study KM and satisfaction with the course.
Methods
Content validity and face validity tests were conducted while developing the questionnaires. Research was conducted amongst all KM colleges in South Korea and of the 744 premedical KM 2nd year students, 420 participated. Analysis was performed on how much the mean values changed between the items and sub-items. Factors were also correlated with the students’ satisfaction and willingness to reenter KM colleges.
Results
The means of stable incumbency items were the highest of all the items, while items concerning experience of chronic disease had the lowest mean values. For enrollment, the latent value that most questionnaire items were changed positively by was interest in KM. Items related to students’ choice or KM doctor status were closely tied to students’ current satisfaction with their choice to enroll at a KM college, rather than their college entrance examination scores.
Conclusion
Identifying which factors are considered before entering KM college and during the course can help students to be more satisfied with their academic progress. To satisfy the KM students, educators should focus on providing both qualified clinical training and guidance to enter diverse career fields. This study highlights factors that can be applied to college curriculum or subject teaching.
- Structural and Criterion Validity of a New 6-item Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ-6) on Patients with Chronic Lower Back Pain Receiving Integrative Medicine
- Yoon Jae Lee, Gyu Chan Shim, Changsop Yang, Chang-Hyun Han
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):182-189. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.006
- 917 View
- 20 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 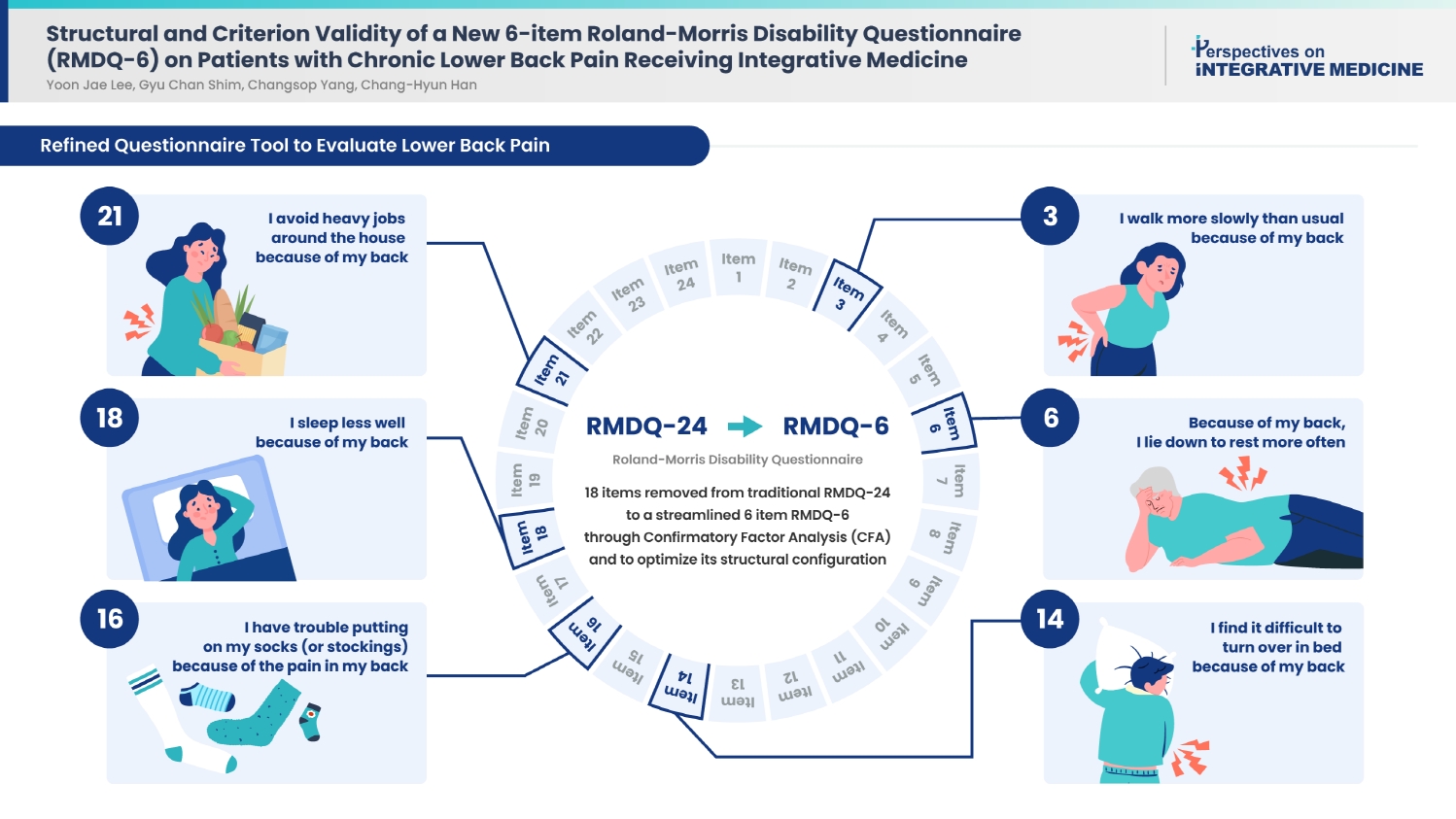
- Background
Lower back pain (LBP) is a leading cause of disability worldwide. The Roland–Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ) has been widely used to assess functional impairment in patients with LBP. However, its length and redundancy calls for a more concise and optimized version.
Methods
We conducted a secondary analysis of data from two randomized controlled trials comparing pharmacopuncture and physical therapy for chronic LBP. We focused on 132 patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms and analyzed their baseline data to evaluate the structural validity of the RMDQ. We used R packages lavaan and semPlot for confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Model fit were assessed through various indices, including comparative fit index, Tucker–Lewis index, root mean square error of approximation, and standardized root mean squared residual.
Results
A total of 18 items were ultimately removed to produce a streamlined 6-item structure. Our model met the fit index criteria, yielding a one-domain, 6-item RMDQ structure. While the relative indices fell slightly short of the ideal values, the RMDQ-6 derived through CFA correlated well with the original version.
Conclusion
This study developed a more concise version of RMDQ through CFA to optimize its structural configuration. This concise instrument can be proposed as an efficient tool to assess the functionality of patients with LBP.
Short Communication
- Perspectives and Ideas to Advance Integrative Medicine and Healthcare: Proceedings of the 4th Annual Jaseng Academic Conference
- Andrew Jang, Jinho Lee, Catherine Donahue, David Coggin-Carr, Mike Cummings, Kien Trinh, Myeong Soo Lee, Susan Wieland, Christopher Zaslawski, Lawrence Prokop, Joon Shik Shin
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):190-194. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.007
- 526 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The 4th Annual Jaseng Academic conference (August 13, 2023) in Seoul, South Korea, was a pivotal event in the realm of integrative medicine. Cohosted by Jaseng Hospital of Korean Medicine and Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine, over 500 professionals including Korean medicine doctors, medical doctors, doctors of osteopathic medicine, acupuncturists, researchers, and students gathered at the conference. The theme, “Perspectives on Integrative Medicine,” marked a departure from previous conference themes and embraced a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare. The event highlighted the importance of holistic patient care and cross-disciplinary collaboration within healthcare. It offered a comprehensive overview of the current state of integrative medicine approaches in manual medicine, evidence-based acupuncture treatment, and acupuncture research. The Annual Jaseng Academic conference continues to serve as a platform for healthcare professionals to exchange ideas and perspectives, and bridges the gap between diverse medical systems to promote improved patient outcome and wellbeing.
Protocol
- Acupuncture for Rectal Cancer Patients with Low Anterior Resection Syndrome: A Mixed Method Pilot Study Protocol
- Ming Yang, Honglin Jiang, Lin Xu, Qiaoli Zhang, Xun Li, Liu Han, Yudong Bao, Lu Yang, Mi Zhang, Lihua Zheng, Ningyuan Liu, Jianping Liu, Jinchang Huang
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):195-201. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.008
- 938 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This protocol aims to facilitate the evaluation of acupuncture in the treatment of low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) on the bowel in rectal cancer patients.
Methods
This pragmatic pilot study was designed using a convergent parallel mixed methods design combining a single-arm trial and semi-structured qualitative interview.
Results
Sixty patients with LARS will be recruited from out/inpatient departments. For evaluation of efficacy, the single-arm objective performance criteria will be used in the pilot study in which all eligible participants will receive electroacupuncture mainly on Baliao acupoints three times a week for four weeks. The LARS scale, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre Bowel Function Index, and anorectal manometry will be used to assess symptoms and pressure changes. The European Quality of Life Five Dimensions Questionnaire and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Quality of Life Questionnaire-Core 30 will be used to evaluate quality of life. Semi-structured interviews will be conducted among twenty participants to understand their experience and feelings. The qualitative and quantitative data will be analyzed and summarized before comparative analysis. Qualitative themes derived from qualitative analysis will be ranked with the variables of quantitative statistics. Finally, we will answer the research question from multiple perspectives by comparing different types of evidence for the same dimension.
Conclusion
This mixed method study design will potentially evaluate the feasibility and effects of electroacupuncture for LARS and gain an in-depth understanding of the attitudes, experiences, feelings, and acceptance among patients with LARS.
Letter
- Does the Chinese Literature Indicate Larger Effect Sizes? This Might Indeed be the Case
- Tae-Hun Kim, Jung Won Kang
- Perspect Integr Med. 2023;2(3):202-203. Published online October 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.56986/pim.2023.10.009
- 578 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This letter discusses concerns in a currently published meta-epidemiological study on commonly observed large effect sizes in the Chinese literature, focusing on potential selection bias and analysis methods. Researchers should be cautious when conducting systematic reviews that include the literature from specific countries or regions. Regardless of the country, the key issue is to enhance future research quality.






 First
First Prev
Prev


